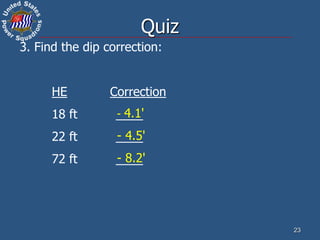
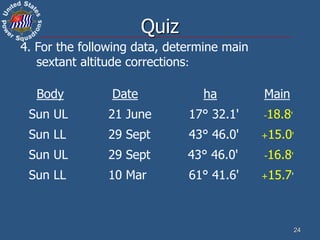
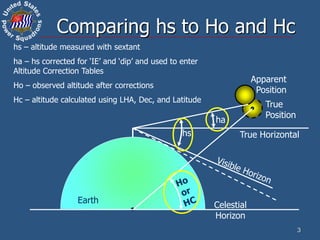
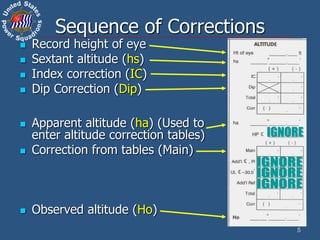
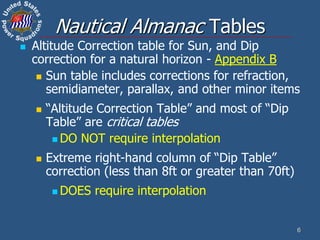
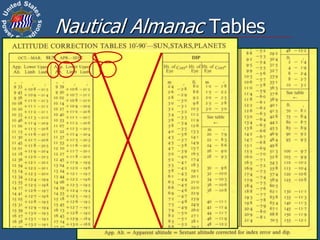
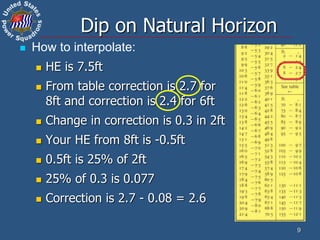
This document discusses altitude corrections that must be applied when taking celestial sights. It explains factors like dip, refraction, parallax, and semidiameter that affect observed altitudes. It provides examples of applying corrections from the Nautical Almanac to reduce sights of the sun. It also describes celestial tools that can help with sight reduction and navigation calculations.



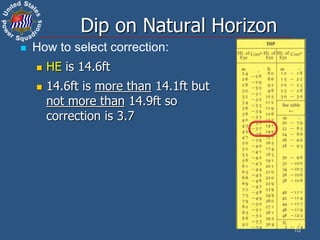
![Sight taken with HE of 10.6 ft,
across a distance of 670 yards.
(Dip to NH would be -3.2’)
Use Almanac tables if:
Height
of Eye
Distance to Horizon
at least
Feet nm sm yds
3 2.0 2.3 4103
5 2.6 3.0 5296
7 3.1 3.6 6267
9 3.5 4.0 7106
10 3.7 4.3 7490
15 4.5 5.2 9174
20 5.2 6.0 10593
Distance to
shore in
Height of
Eye in
Dip Short (Ds) Formula
d = distance & h = height of eye
Yards Feet Ds = (0.0002052 x d) + [1146 x (h/d)]
Meters Meters Ds = (0.0002244 x d) + [3438 x (h/d)]
Nautical miles Feet Ds = (0.4156 x d) + [0.5658 x (h/d)]
Statute miles Feet Ds = (0.3611 x d) + [0.6511 x (h/d)]
11
Dip Short (Appendix A)
Ds = (0.0002052 x d) + [1146 x (h/d)]
Ds = (0.0002052 x 670) + [1146 x (10.6 / 670)]
Ds = 0.137484 + (1146 x 0.015820896)
Ds = 18.268’, rounded to 18.3’
Dip correction is -18.3’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2520633-230118083116-ed57533d/85/2520633-ppt-11-320.jpg)
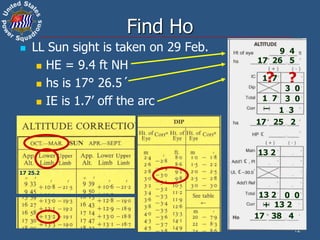


![15
LL Sun sight is taken on 10 May.
HE is 5.5 ft Ds 345 yds
IE is 0.5´ off the arc
hs is 43° 50.0´
Find Ho
5 5
43 50 0
0 5
18 3
43 32 2
0 5 18 3
17 8
-
15 0
15 0
+ 15 0
0 0
43 47 2
Use excerpts (Appendix B), pg 212
Ds = (0.0002052 x d) + [1146 x (h/d)]
Ds = (0.0002052 x 345) + [1146 x (5.5 / 345)]
Ds = 0.070794 + (1146 x 0.015942029)
Ds = 18.34036’, rounded to 18.3’
Dip correction is -18.3’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2520633-230118083116-ed57533d/85/2520633-ppt-15-320.jpg)