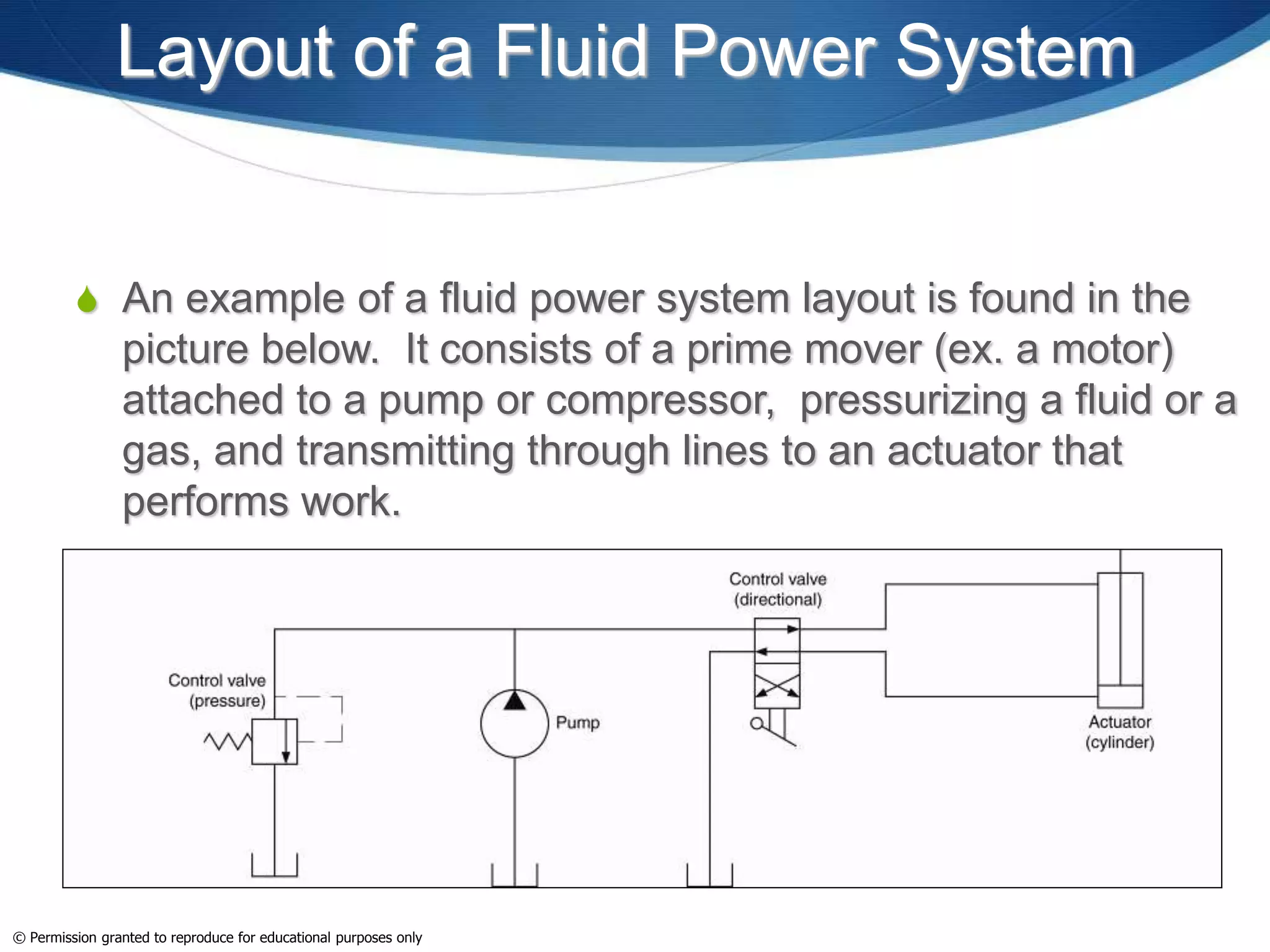
