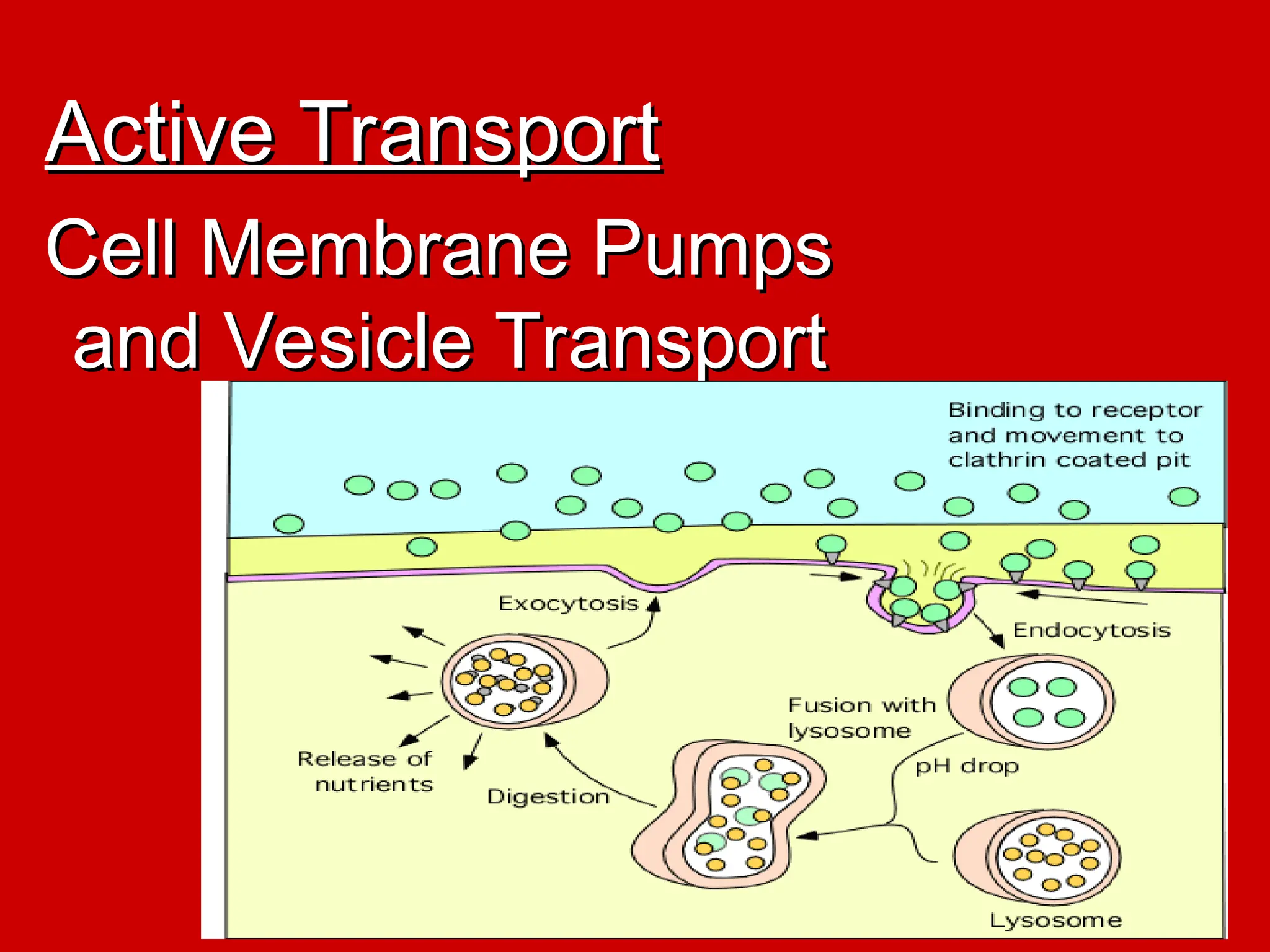
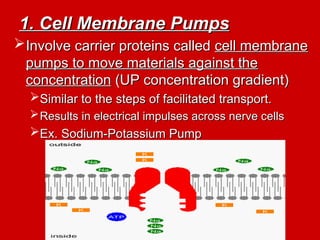
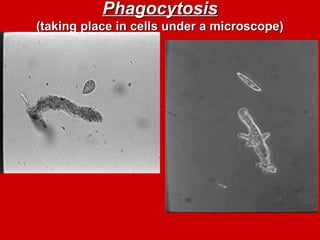
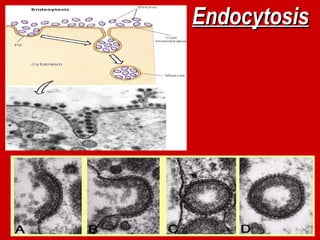
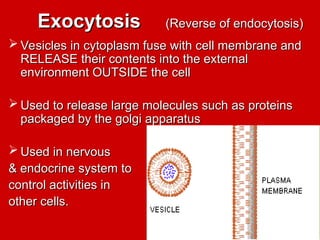
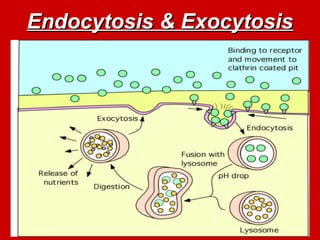
The document explains active transport, a cellular process that moves materials against a concentration gradient, requiring energy from ATP. It details two main types of active transport: membrane pumps, such as the sodium-potassium pump, and vesicle transport, which includes endocytosis and exocytosis for larger substances. Endocytosis involves the intake of external materials, while exocytosis describes the release of contents outside the cell, playing crucial roles in cellular activities.