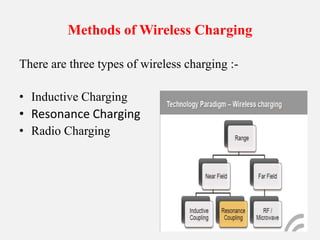
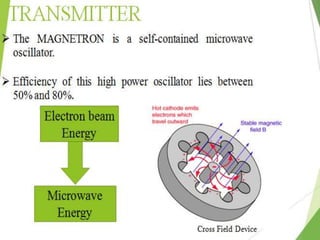
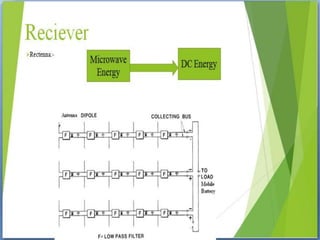
The document presents information on wireless charging. It discusses how wireless charging works using electromagnetic induction between two coils. It describes the three main types of wireless charging: inductive, resonance, and radio charging. It provides examples of applications for wireless charging and discusses standards like Qi. It covers advantages like convenience, disadvantages like slower charging, and the future scope of using data exchange and nanotechnology to power devices wirelessly.