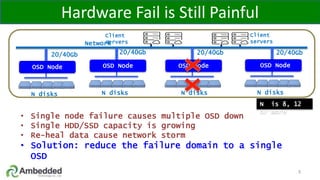
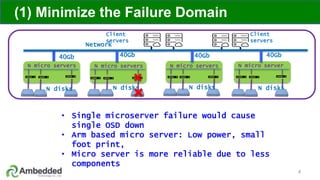
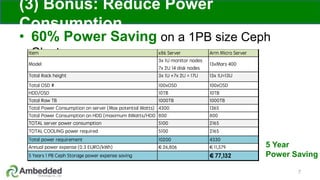
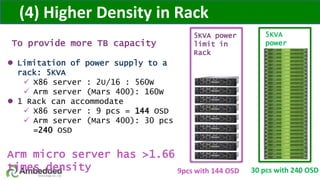
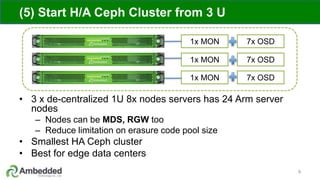
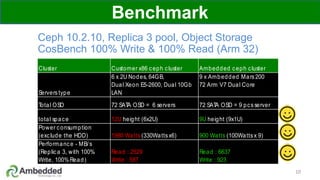
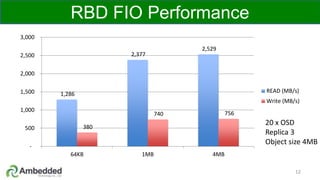
The document outlines five key advantages of using arm-based micro-server architecture for Ceph clusters, emphasizing scalability, reliability, power efficiency, and higher density. It highlights the unique characteristics of Ceph, including its self-healing capabilities and the benefits of reducing the failure domain. The arm micro-servers provide significant power savings and allow for greater object storage density in a smaller footprint compared to traditional x86 servers.