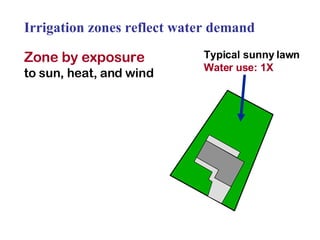
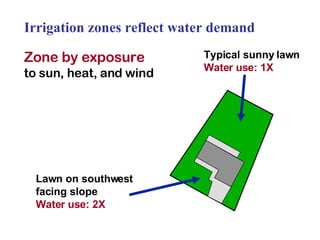
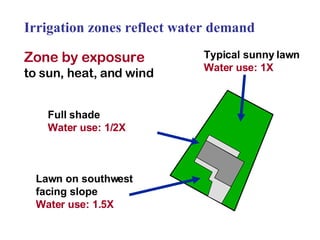
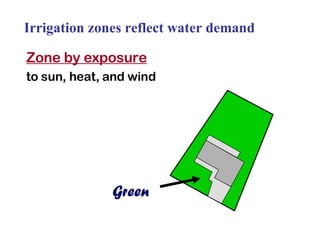
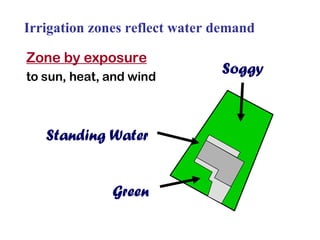
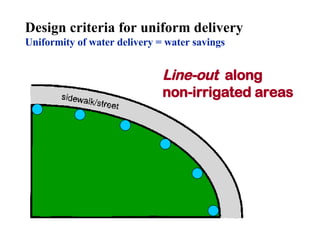
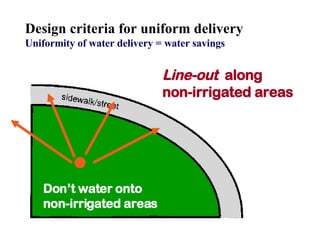
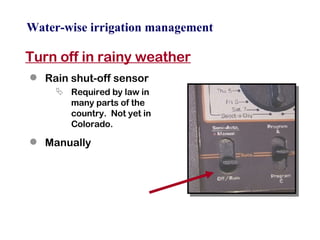
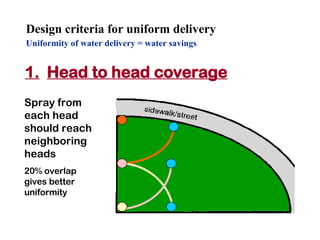
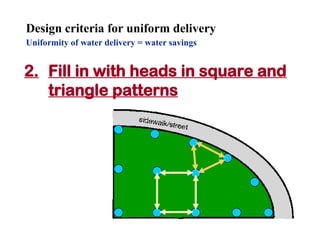
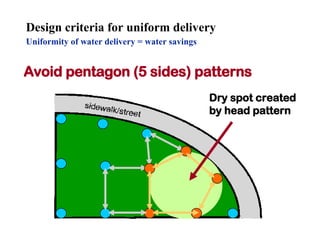
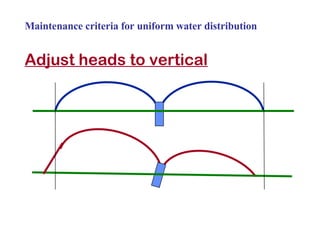
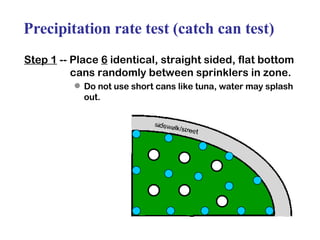
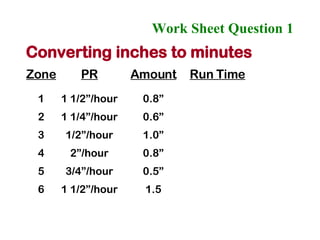
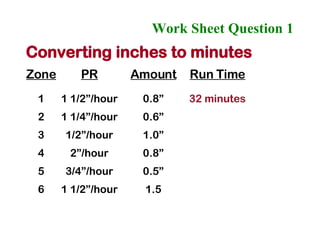
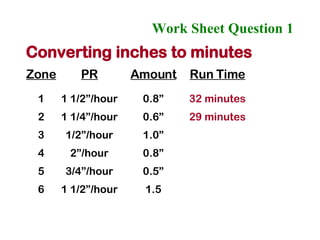
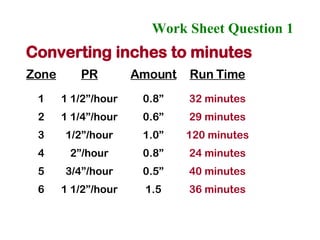
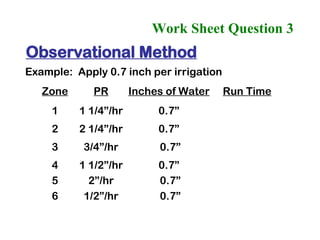
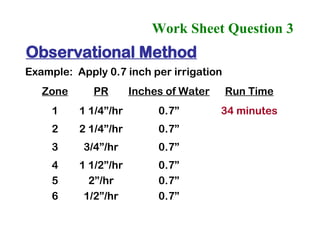
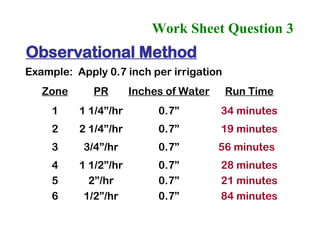
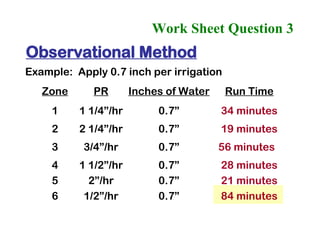
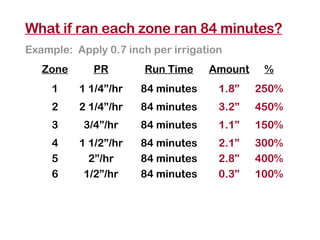
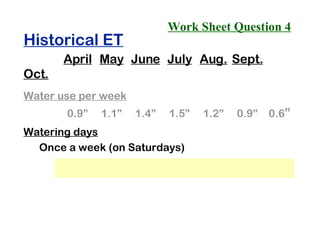
