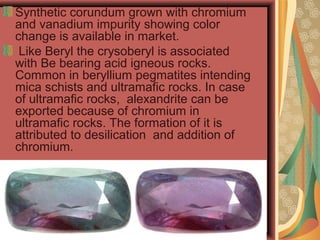
Alexandrite is a variety of the mineral chrysoberyl that exhibits dichroism or a change in color depending on the light source. It can appear green in daylight and red in incandescent light, earning it the nickname of "emerald by day, ruby by night." This phenomenon is caused by trace amounts of chromium in the crystal structure. The best alexandrite exhibits a vivid color change, and rare high-quality stones can be valued above diamonds. Alexandrite is found in pegmatites and ultramafic rocks in India, Sri Lanka, Russia, and Brazil.