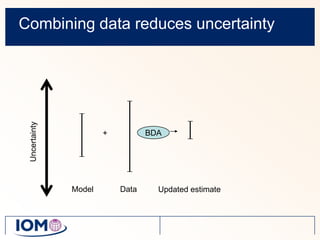
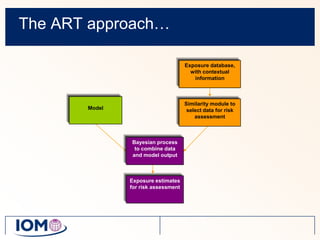
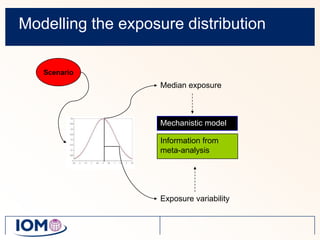
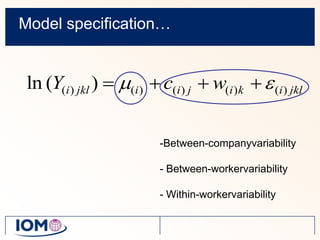
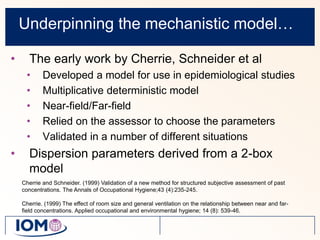
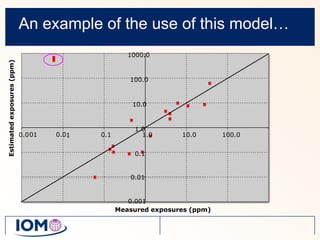
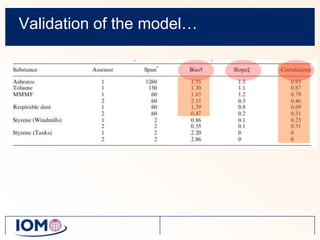
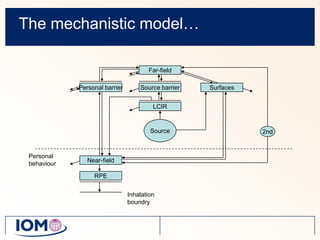
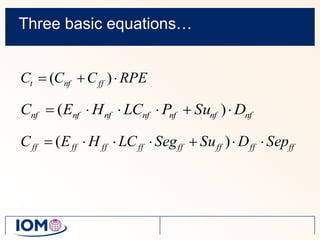
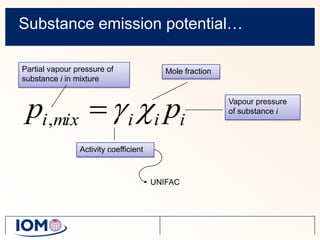
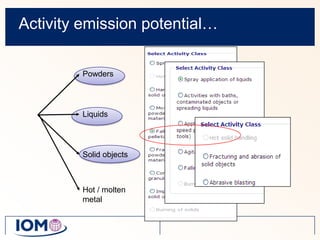
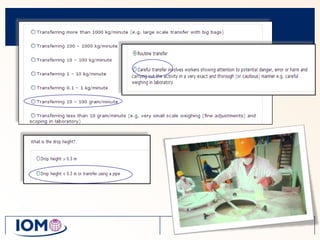
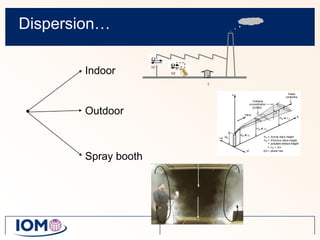
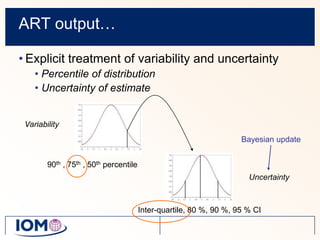
The Advanced REACH Tool (ART) is a generic higher tier tool developed to estimate occupational exposure that incorporates both measurement data and modeling. It uses a mechanistic model based on earlier work by Cherrie and Schneider that considers nine modifying factors that influence exposure. ART integrates this model with a user's own exposure data using Bayesian statistics to provide probabilistic exposure estimates along with uncertainties. Key developers of ART include scientists from TNO, IOM, HSL, BAuA, and other organizations.