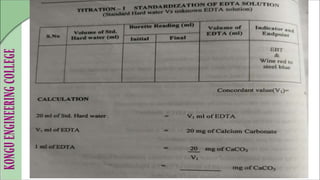
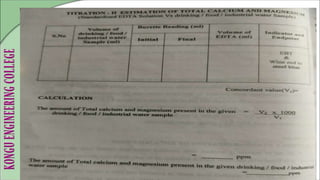
This document provides instructions for estimating the amount of calcium and magnesium in food samples using complexometric titration with EDTA. It describes titrating a standard hard water sample against a standardized EDTA solution to determine the EDTA concentration. This standardized EDTA is then used to titrate sample hard water and determine total, calcium, and magnesium hardness levels present. The document lists the materials, procedure, and questions to ask during the experiment. The results will provide the concentration of total hardness, calcium hardness, and magnesium hardness in the sample water in ppm units.