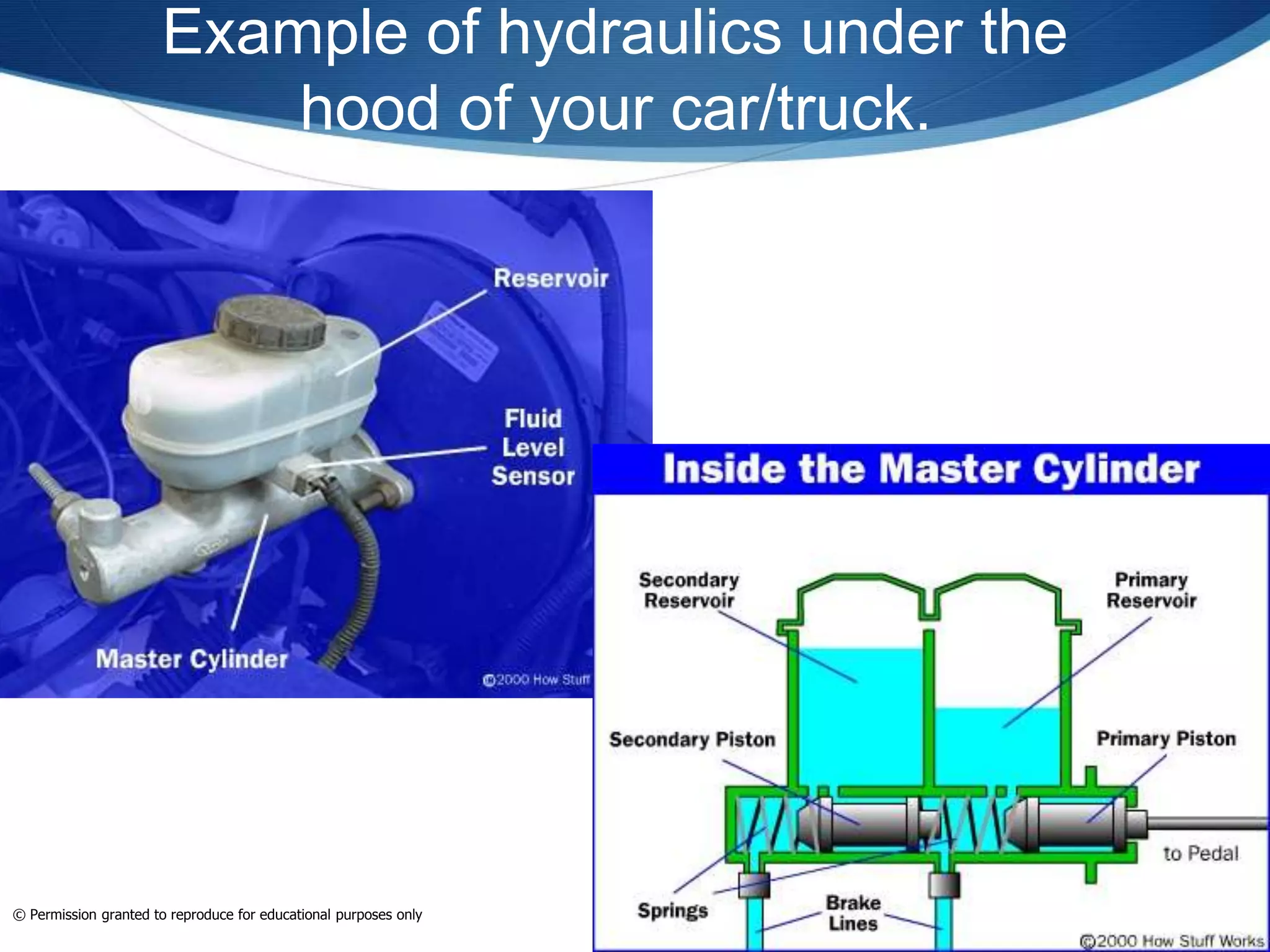
