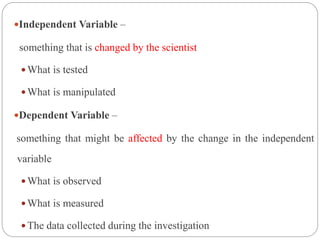
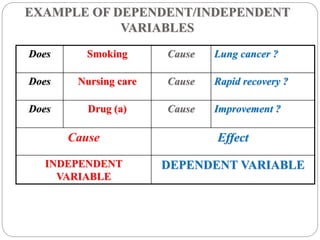
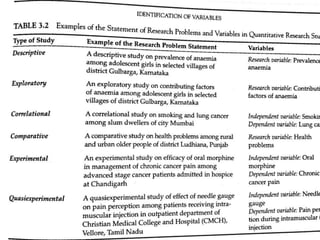
This document defines and describes different types of variables that are used in research. It discusses dichotomous, attribute, active, dependent, independent, and extraneous variables. Dichotomous variables have two possible values, attribute variables are pre-existing characteristics like age or gender, and active variables are created by the researcher, like different drug treatments. The independent variable is what is manipulated or tested, while the dependent variable is what is observed and measured in response to changes in the independent variable. Extraneous variables can interfere with the relationship between dependent and independent variables.