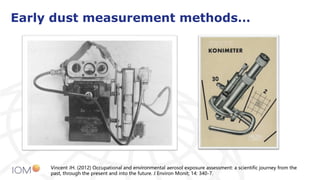
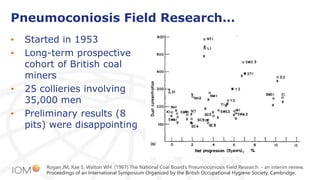
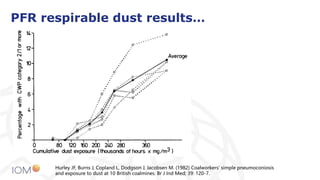
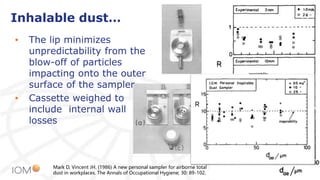
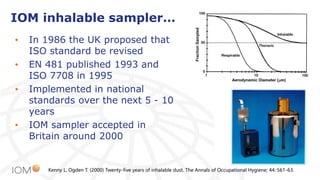
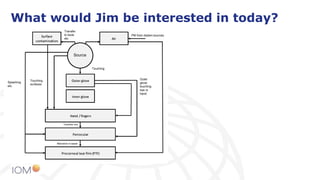
The document highlights the contributions of Professor Jim Vincent to the field of occupational health and aerosol science, detailing his academic journey, significant research, and numerous publications. It discusses the evolution of dust measurement techniques, including the development of inhalable dust samplers and the need for standardization in measuring dust exposure. The document also speculates on current interests Vincent might have if he were active today, particularly regarding nanomaterials and ocular exposure to dust.