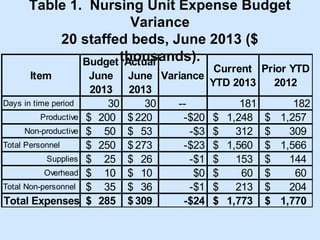
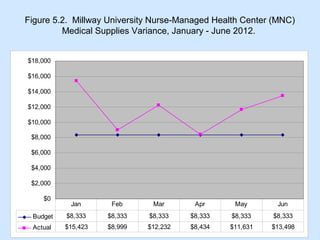
Chapter 5 focuses on managing budgets, particularly budget variance, which is the difference between budgeted targets and actual performance, distinguishing between favorable and unfavorable variances. It discusses methods for calculating these variances, the importance of investigating trends, and outlines strategies for budget control and balancing, such as line item flexibility and adjustment authority. Key points emphasize the need for effective monitoring, investigation, and control in budget management.