Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX
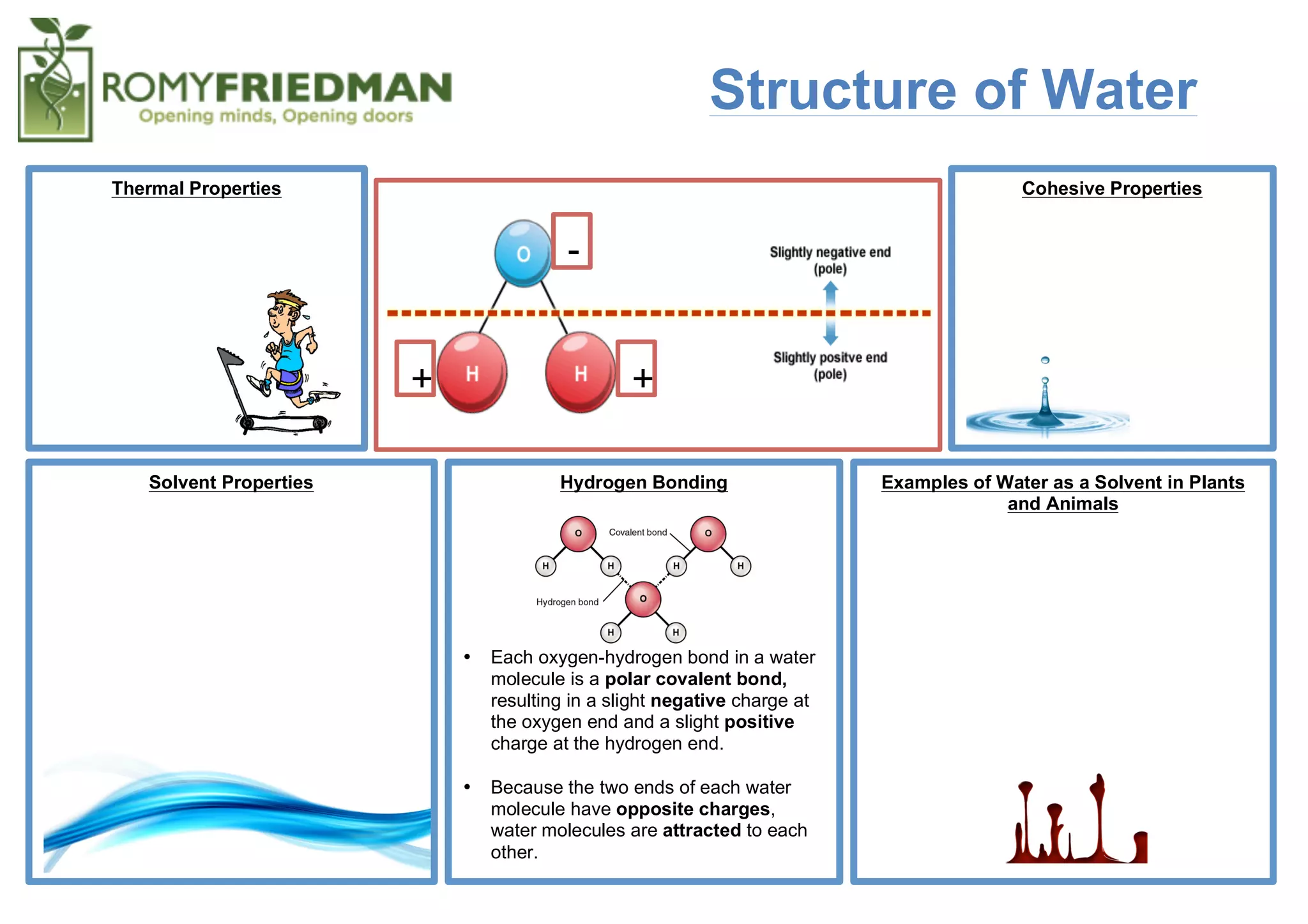

Water molecules are polar, with slightly positive and negative charges, allowing them to form hydrogen bonds between oxygen and hydrogen atoms of other water molecules. This hydrogen bonding gives water high surface tension and ability to dissolve many substances, making it an excellent solvent for biological and chemical processes in plants, animals, and the environment. Water also has unique thermal properties like a high specific heat capacity that buffers temperature changes.
