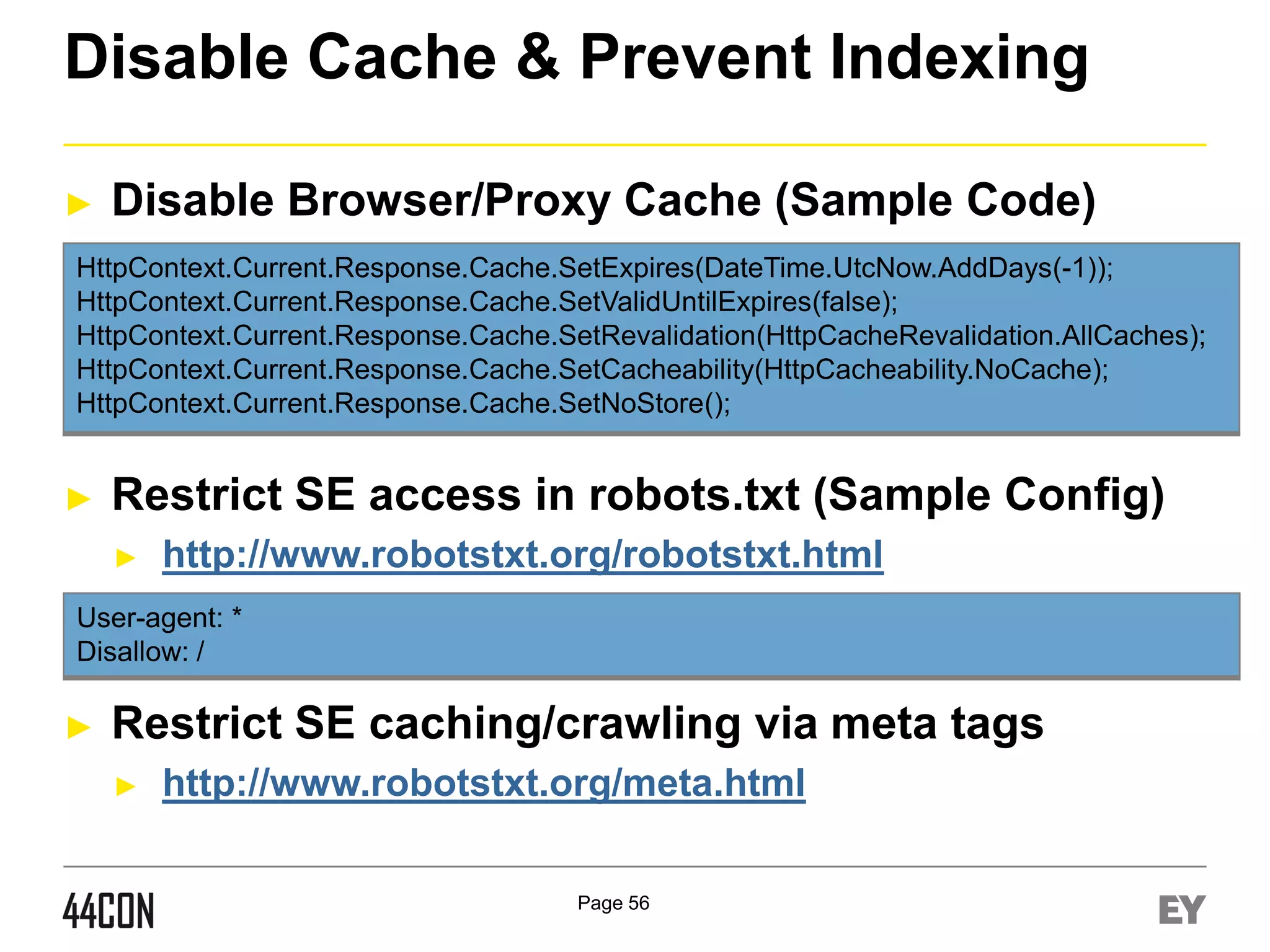
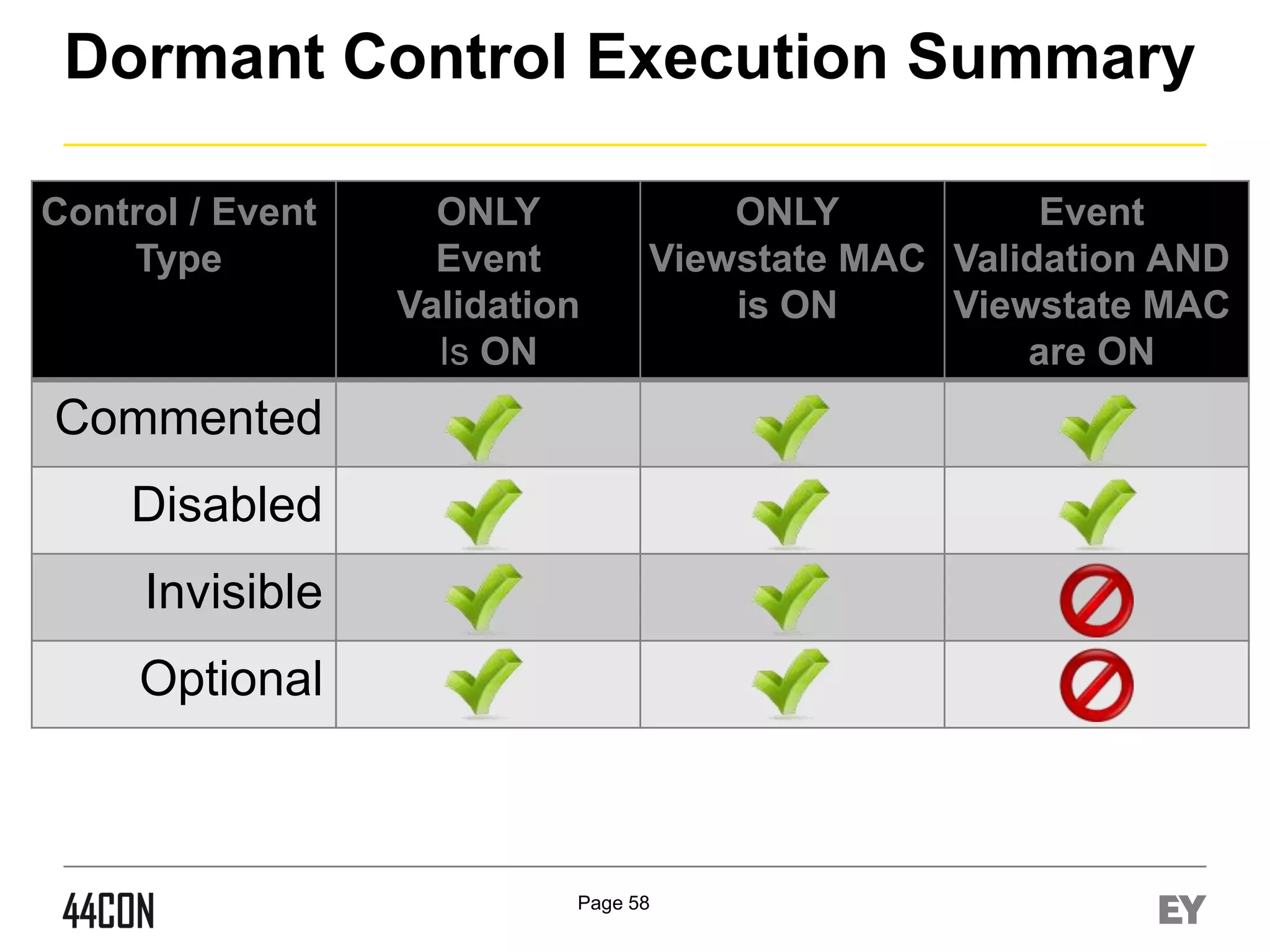
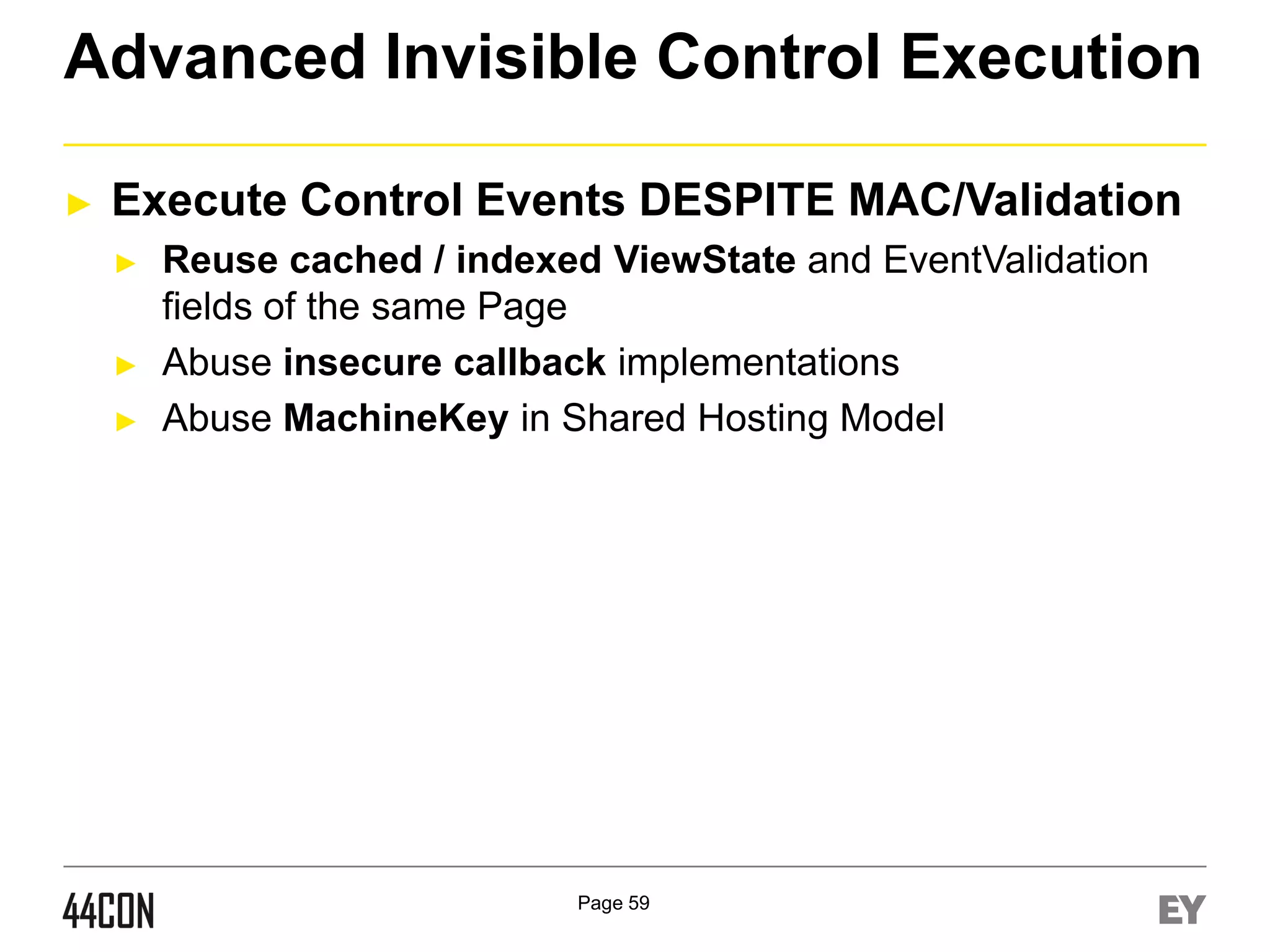
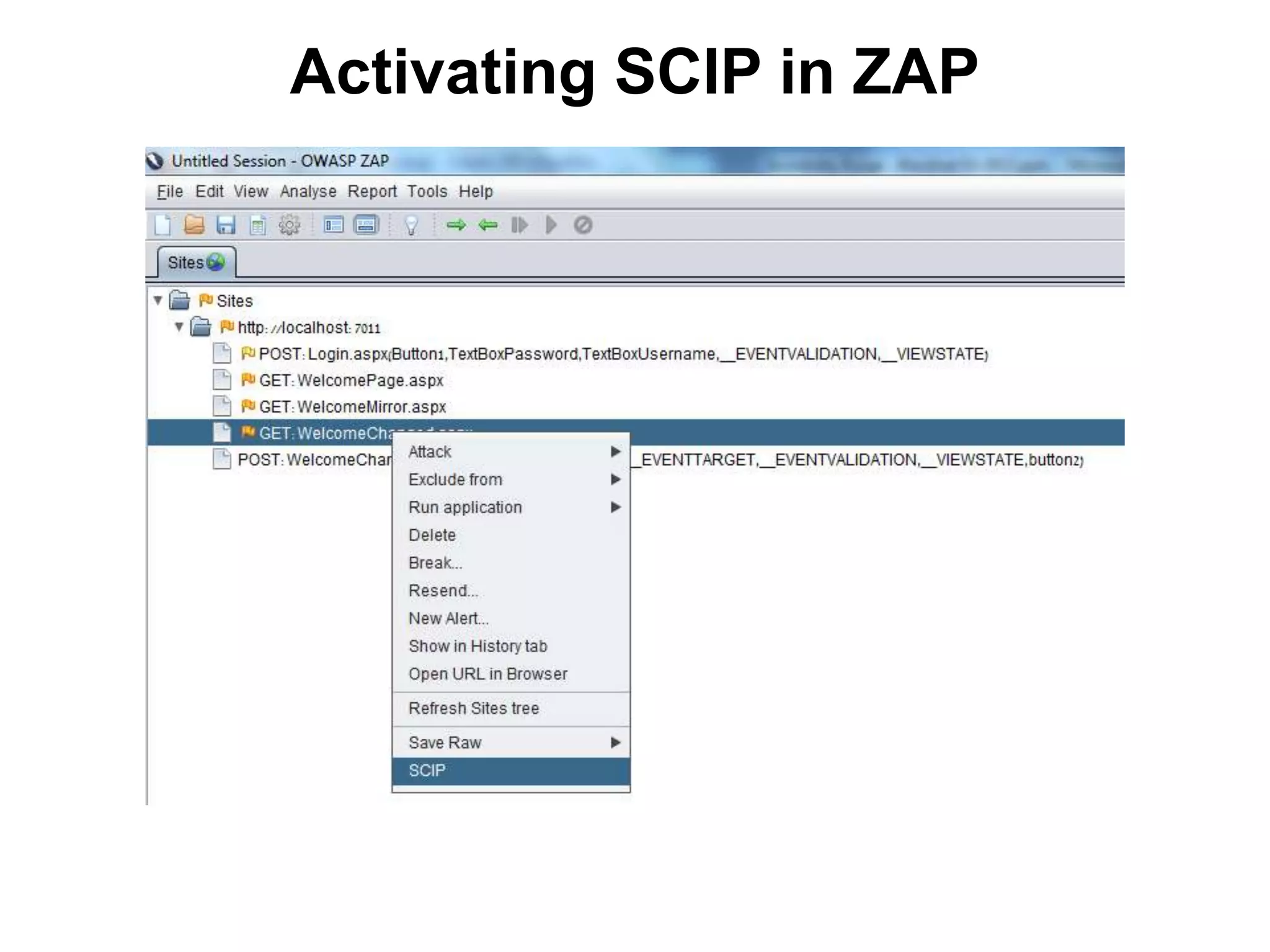
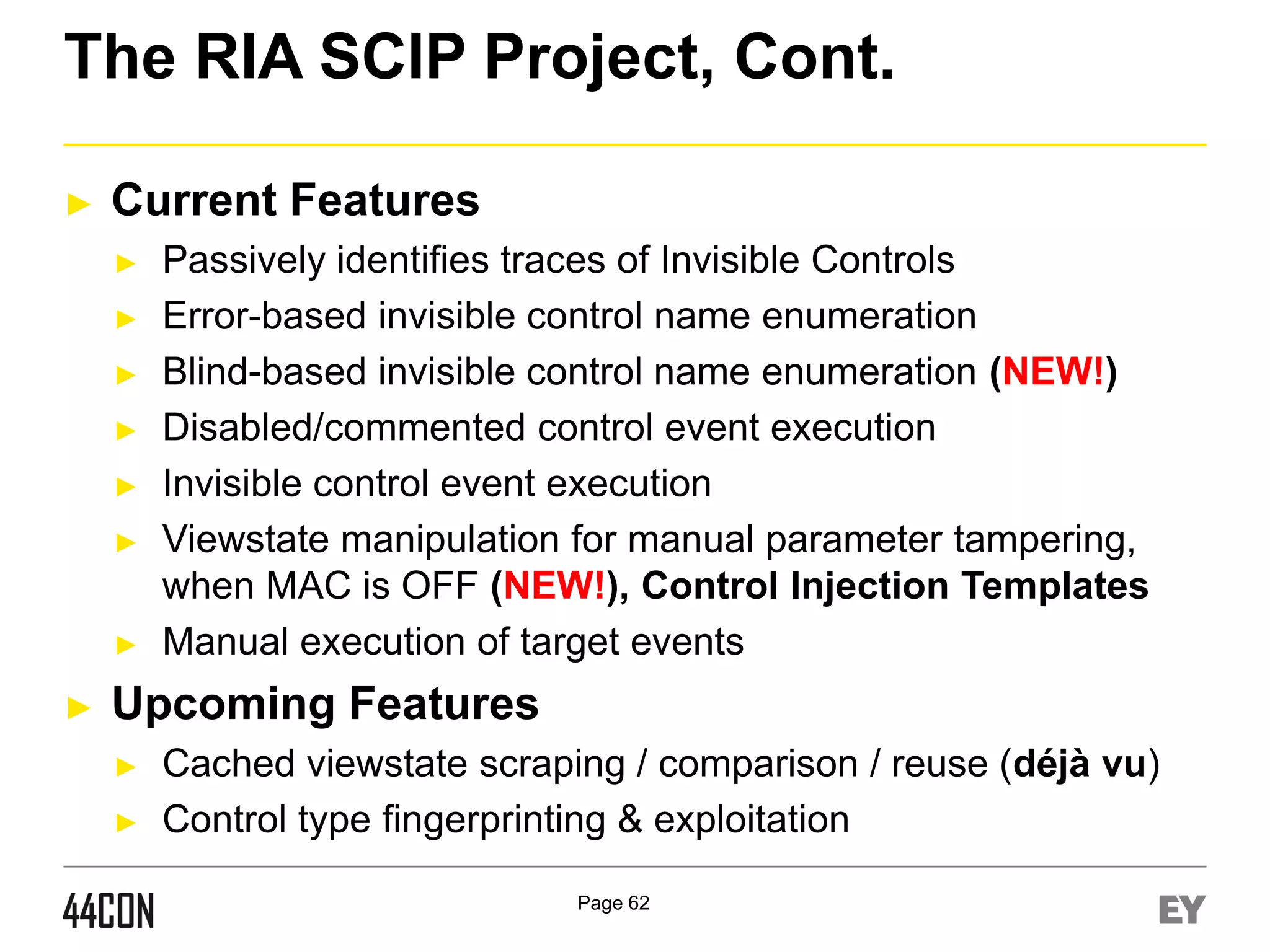
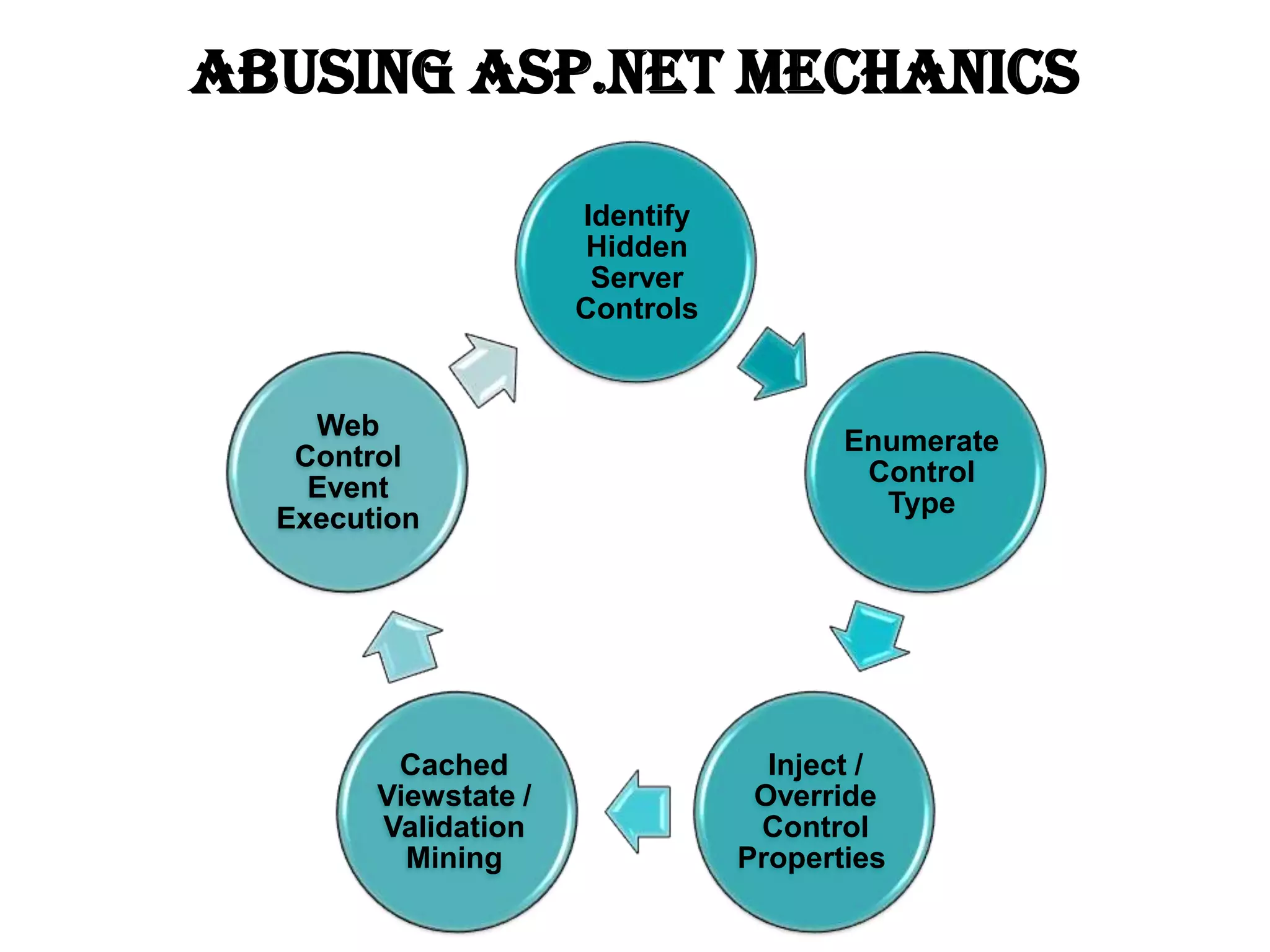
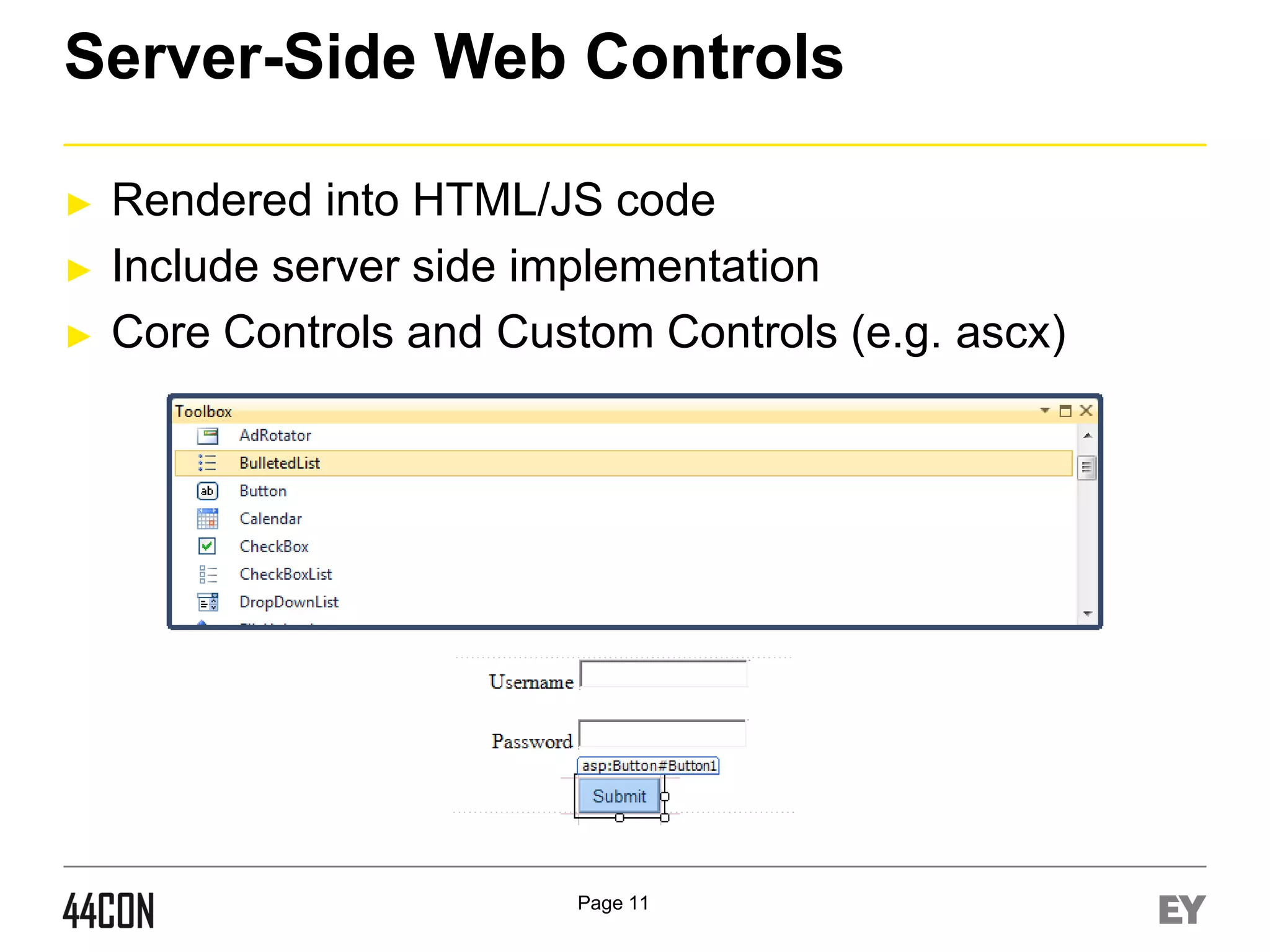
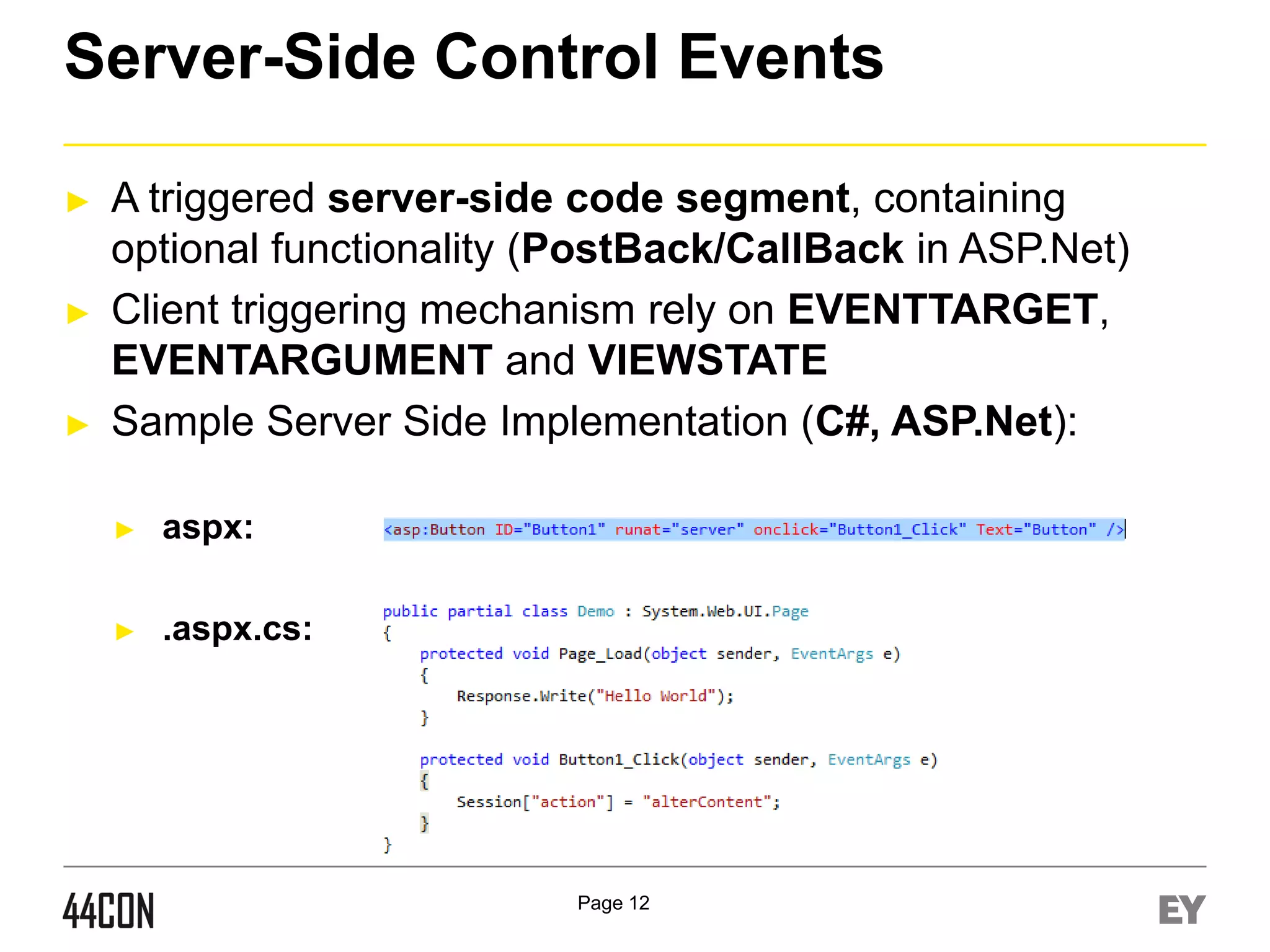
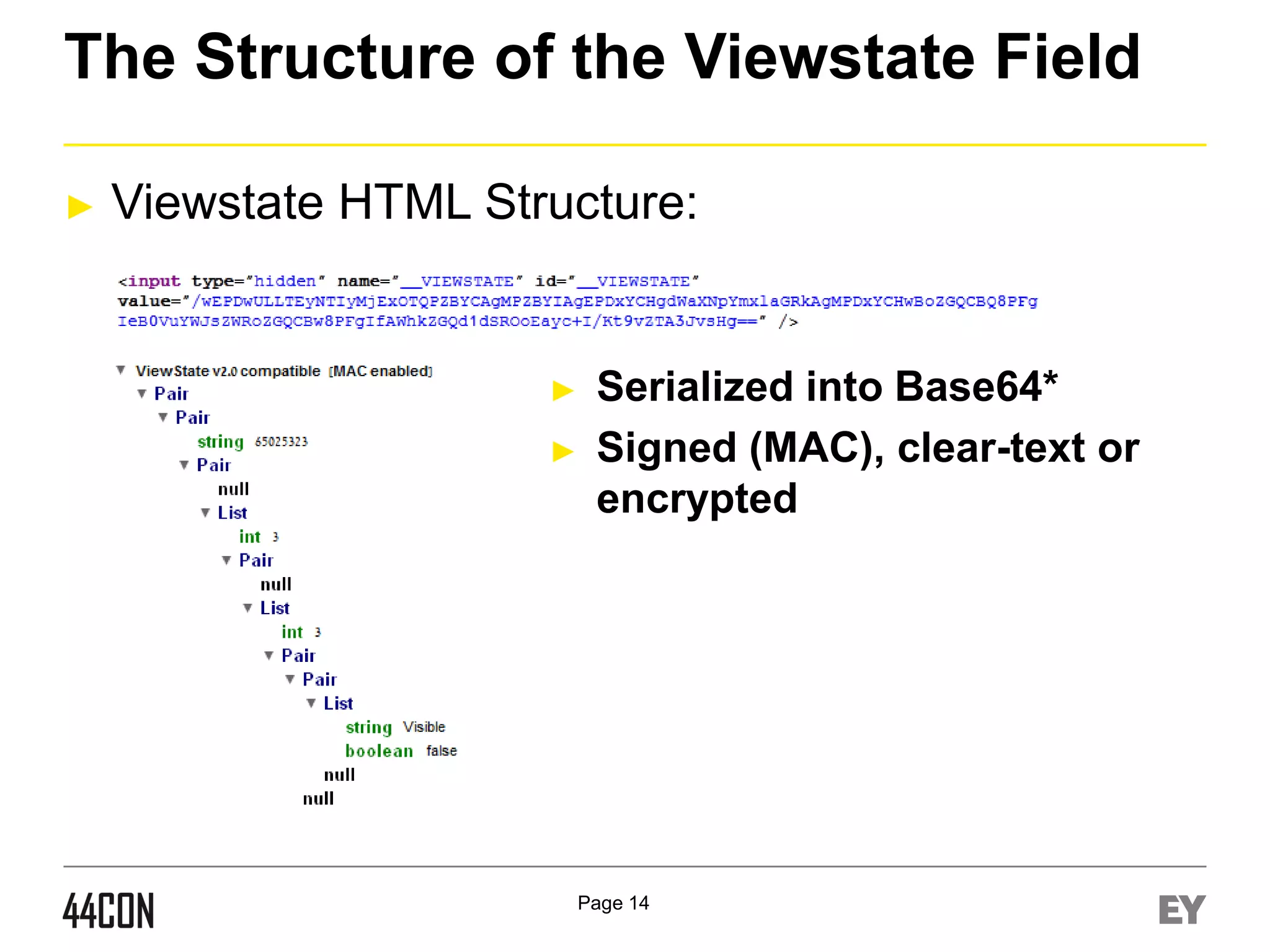