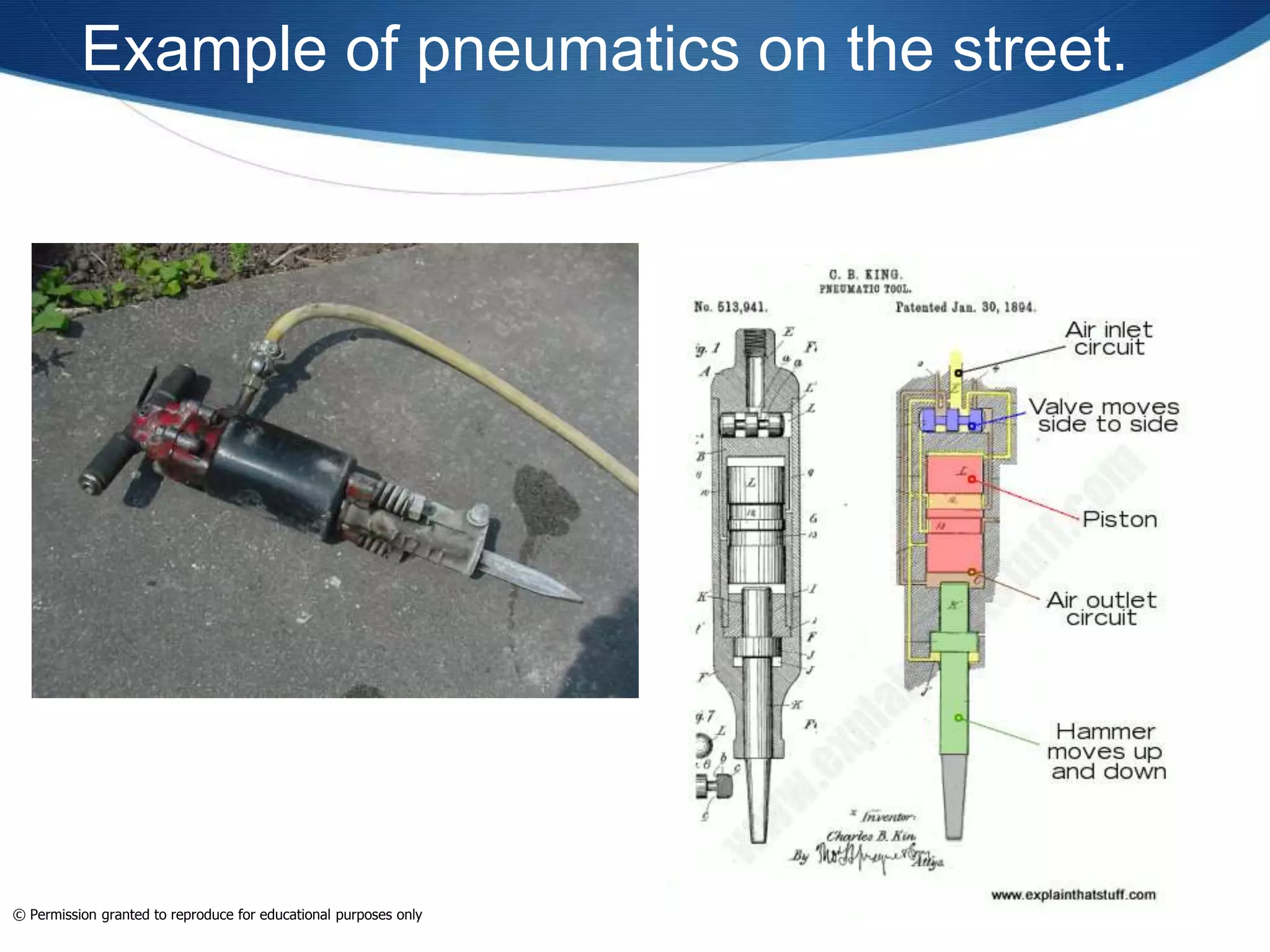
