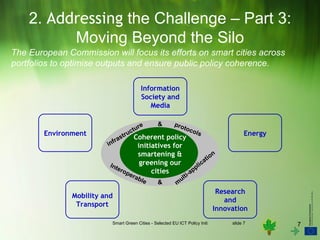
The document discusses the concept of 'smart green cities' which utilize ICT infrastructure and services for sustainability, focusing on energy efficiency, carbon neutrality, and resource optimization. It highlights EU initiatives and a common framework needed to measure the environmental impact of ICT in urban settings, while promoting collaboration among cities through commitments like the Green Digital Charter. The European Commission aims to enhance policy coherence across portfolios to support the development of smart green cities.