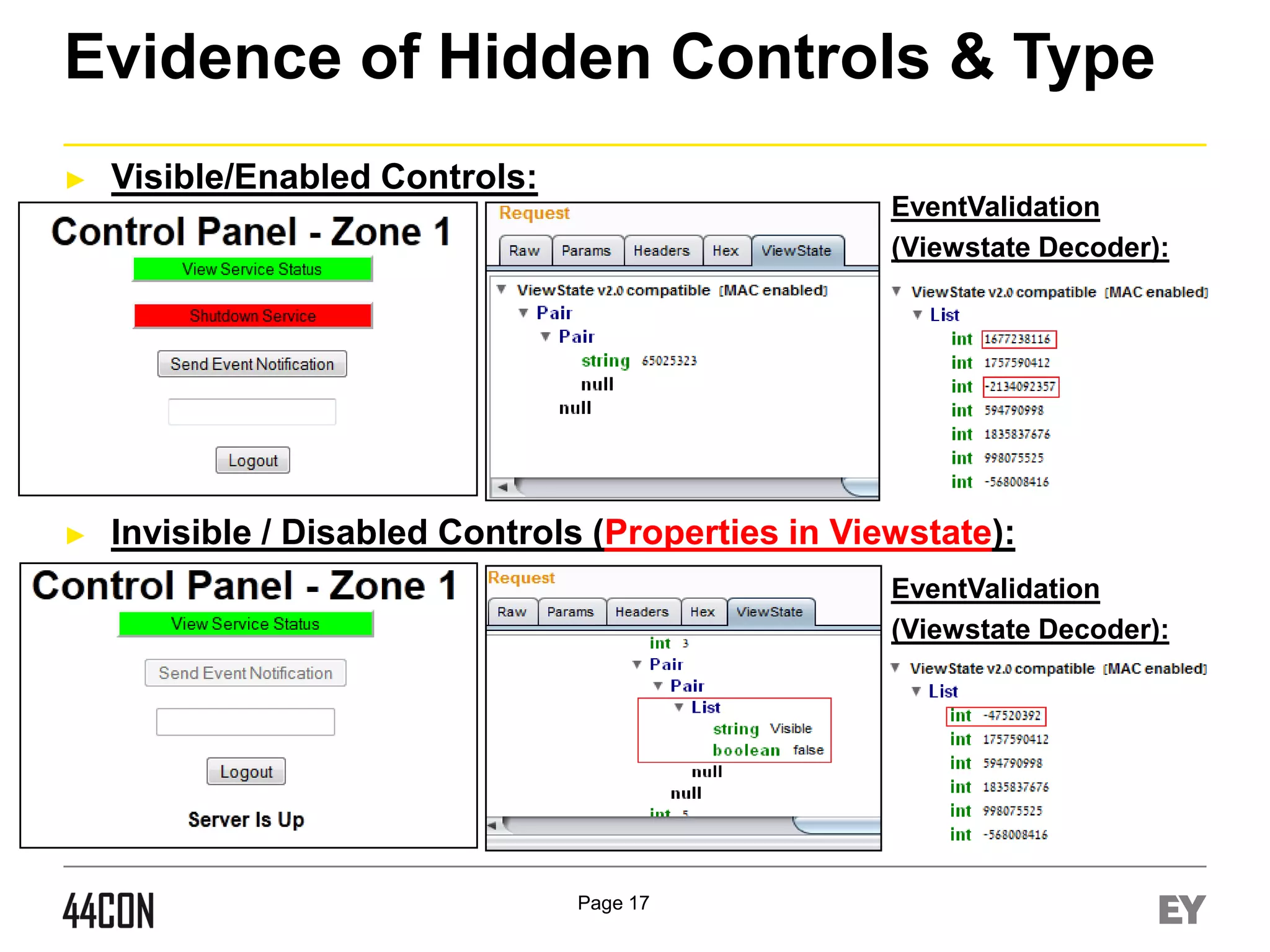
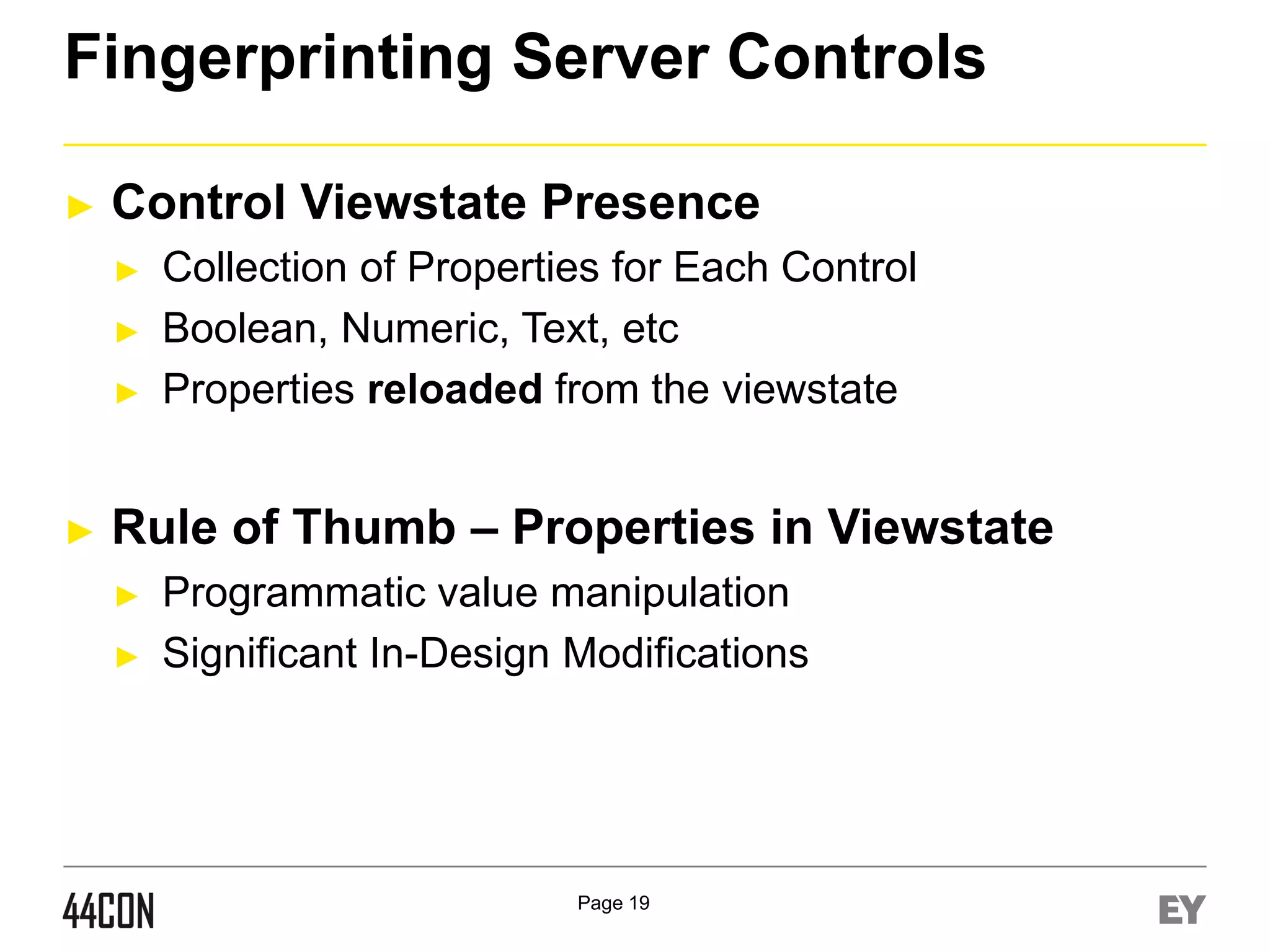
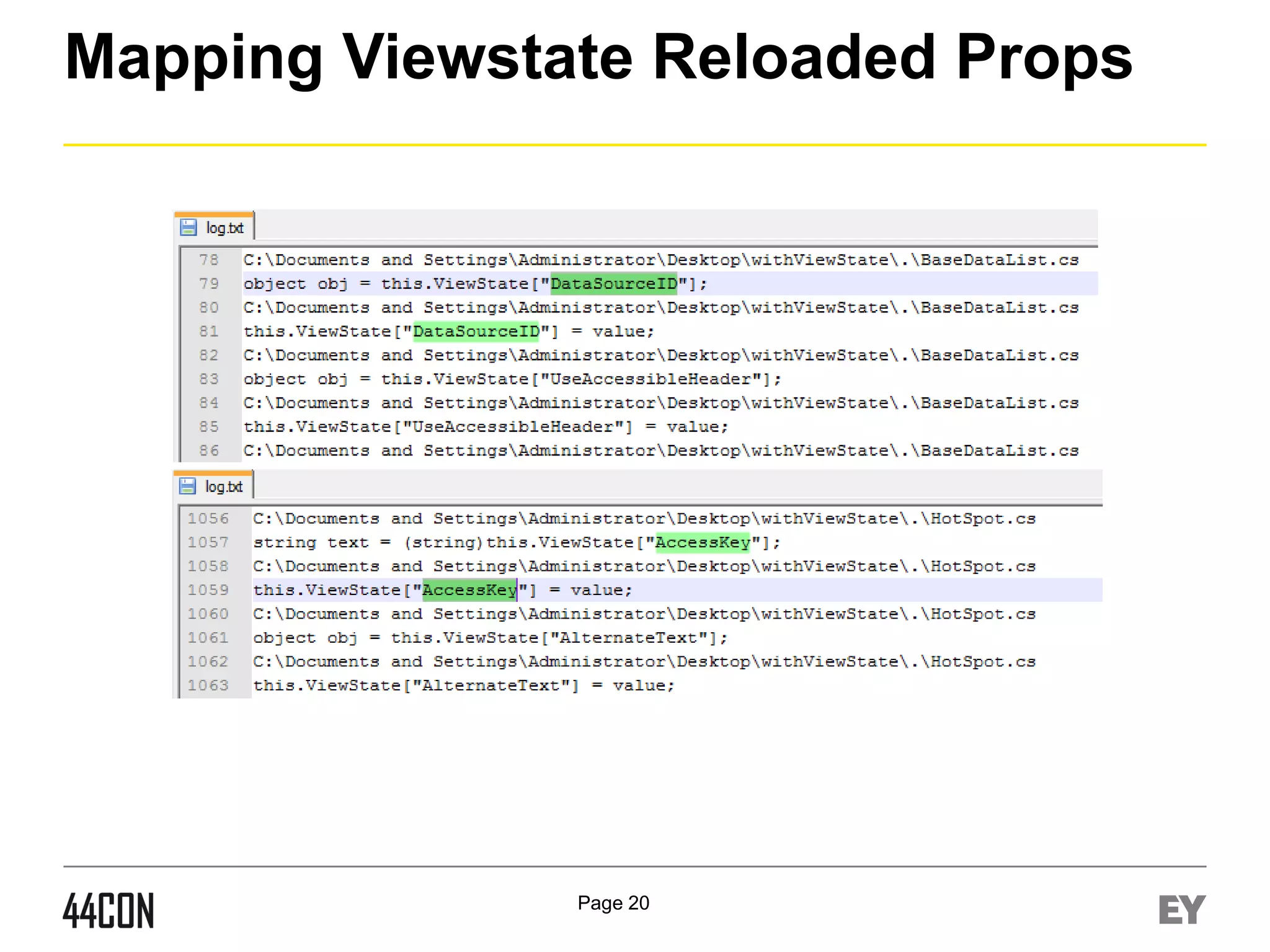
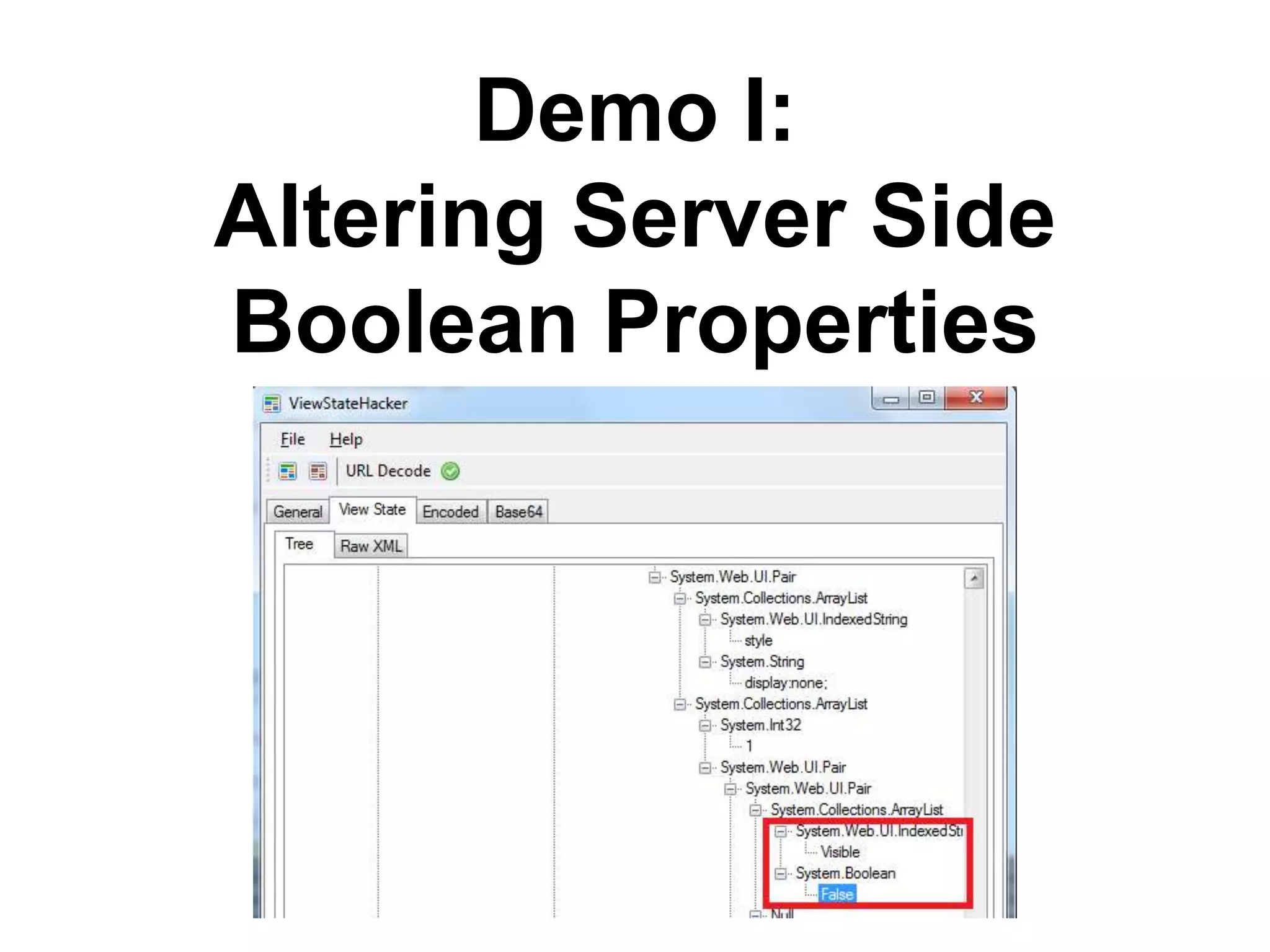
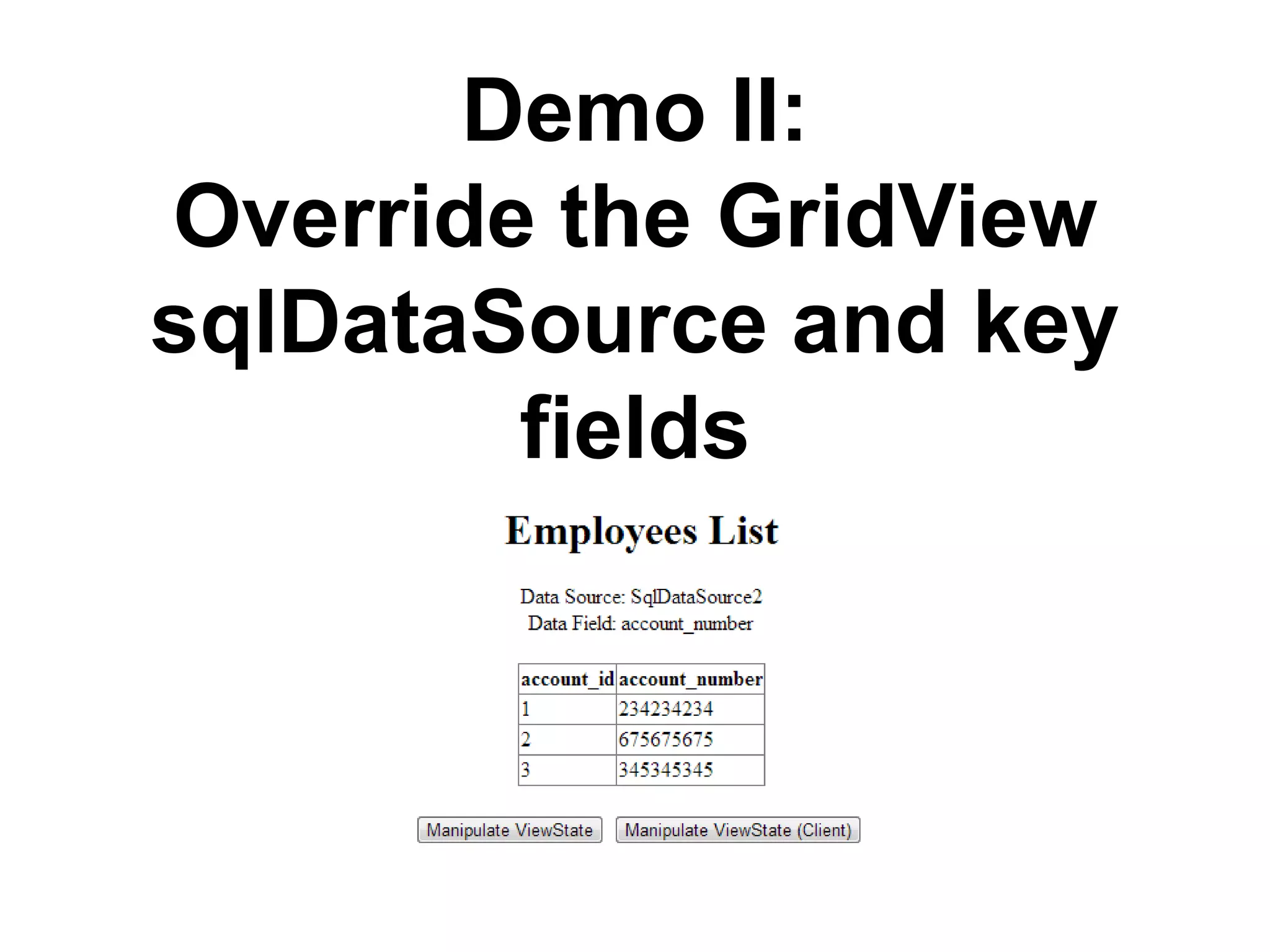
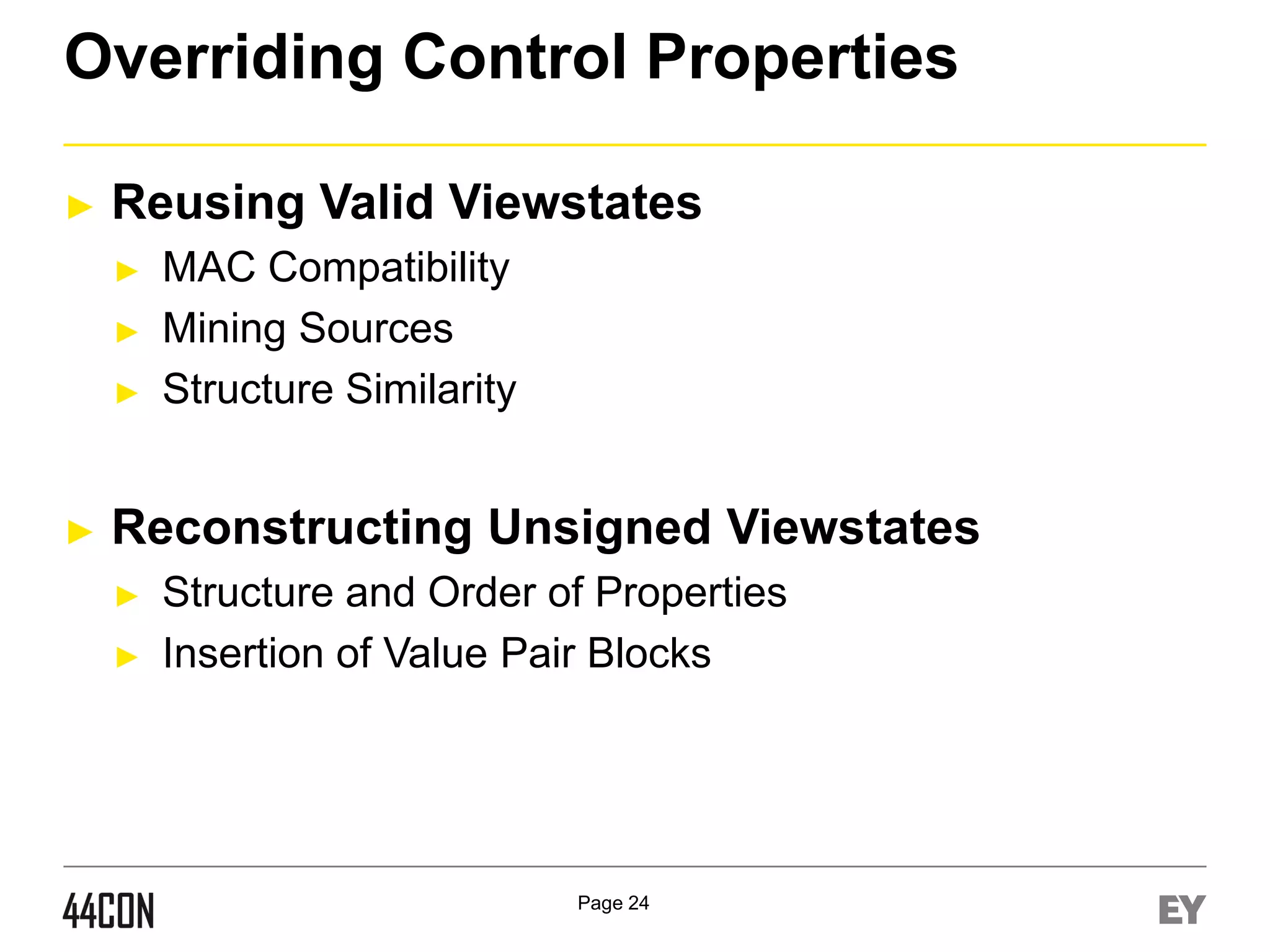
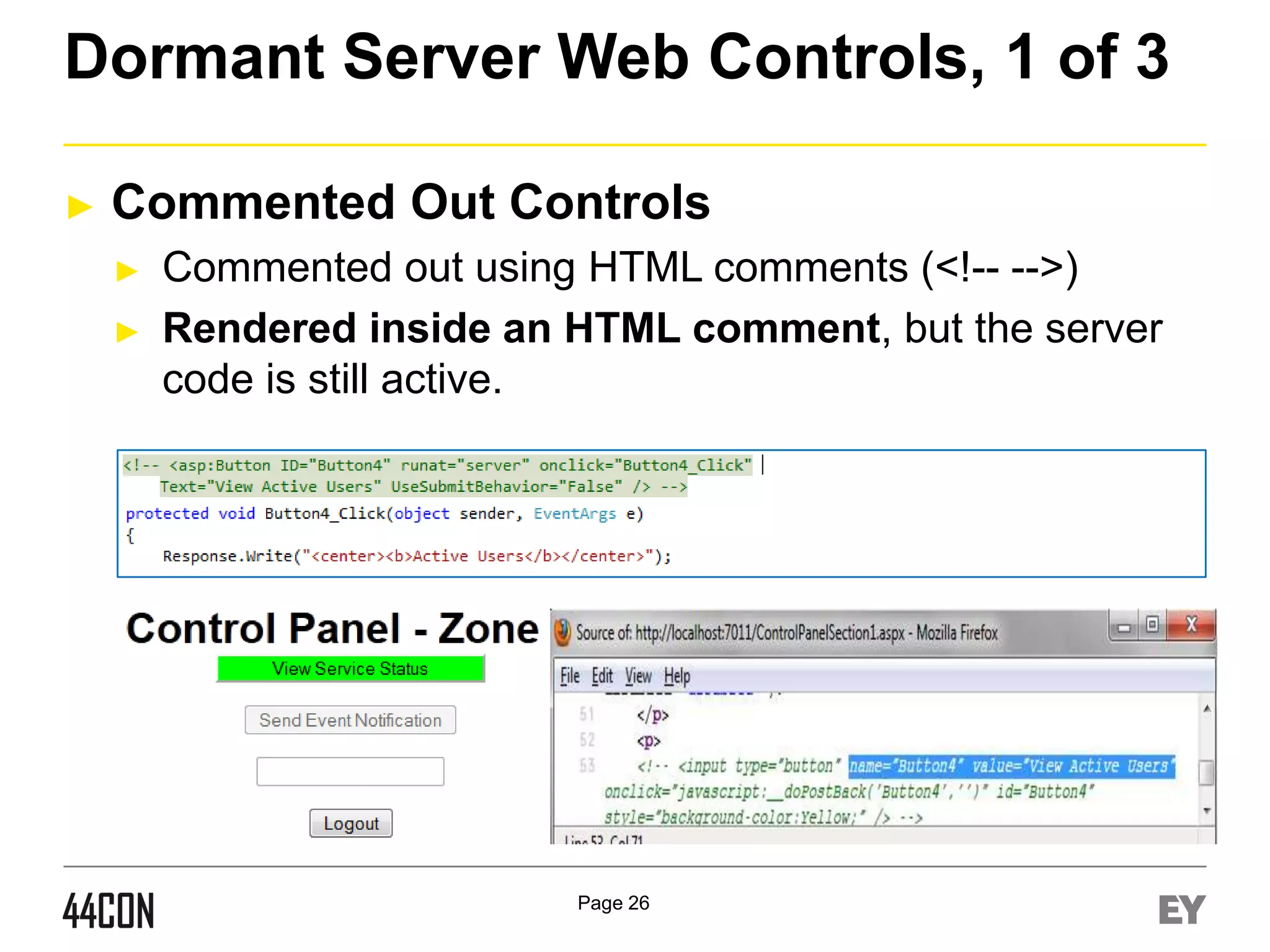
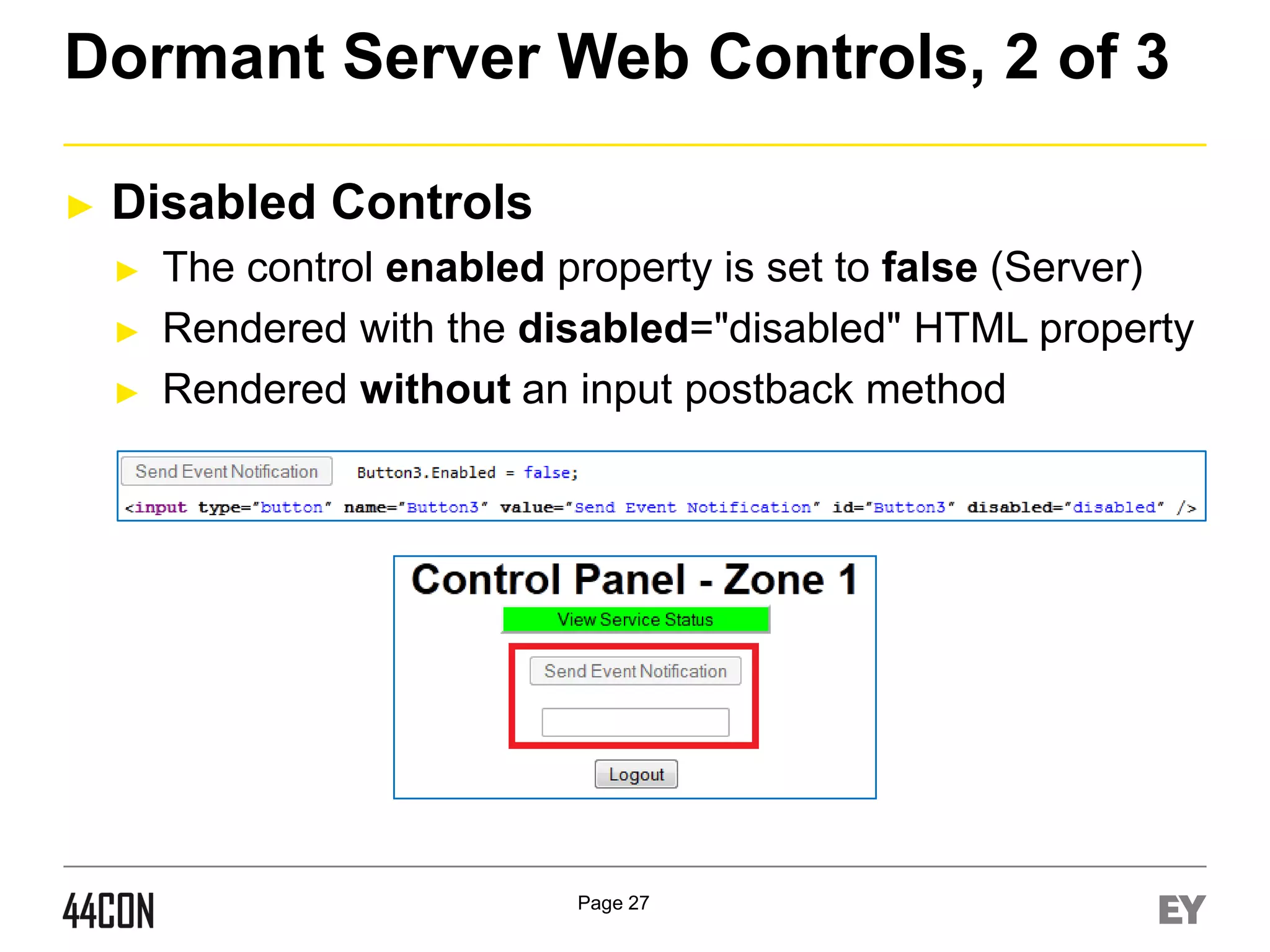
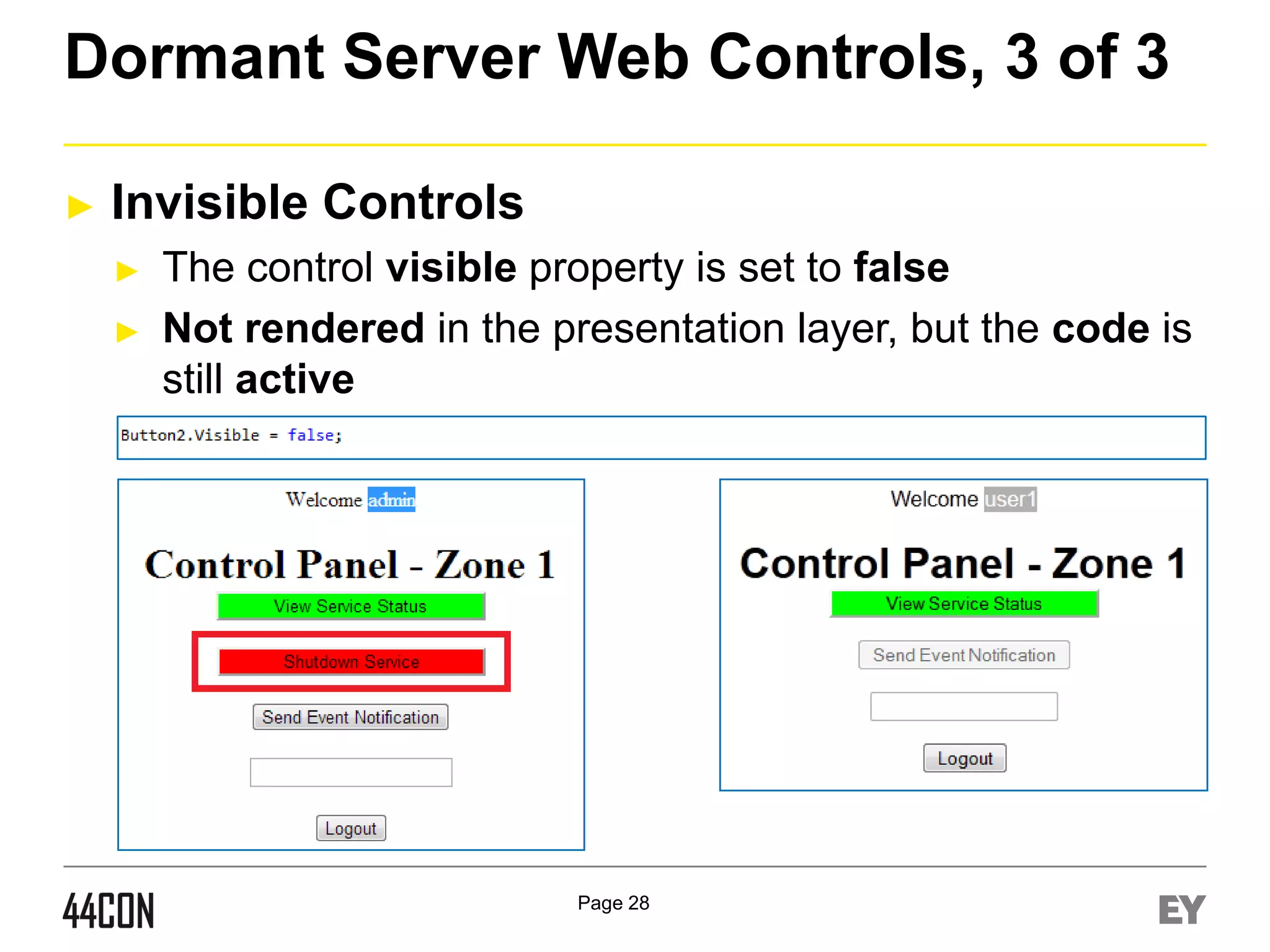
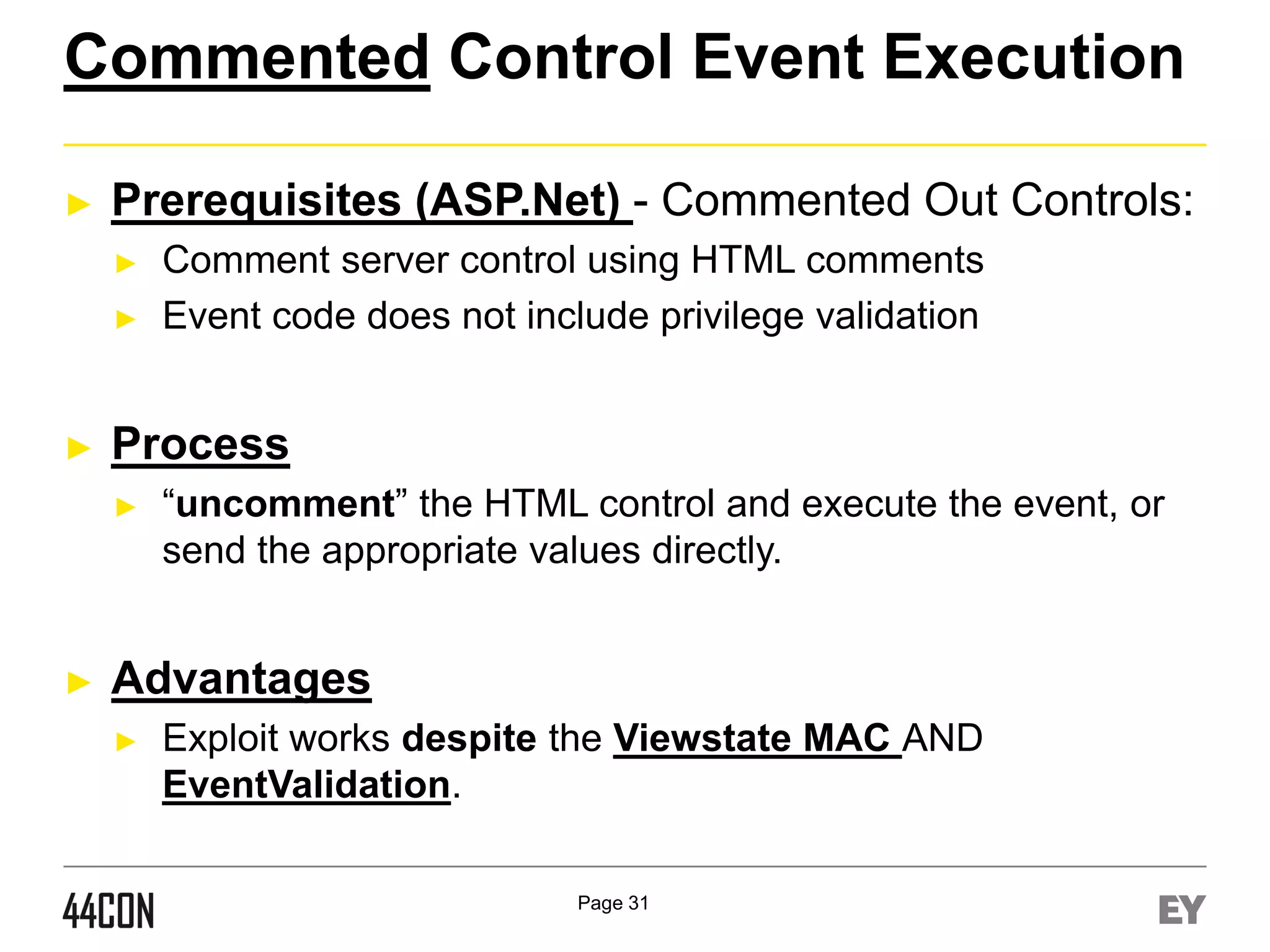
