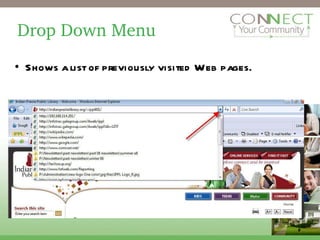
The document provides an overview of how to use a web browser. It explains that the Internet is a global network that connects computers to share data, while the World Wide Web is a system of linked web pages. It describes the basic elements of a browser like the address bar, back and forward buttons, and bookmarks. It also explains how to navigate to websites by entering URLs, following links, or using search engines. Key terms covered include the home page, hyperlinks, and top-level domains.