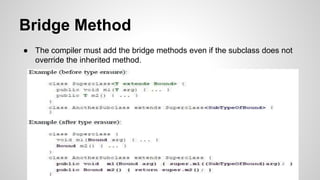
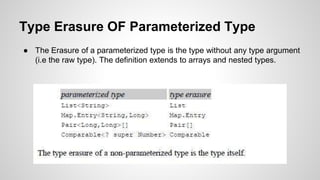
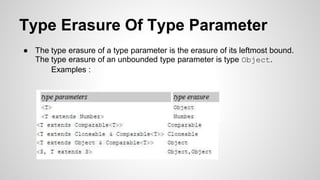
The document provides an in-depth exploration of Java generics, including concepts such as generic types, wildcards, unchecked warnings, and type erasure. It explains key elements like type parameters, bridge methods, and reifiable types, detailing how the Java compiler handles generics under the hood. Acknowledgments are made to Angelika Langer for her contributions to the topic.