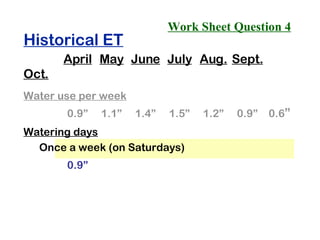
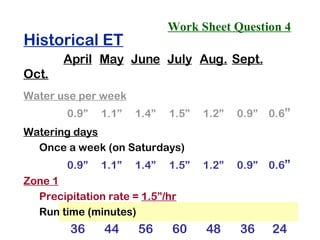
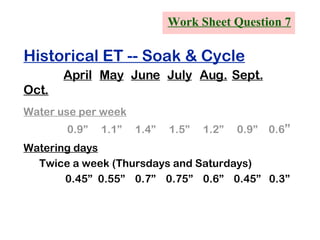
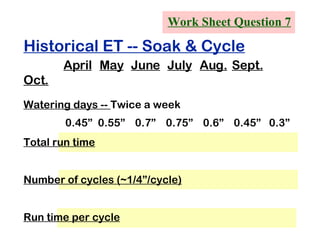
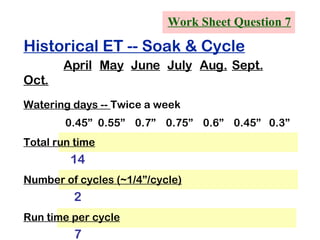
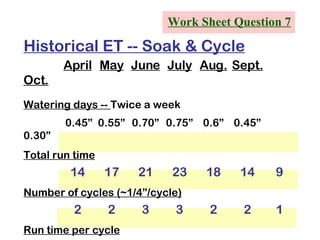
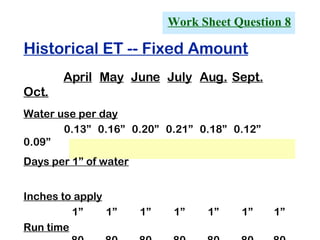
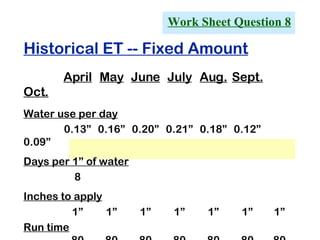
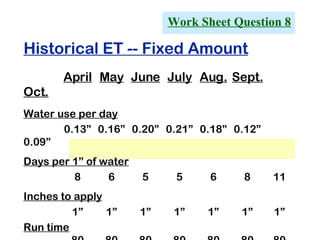
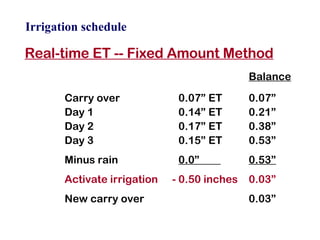
The document provides guidance on performing an irrigation audit to evaluate the efficiency of an irrigation system and identify opportunities for water savings. It outlines 8 steps: 1) water the day before the audit; 2) visually inspect landscaping; 3) record controller settings; 4) identify irrigation zones; 5) evaluate zone performance and precipitation rates; 6) calculate optimized run times for each zone based on precipitation rates; 7) consider soak vs cycle watering and timing; and 8) implement optimized settings and re-evaluate for water savings of 20-70%.