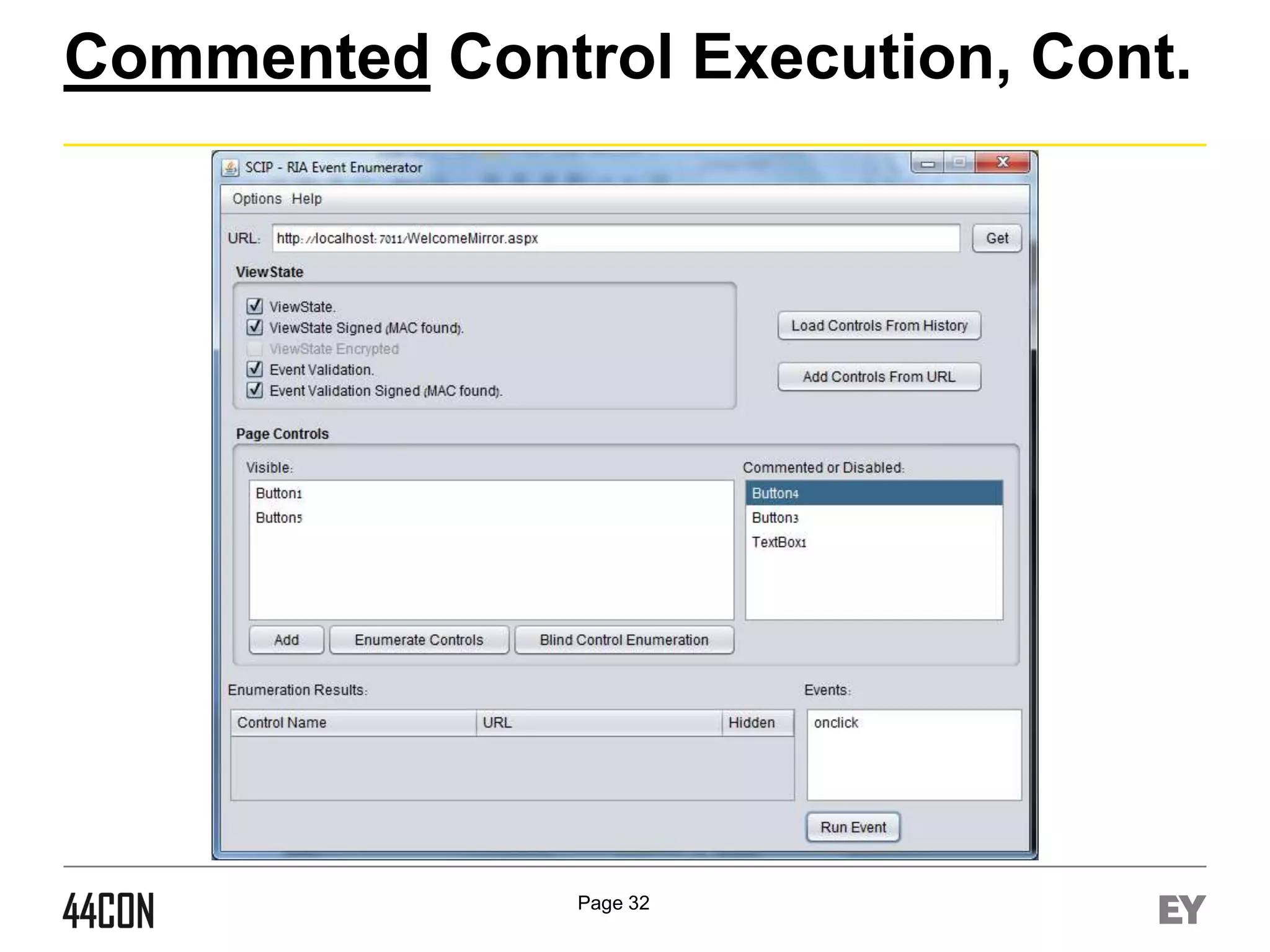
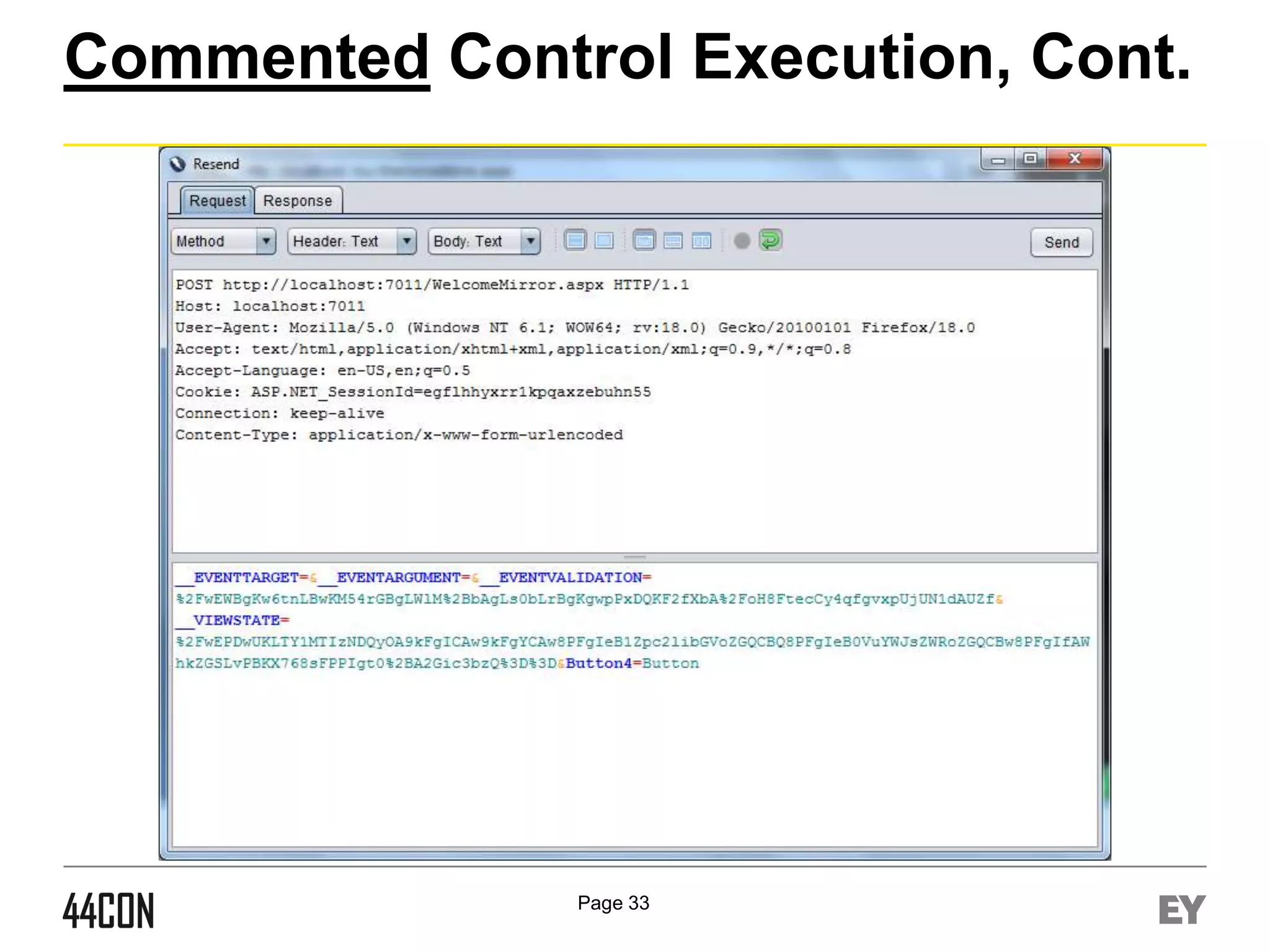
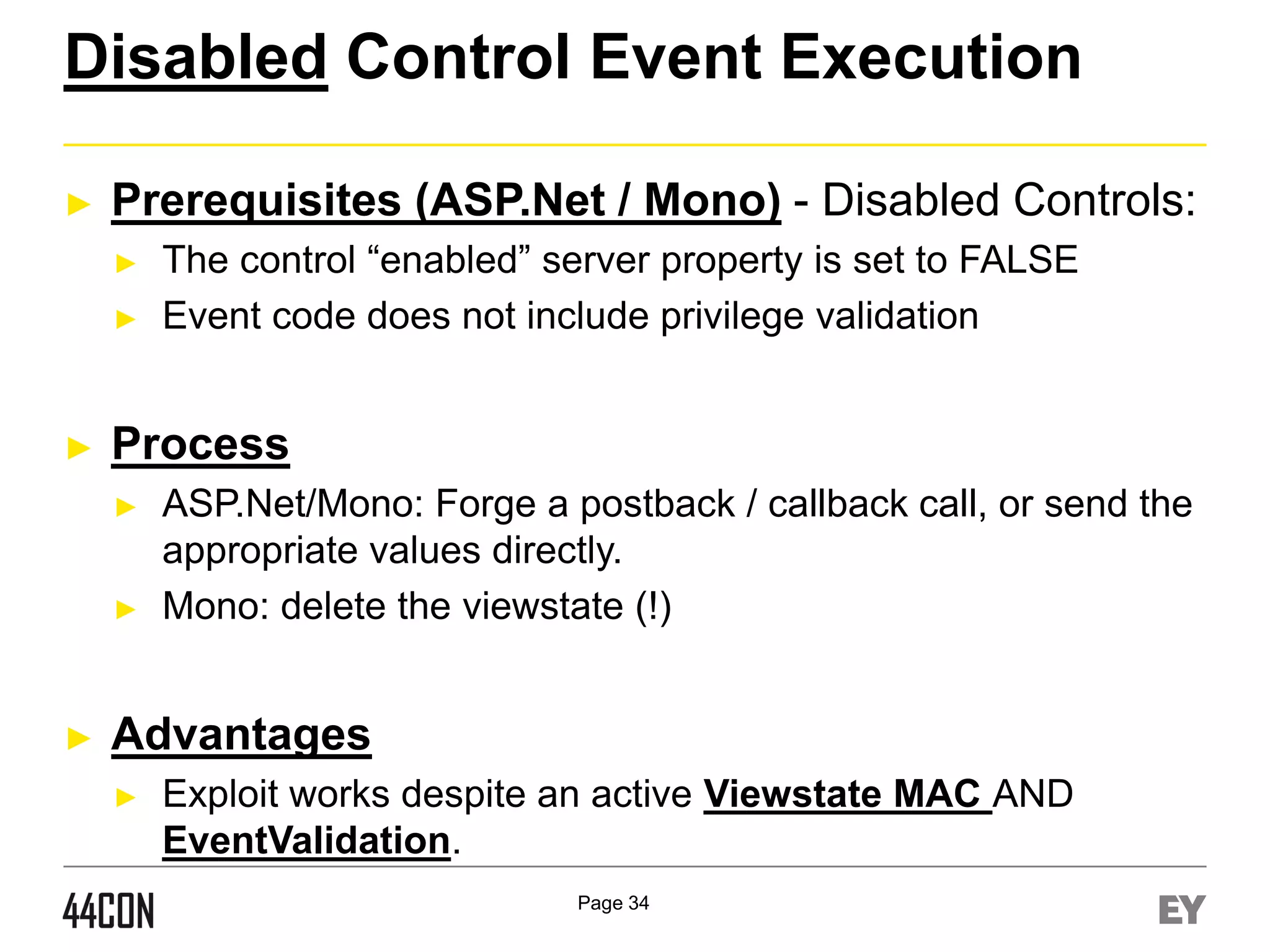
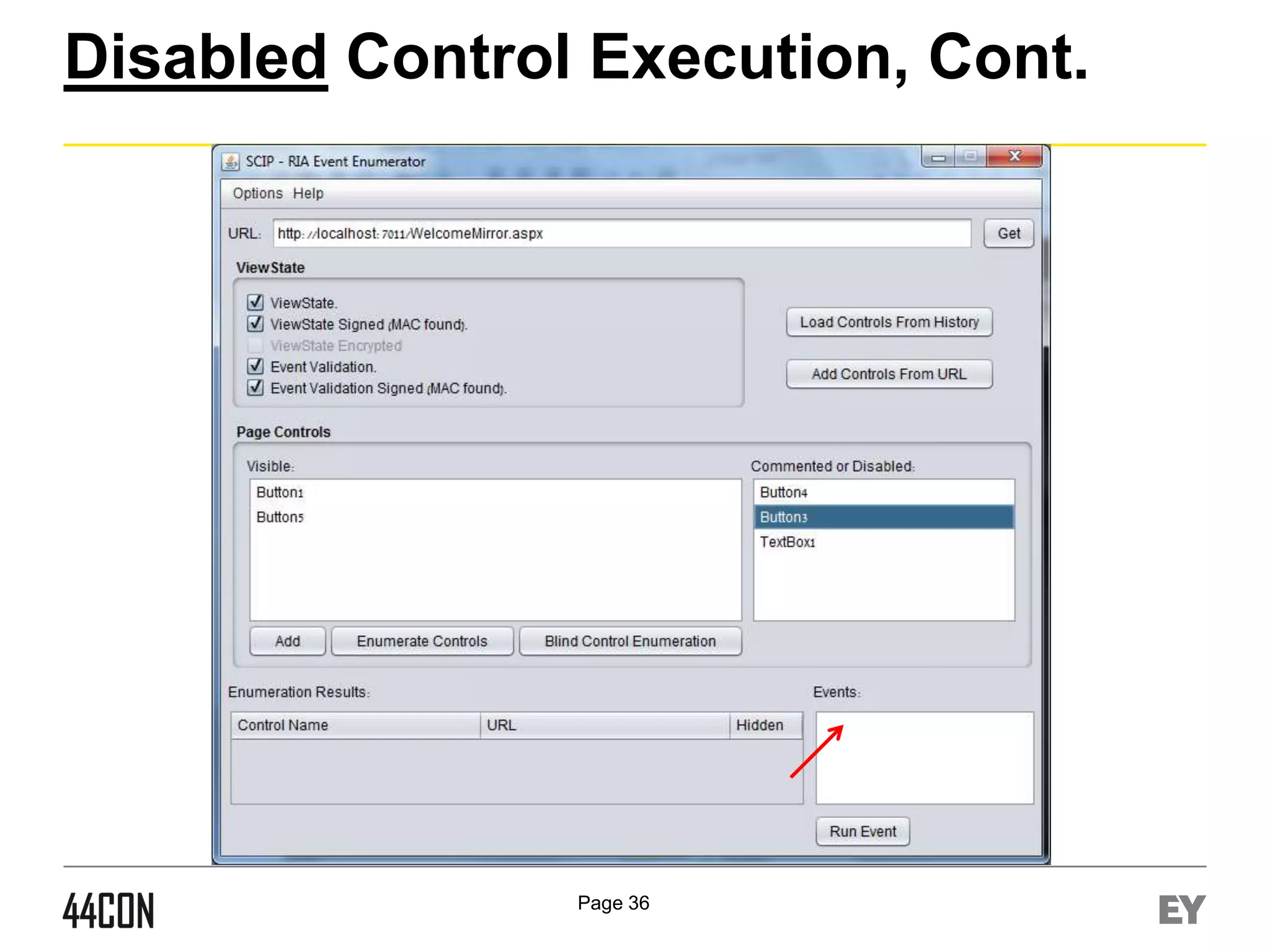
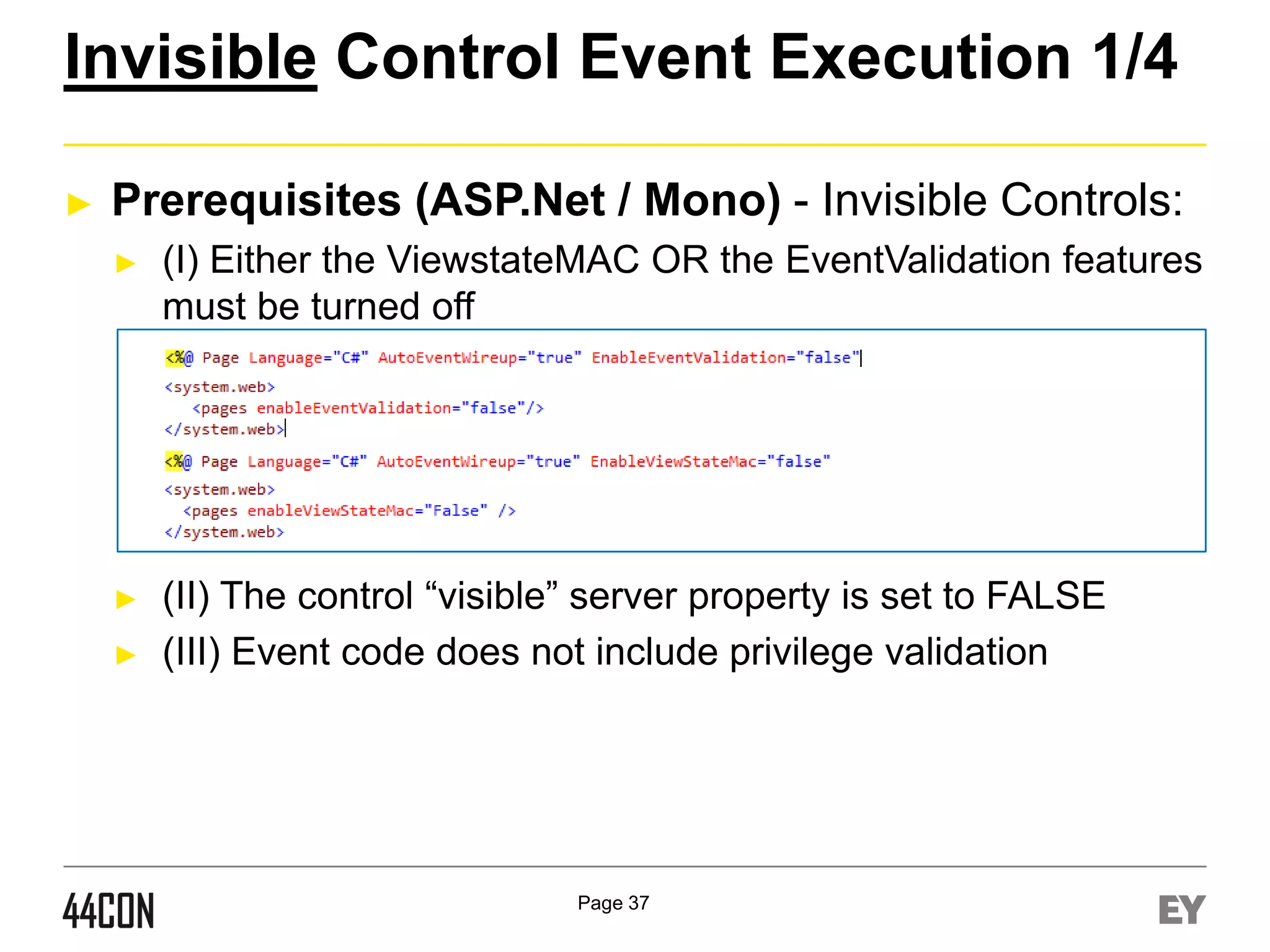
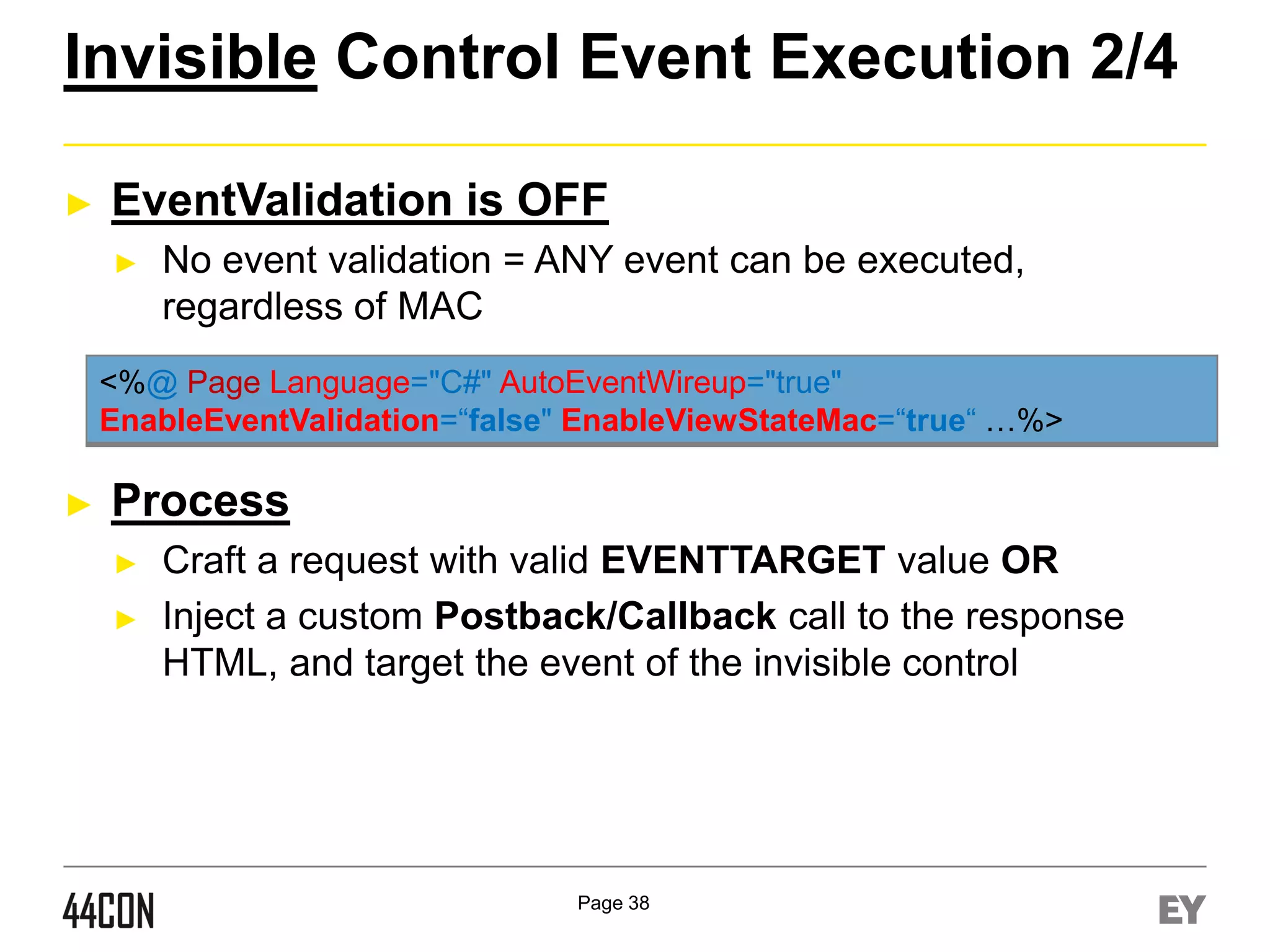
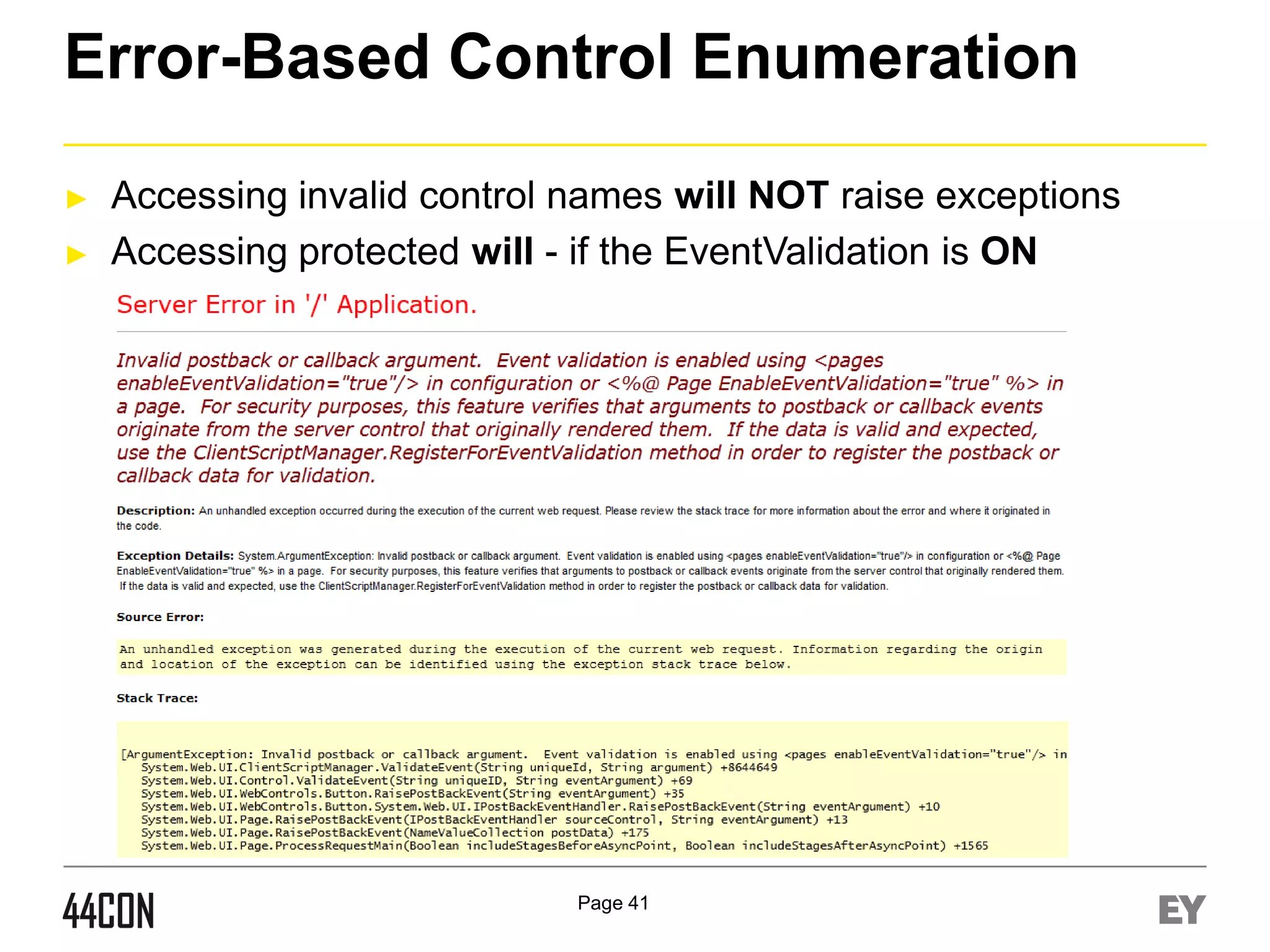
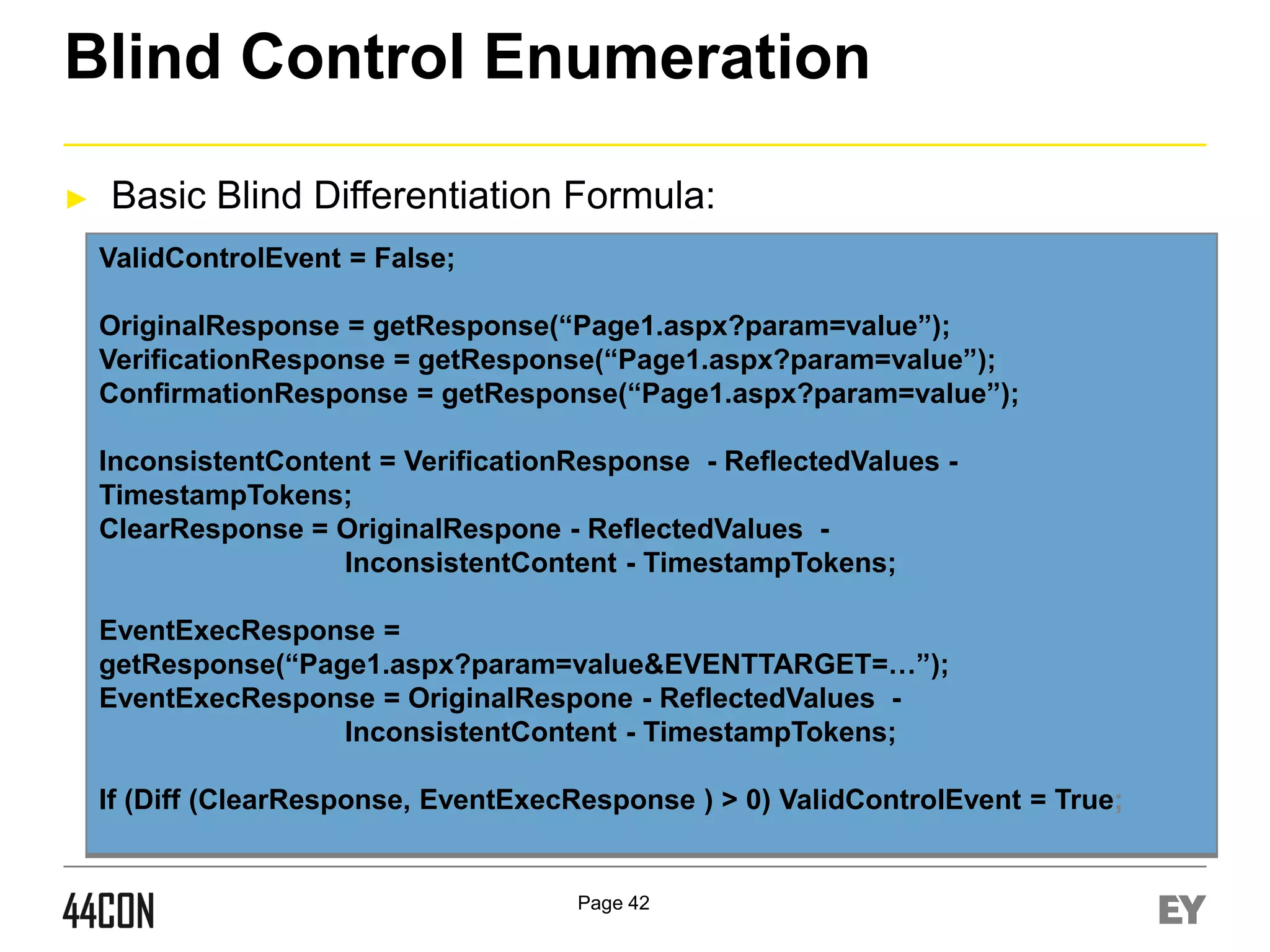
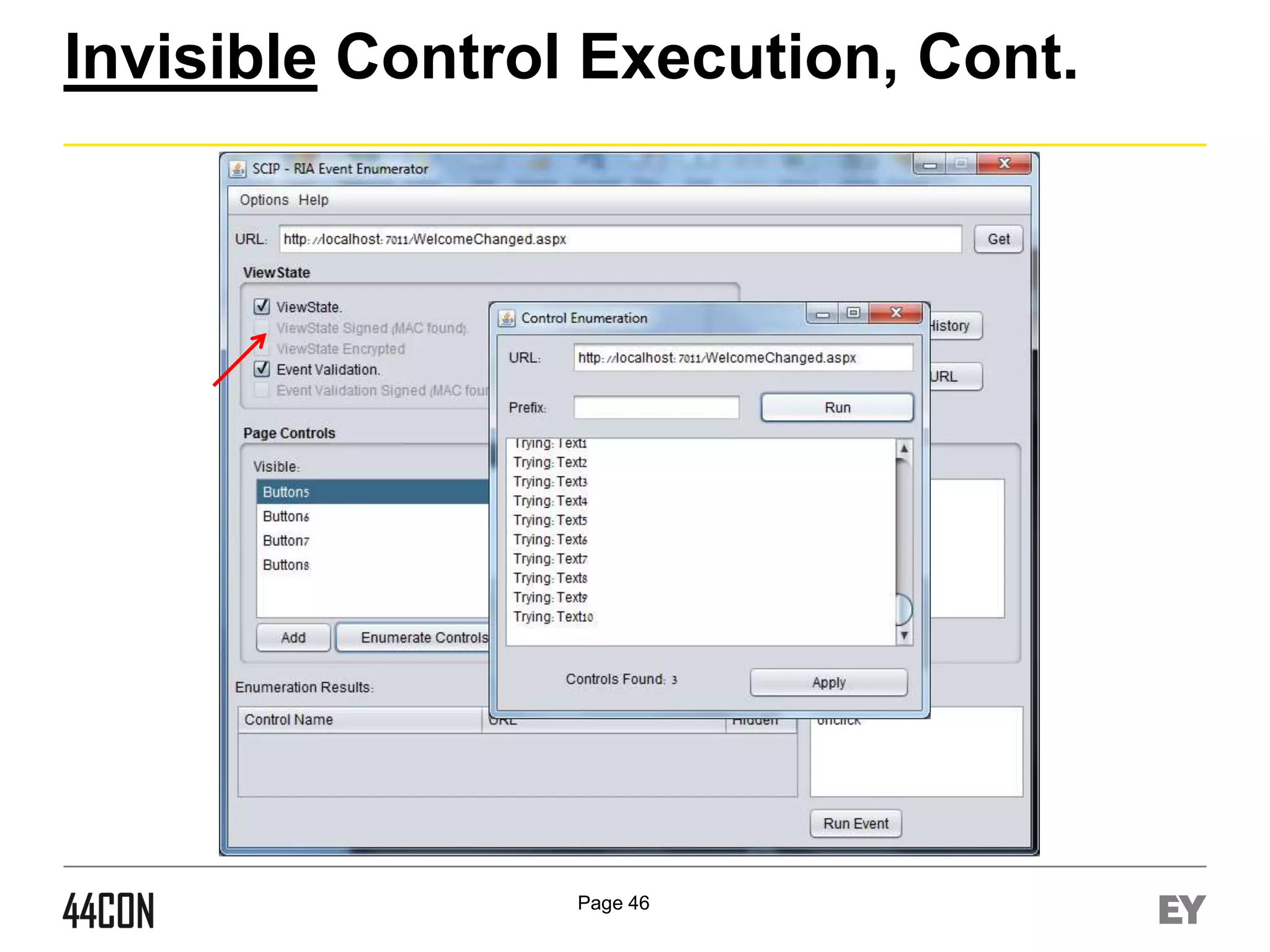
