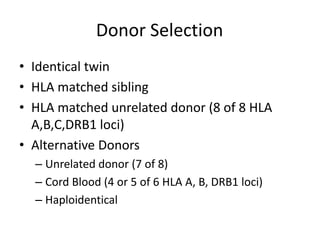
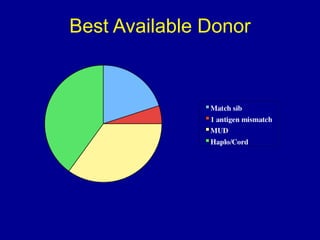
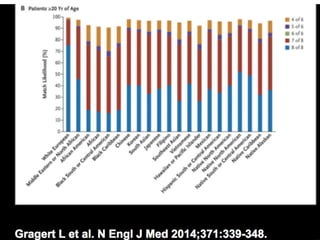
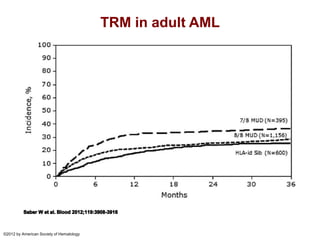
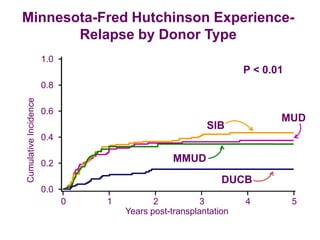
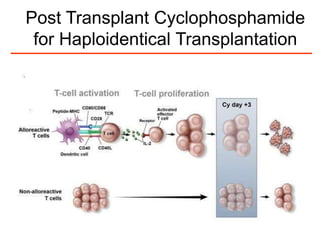
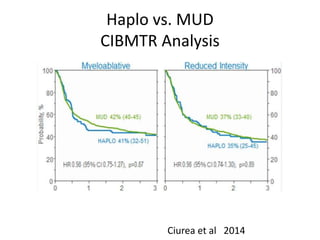
Richard Champlin is a professor and chair of the Department of Stem Cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapy at MD Anderson Cancer Center. He has over 30 years of experience in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation research. In this presentation, he discusses the pros and cons of different stem cell donor sources for transplantation including matched sibling, matched unrelated donor, cord blood, and haploidentical related donors. While matched siblings remain the preferred donor source, innovative strategies are improving outcomes with alternative donor sources like cord blood and haploidentical transplants. Prospective studies are still needed to directly compare outcomes between donor modalities.