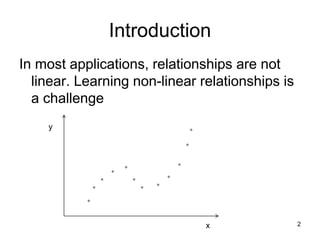
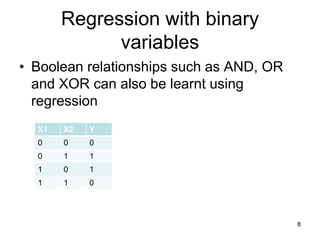
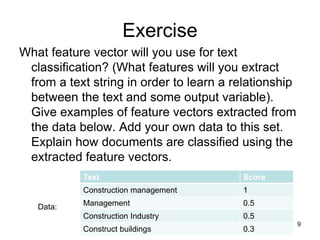
The document discusses the application of machine learning in civil engineering, focusing on learning non-linear relationships through feature space analysis. It emphasizes the importance of feature selection and provides examples of how feature vectors can be used to understand relationships in data, such as beam deflection and text classification. Additionally, it touches on regression with binary variables and the use of principal components for dimensionality reduction.