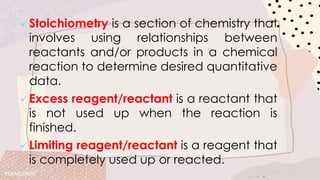
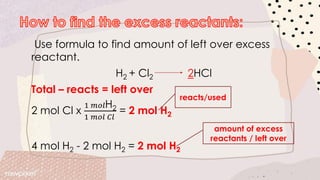
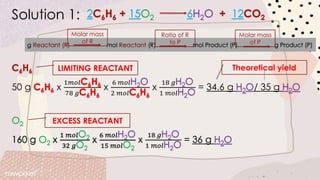
Stoichiometry involves using the mole ratios from a balanced chemical equation to determine quantitative information such as amounts of reactants/products, limiting reagents, theoretical and percent yields. When reactants are mixed, one will be completely used up while the other remains in excess. The limiting reagent determines the maximum theoretical yield, while the actual yield over theoretical yield gives the percent yield of the reaction. Excess reactant remains unused after the limiting reagent is fully consumed.