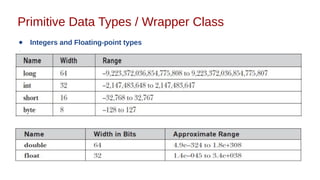
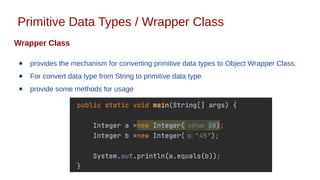
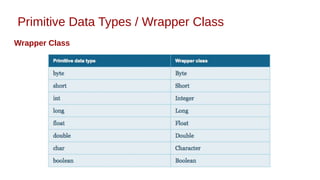
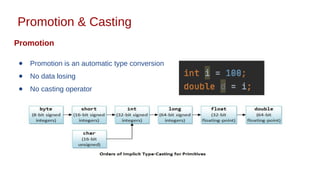
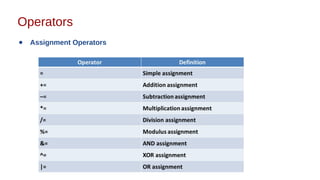
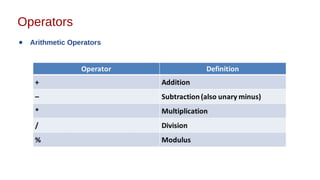
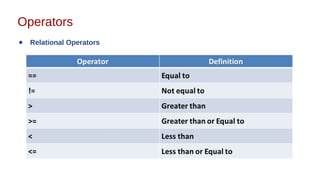
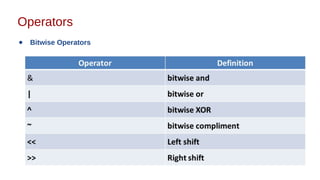
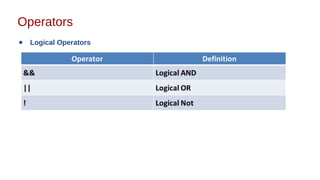
This document discusses Java syntax and data types. It covers variable declaration including instance, static, and local variables. It also discusses Java naming rules, comments, primitive data types including integers, floating-point numbers, characters, and booleans. It describes wrapper classes and how autoboxing and unboxing works. It explains promotion and casting. Finally, it provides an overview of common operators in Java like assignment, arithmetic, relational, bitwise, and logical operators.


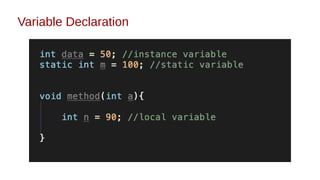
![Variable Declaration
● Variable is a name of memory location.
● Variable Declaration:
[access_modifier] Datatype varName [ = value];
● There are three types of variables in Java:
○ Instance variable
○ Class Variable or Static variable
○ Local variable](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-240211132042-5fd93f31/85/2-_Java_Syntax_and_Data_Type-pptx-pdf-3-320.jpg)