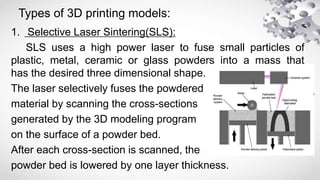
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves using a 3D printer to build a physical object from a 3D digital model by laying down successive layers of material. It was invented in the 1980s and commercialized in the early 1990s. There are several types of 3D printing that use different processes like selective laser sintering (SLS), fused deposition modeling (FDM), and stereolithography (SLA) to fuse or deposit materials like plastic, metal, ceramic, or glass powder layer by layer. 3D printing begins with a virtual 3D model that is then converted into thin slices and printed one layer at a time.