The document discusses different types of covenants including:
1) Ancient covenants made between parties that involved cutting each other and mixing blood to become "brothers of the covenant".
2) The Hebrew word for covenant, "B'rit", appears 270 times in the Bible and implies the shedding of blood in agreements.
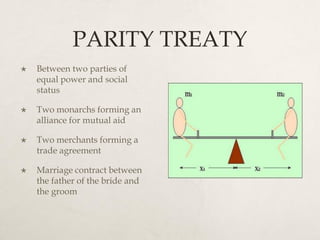
3) Different types of treaties are examined such as suzerainty-vassal treaties between unequal parties, and parity treaties between equal powers.
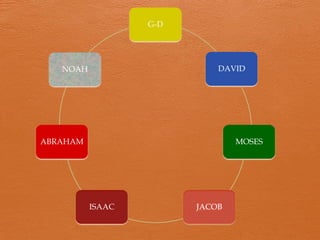
4) Specific biblical covenants with Noah, Abraham, Moses, and David are summarized highlighting the key terms of each agreement.