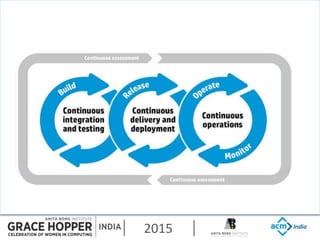
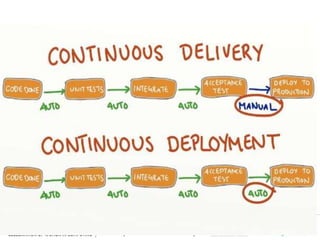
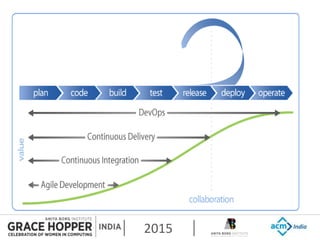
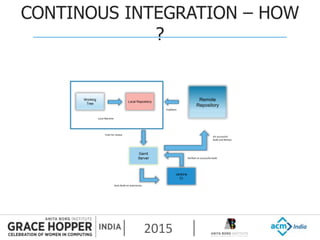
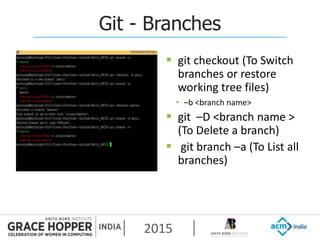
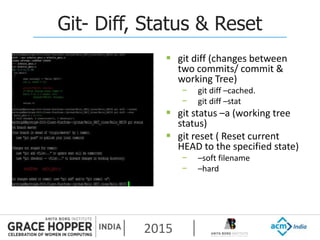
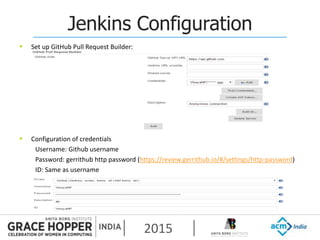
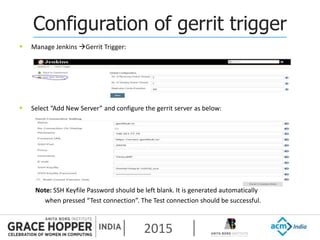
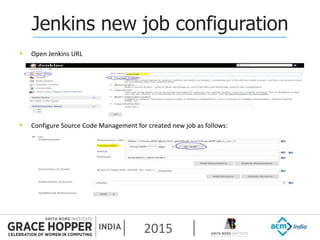
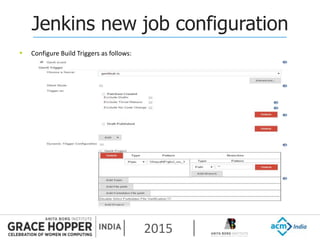
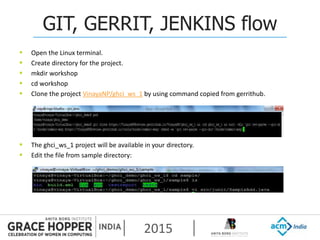
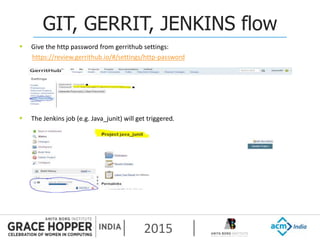
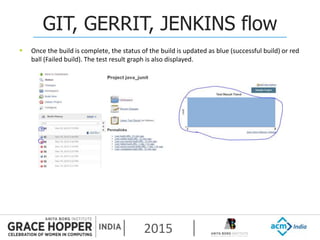
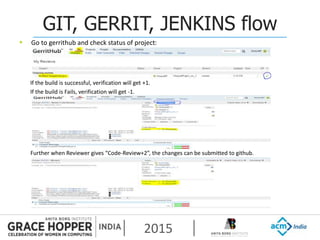
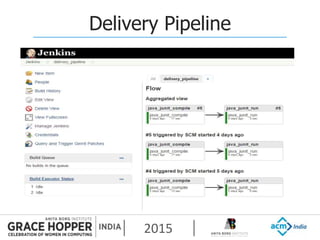
This document provides an overview of continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) using open source tools Git, Gerrit, and Jenkins. It discusses the key principles of DevOps, continuous delivery and continuous deployment. It then describes how Git is used for version control, Gerrit for code reviews, and Jenkins for continuous integration. The rest of the document demonstrates setting up these tools, configuring Jenkins plugins, and walking through the workflow of making a code change in Git, pushing to Gerrit for review, and triggering an automated build in Jenkins.