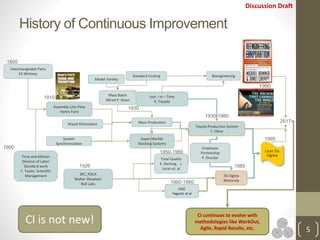
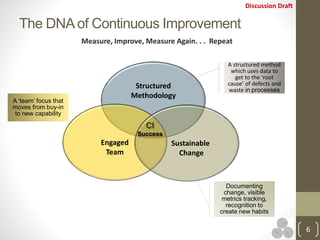
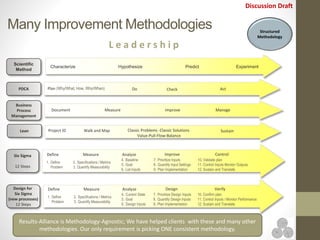
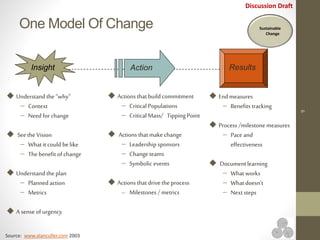
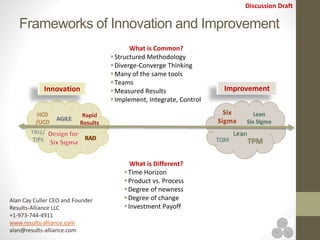
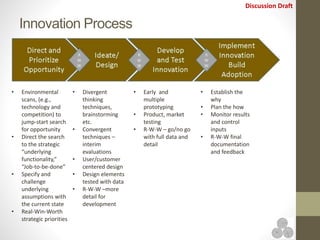
The document discusses continuous improvement (CI) methodologies and their importance for organizational growth, outlining key processes for innovation, integration, and improvement. It emphasizes a structured, team-focused approach, detailing implementation steps, critical success factors, and the role of leadership in establishing and sustaining CI initiatives. Results-Alliance, the consulting firm featured, provides resources and expertise to support clients in achieving their continuous improvement goals.