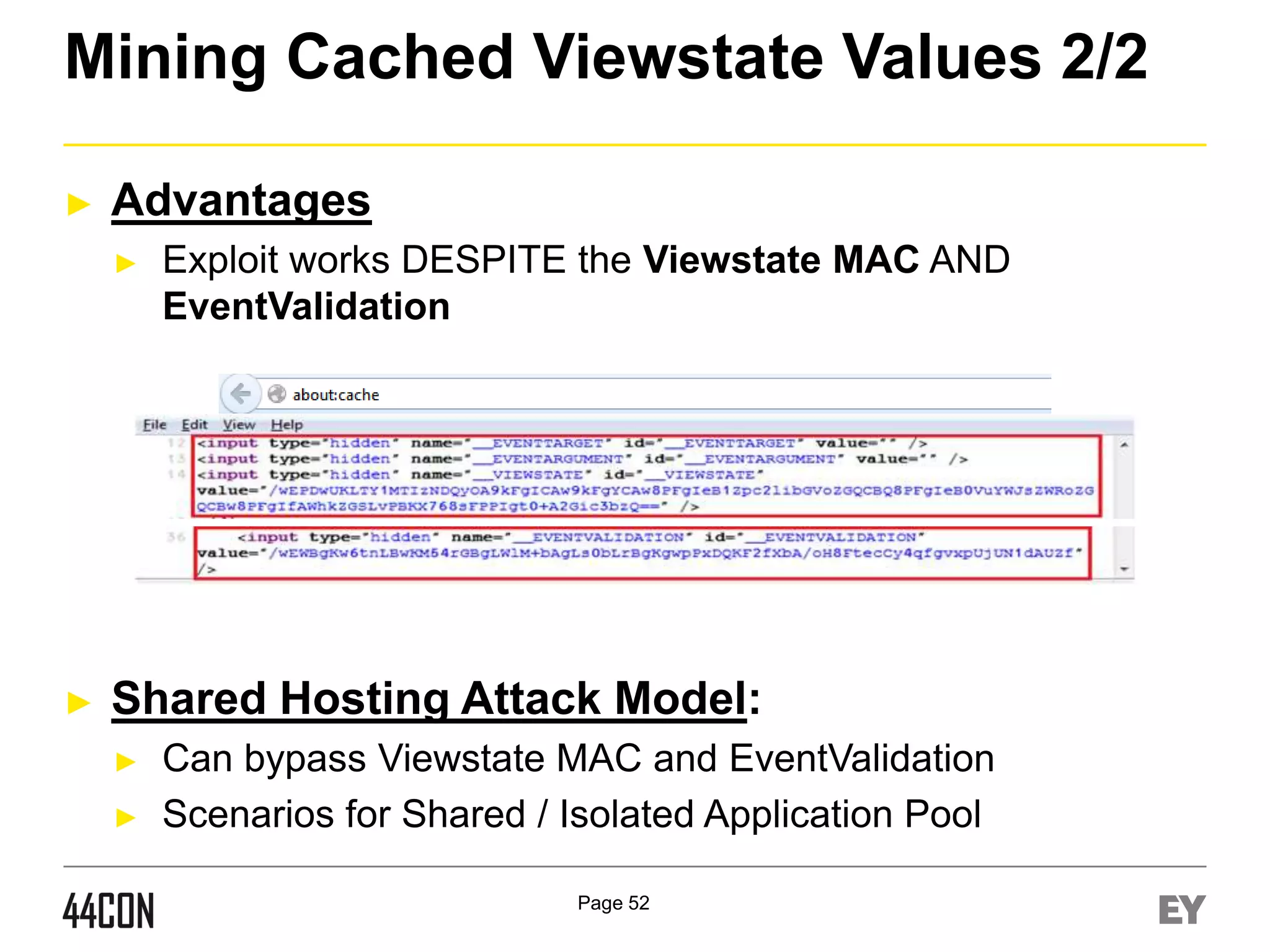
This document discusses exploiting vulnerabilities in ASP.net server-side web controls. It describes how dormant or hidden server controls can still be executed to abuse application logic, even when protections like event validation and viewstate MAC are enabled. Specific attacks covered include executing events of commented out, disabled, and invisible controls by manipulating POST data. The document also outlines techniques for fingerprinting server control properties and overriding them to alter application behavior. It introduces the RIA SCIP ZAP extension for analyzing these issues and demonstrates attacks. Risk mitigation recommendations are provided focusing on secure coding practices.






![The Event Validation Mechanism
►
Name/Value HashCode Formula
if ([ControlValue] == null)
return GetStringHashCode([ControlName]);
else
return GetStringHashCode([ControlName]) ^ GetStringHashCode([ControlValue]);
The EventValidation Field
►
<-Viewstate
Hashcode
►
<-Control
Hashcodes
►
►
MachineKey and MAC
Control Name/Value
Verification, Prior to Event
Execution
Include viewstate hashcode
Included in the HTML:
Page 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sheychen-dotnethavoc-44con2013-131219093550-phpapp02/75/44CON-2013-Net-Havoc-Manipulating-Properties-of-Dormant-Server-Side-Web-Controls-Shay-Chen-16-2048.jpg)







![Control Naming Conventions
►
Default: [ControlType][Number]
►
►
Default II (v1.1-v3.5/Master): ctl[ID]$[contentScope]$...
