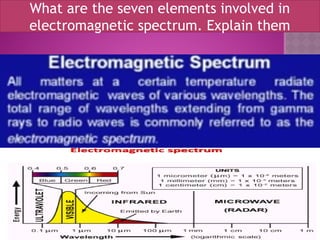
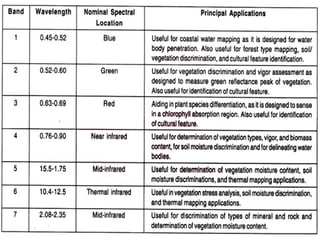
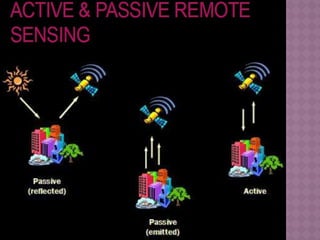
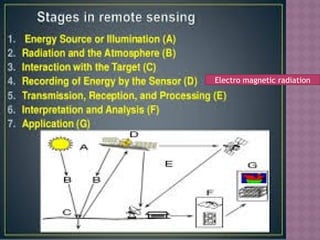
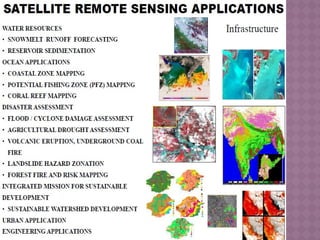
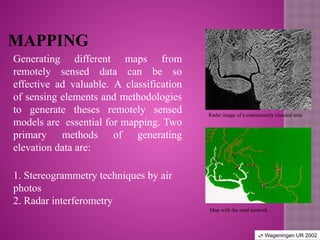
Remote sensing is defined as the science and art of acquiring information about objects or phenomena without physical contact, primarily through the analysis of electromagnetic radiation data. It offers significant advantages, such as the ability to capture large regions, acquire data in various weather conditions, and access hard-to-reach areas. Applications of remote sensing include land use and cover analysis, mapping, and generating elevation data through techniques like stereogrammetry and radar interferometry.