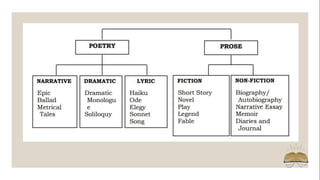
This document provides an overview of Philippine literature, including its characteristics, genres, elements, and historical periods. It discusses that Philippine literature reflects the country's diverse languages and regions. Literature can be oral or written, and includes imaginative works in poetry and prose. Key genres are fiction, non-fiction, poetry which can be narrative, dramatic or lyric. Literary elements include themes, plots, characters. Philippine literature is discussed in three periods: pre-colonial oral traditions, colonial works under Spanish rule, and post-colonial works after independence to present.