►
►
txtUsername, txtPassword, btnSubmit, cmdAddUser …
Plain: [Logic]
►
►
txt1, txt2, btn1, btn2, cmd1, cmd2, lst1, lst2 …
Custom Legacy: [ControlTypeShortCut][Logic]
►
►
ctl00$MainContent$txtName, ctl00$Content$cmdSubmit
Legacy: [ControlTypeShortCut][Number]
►
►
Button1, Button2, TextBox1, TextBox2 …
user, pass, submit, delete
Title Match: [Title]
►
Username, Password, Origin, Email, Update
Page 43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sheychen-dotnethavoc-44con2013-131219093550-phpapp02/75/44CON-2013-Net-Havoc-Manipulating-Properties-of-Dormant-Server-Side-Web-Controls-Shay-Chen-43-2048.jpg)
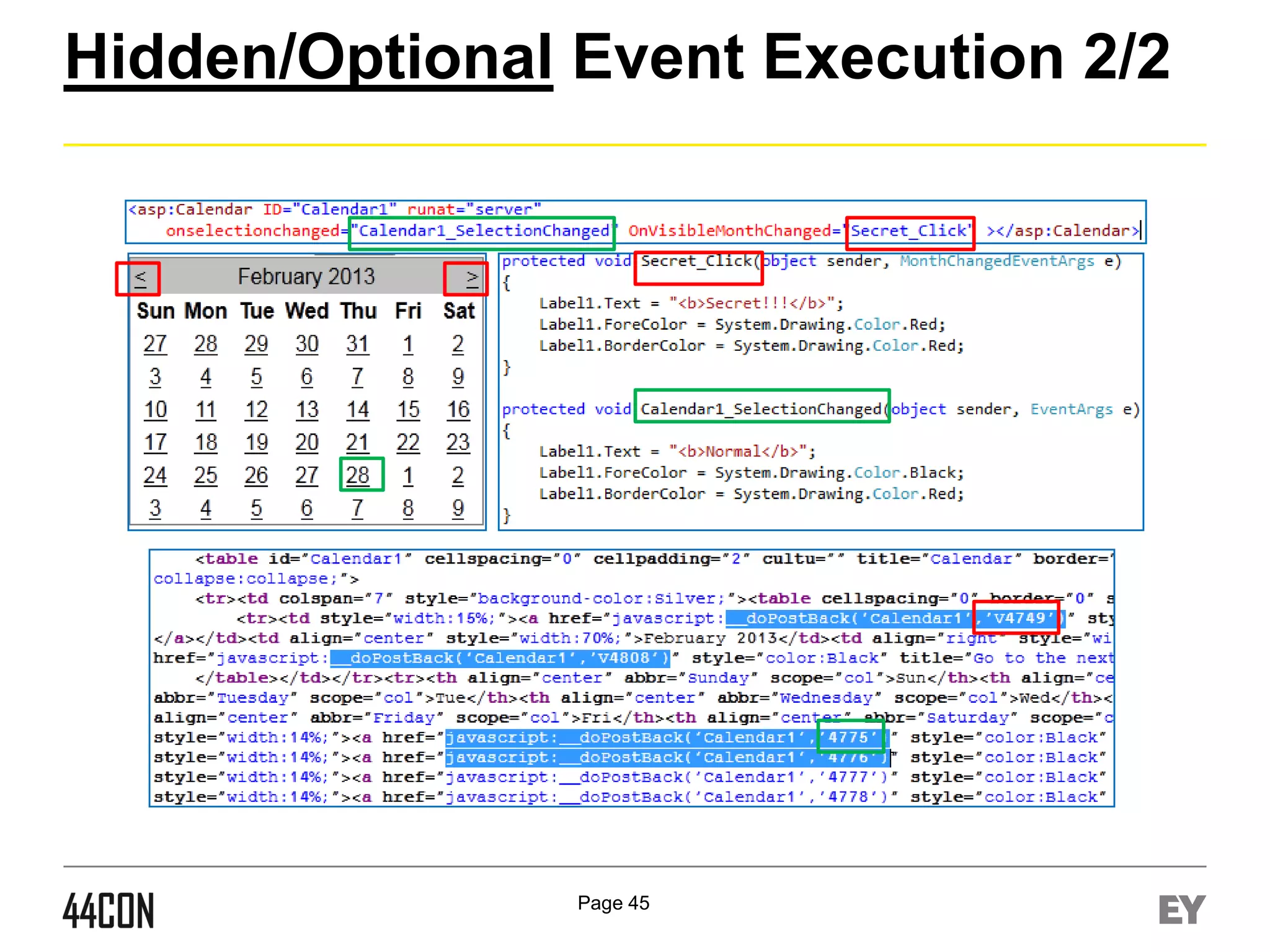
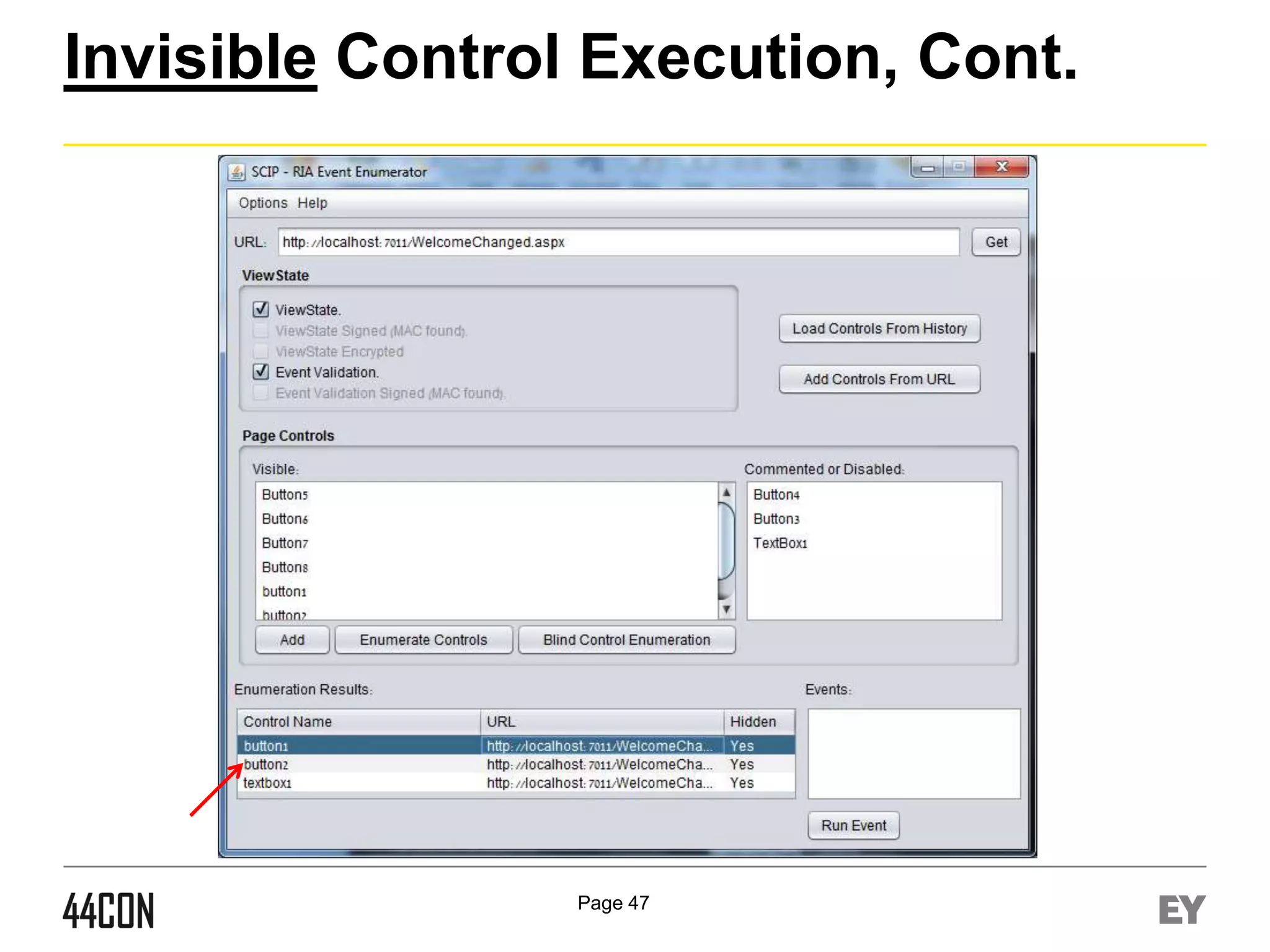
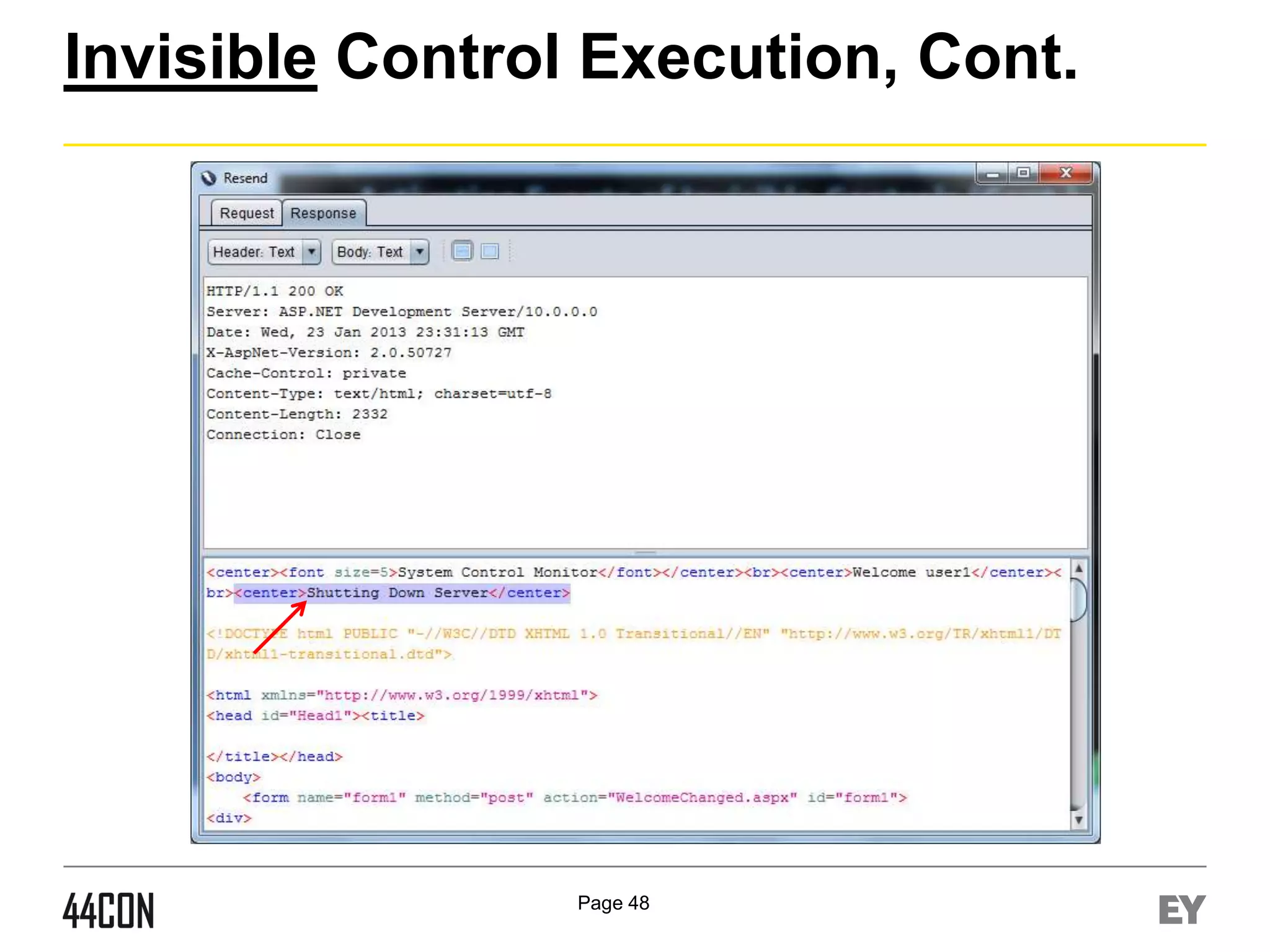
![Hidden/Optional Event Execution 1/2
►
Prerequisites – Multiple Dormant Events of Controls:
►
►
►
Process:
►
►
►
Control assigned with multiple events.
(Calendar control, Custom Controls, etc)
Fuzz the eventargument field, in addition to eventtarget
Eventargument variation can execute different server
events (for example - V[value] vs. [value])
Advanced:
►
►
Core Events vs. Custom Events
Example:
Click, Command, onSelectionChanged, OnVisibleMonthCha
nged, Etc
Page 44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sheychen-dotnethavoc-44con2013-131219093550-phpapp02/75/44CON-2013-Net-Havoc-Manipulating-Properties-of-Dormant-Server-Side-Web-Controls-Shay-Chen-44-2048.jpg)

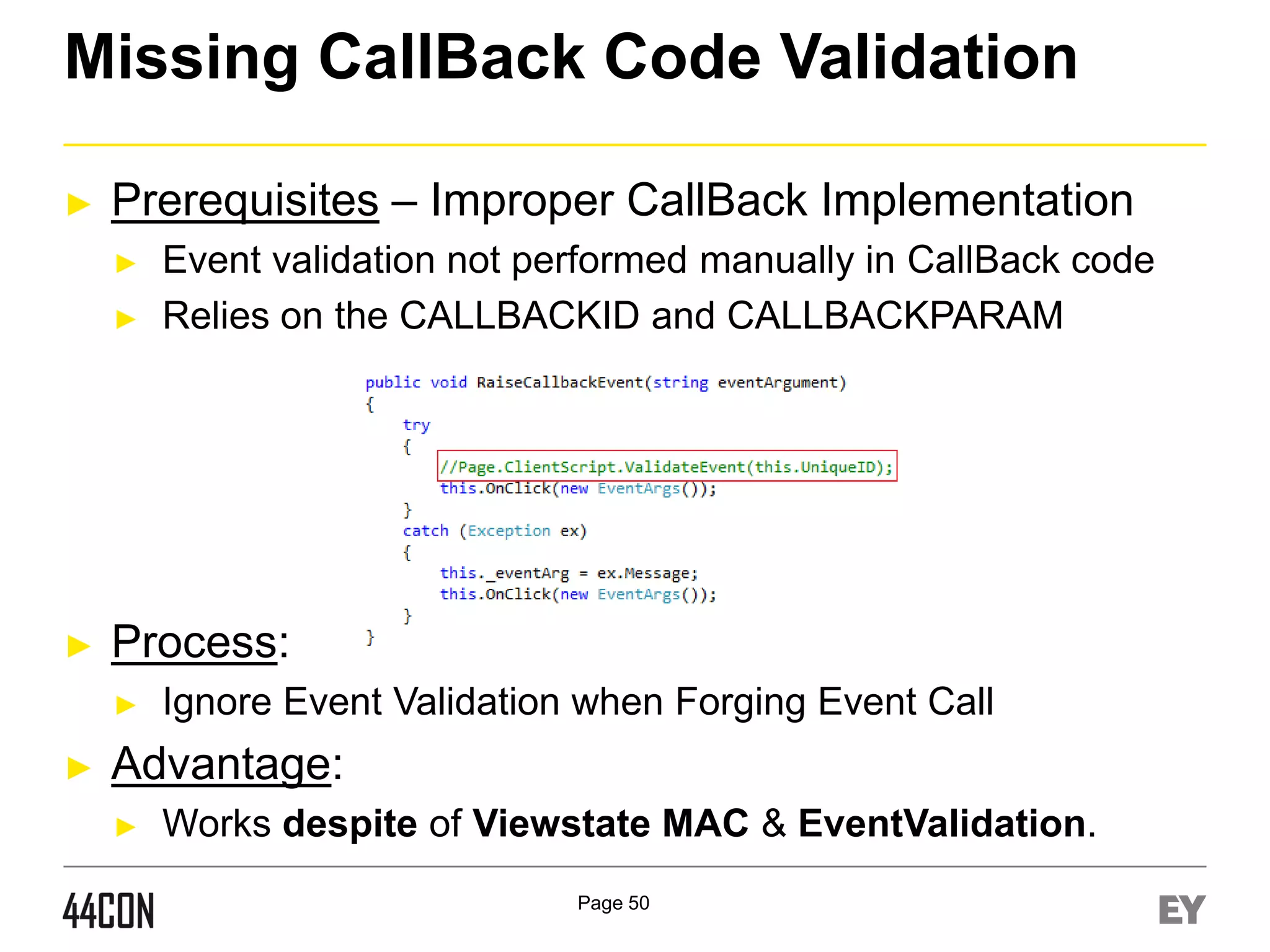
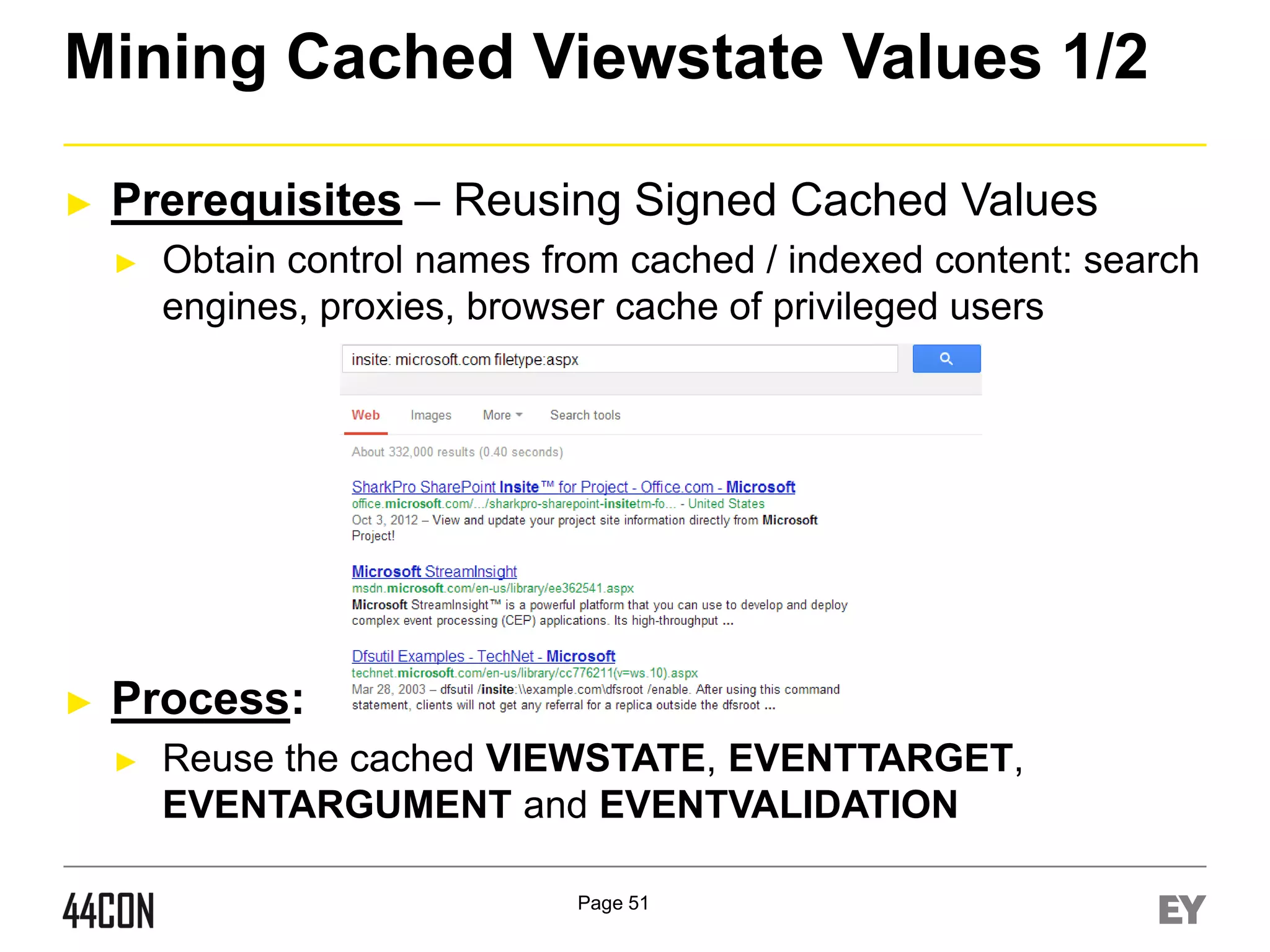


![Event Level Privilege Validation
►
Explicit Privilege Validation in Event Code
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (((String)Session["user"]).Equals("admin"))
{
...
}
}
►
Enable Event Validation / MAC
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true"
EnableEventValidation="true" EnableViewStateMac="true“ …%>
Page 55](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sheychen-dotnethavoc-44con2013-131219093550-phpapp02/75/44CON-2013-Net-Havoc-Manipulating-Properties-of-Dormant-Server-Side-Web-Controls-Shay-Chen-55-2048.jpg)