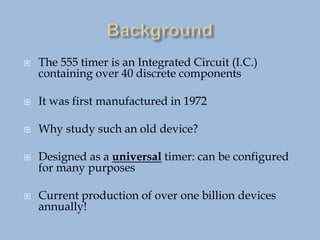
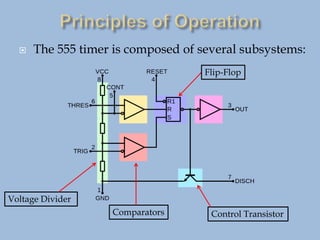
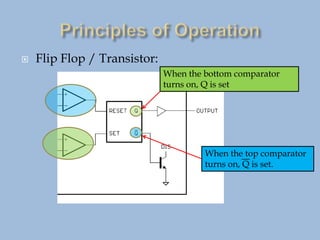
The 555 timer IC is a versatile integrated circuit that can be configured as an oscillator, timer, or flip-flop. It contains over 40 transistors and was first introduced in 1972. Despite its age, it remains in widespread use due to its low cost and ease of use. The 555 timer operates by using two comparators to monitor the voltage of an external capacitor and trigger output states, allowing it to function as an oscillator, timer, or flip-flop depending on external resistor-capacitor configurations. Common applications include oscillators, timers for appliances like coffee makers, and vehicle turn signals. Over one billion are produced annually.
![The Principles of Operation and
Applications of a 555 IC Timer
Figure 1 – Signetics 555 timer [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/555timerpresentation-2022-230810234452-87a01d80/75/555-Timer-presentation-2022-pptx-1-2048.jpg)

![Astable Circuit [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/555timerpresentation-2022-230810234452-87a01d80/85/555-Timer-presentation-2022-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![Astable Circuit [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/555timerpresentation-2022-230810234452-87a01d80/85/555-Timer-presentation-2022-pptx-13-320.jpg)
![Coffee maker clock/timer [5]
Room light controller [4]
Oscillator
and
Timer
Timer
Oscillator
Vehicle Turn Signals [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/555timerpresentation-2022-230810234452-87a01d80/85/555-Timer-presentation-2022-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![Varying the duty cycle controls the
average voltage output:
Pulse Width = 10%
Pulse Width = 50%
Pulse Width = 90%
Power drill speed control [7]
Duty Cycle values [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/555timerpresentation-2022-230810234452-87a01d80/85/555-Timer-presentation-2022-pptx-15-320.jpg)



