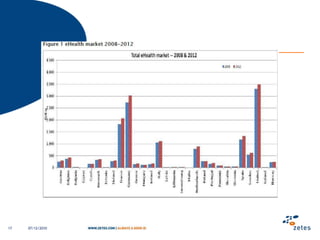
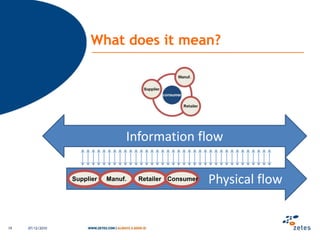
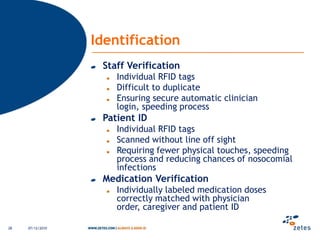
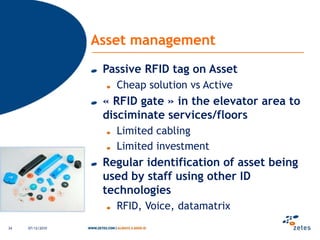
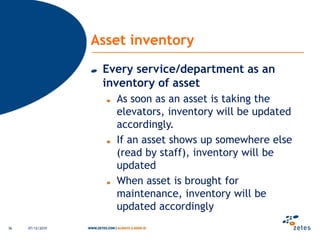
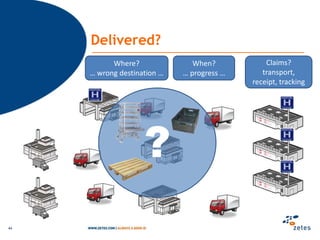
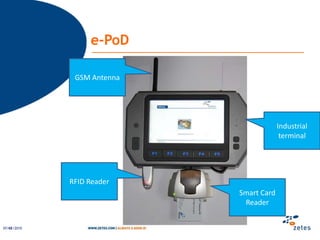
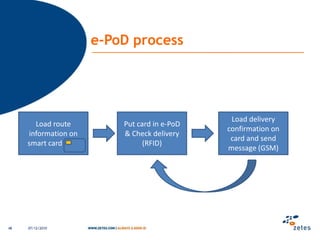
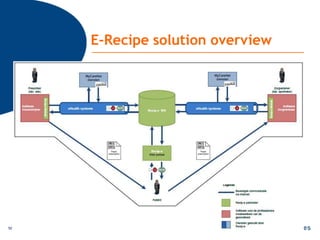
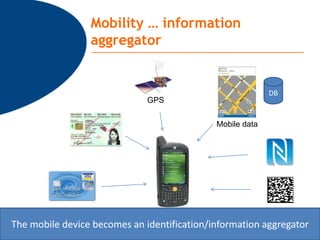
The document discusses various topics relating to e-health solutions. It addresses major e-health topics like clinical information systems and telemedicine. It emphasizes that technologies exist but what is needed is a way to connect them to address real business needs. Specific solutions discussed include voice nursing to improve efficiency, asset tracking to better manage hospital equipment, people tracking for vulnerable patients, and electronic proof of delivery for verifying shipments. Overall the document promotes an open-minded, collaborative approach to developing e-health solutions.














![Build on new regulation: serialisation06/12/201011Manufacturer Product Code 14 digits [GTIN or pseudo-GTIN]Unique Serial Number (randomized) 20 digitsExpiry Date 6 digits (yymmdd)Batch Number up to 20 alpha-numeric charactersGTINSerial nrExpiryBatch nr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3ismartsolutionhealthcaremic-101207093235-phpapp02/85/smart-solutions-healthcare-MIC-16-320.jpg)