1. A jar test was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of chemical coagulation and flocculation in removing suspended solids from water.
2. The jar test involved adding different doses of coagulants to water samples, rapidly mixing to dissolve the coagulant, slowly mixing to allow floc formation, and measuring the clarity of the settled water.
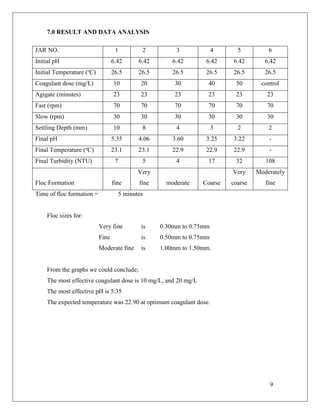
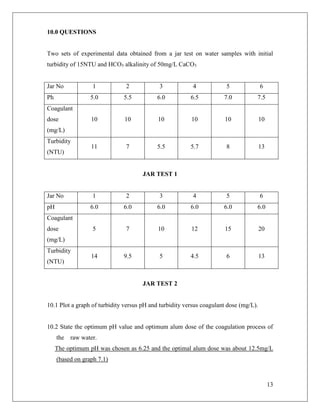
3. The results showed that an optimal coagulant dose produced the lowest turbidity reading, indicating the most effective removal of suspended solids. Graphs of water quality parameters versus coagulant dose aided in analyzing the coagulation-flocculation process.


![3
the solution to absorb light. Color particles can be removed by the methods discussed for
dissolved or colloidal, depending upon the state of the color.
Finely dispersed solid (colloids) suspended in wastewater are stabilized by
negative electric charges on their surfaces, causing them to repel each other. Since this
prevents these charged particles from colliding to form larger masses, called flocs, they
do not settle. To assists in the removal of colloidal particles form suspension, chemical
coagulations and flocculation are required. These processes, usually done in sequence,
are a combination of physical and chemical procedures. Chemicals are mixed with
wastewater to promote the aggregation of the suspended solids into particles large enough
to settle or be removed. Coagulation is the destabilization of colloids by neutralizing the
forces that keep them apart. Cationic coagulants provide positive electric charges to
reduce the negative charge of the colloids. As a result, the particles collide to form larger
particles (floc). Rapid mixing is required to disperse the coagulant throughout the liquid.
The coagulants overdose can cause a complete charge reversal and destabilize the colloid
complex.
A coagulant is the substance (chemical) that is added to the water to accomplish
coagulation. There are three key properties of a coagulant;
1. Trivalent cation: As indicated in the last section, the colloids most commonly
found in natural waters are negatively charged; hence a cation is required to neutralize the
charge. A trivalent cation is the most efficient cation.
2. Nontoxic: This requirement is obvious for the production of safe water.
3. Insoluble in the neutral pH range. The coagulant that is added must precipitate
out of solution so that high concentrations of the ion are not left in the water. Such
precipitation greatly assists the colloid removal process.
The two most commonly used coagulants are aluminum (Al3+
) and ferric iron
(Fe3+
). Both meet above three requirements. Aluminum can be purchased as either dry or
liquid alum [Al2(SO4)3·14H2O]. Commercial alum has an average molecular weight of
594. When alum added to a water containing alkalinity, the following reaction occurs;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/237015090-jar-test-lab-report-doc-221216055143-977387e9/85/237015090-jar-test-lab-report-doc-doc-3-320.jpg)