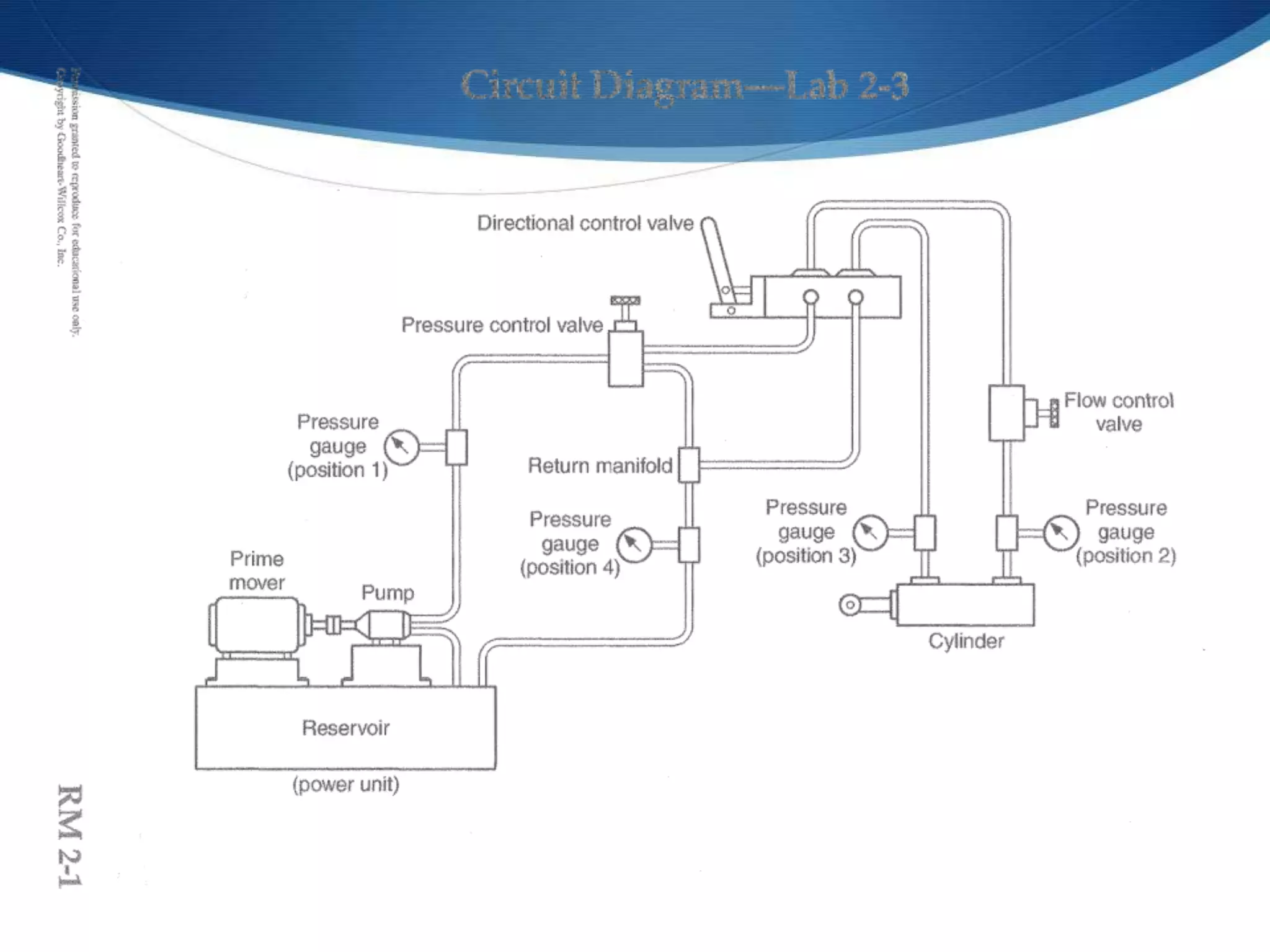
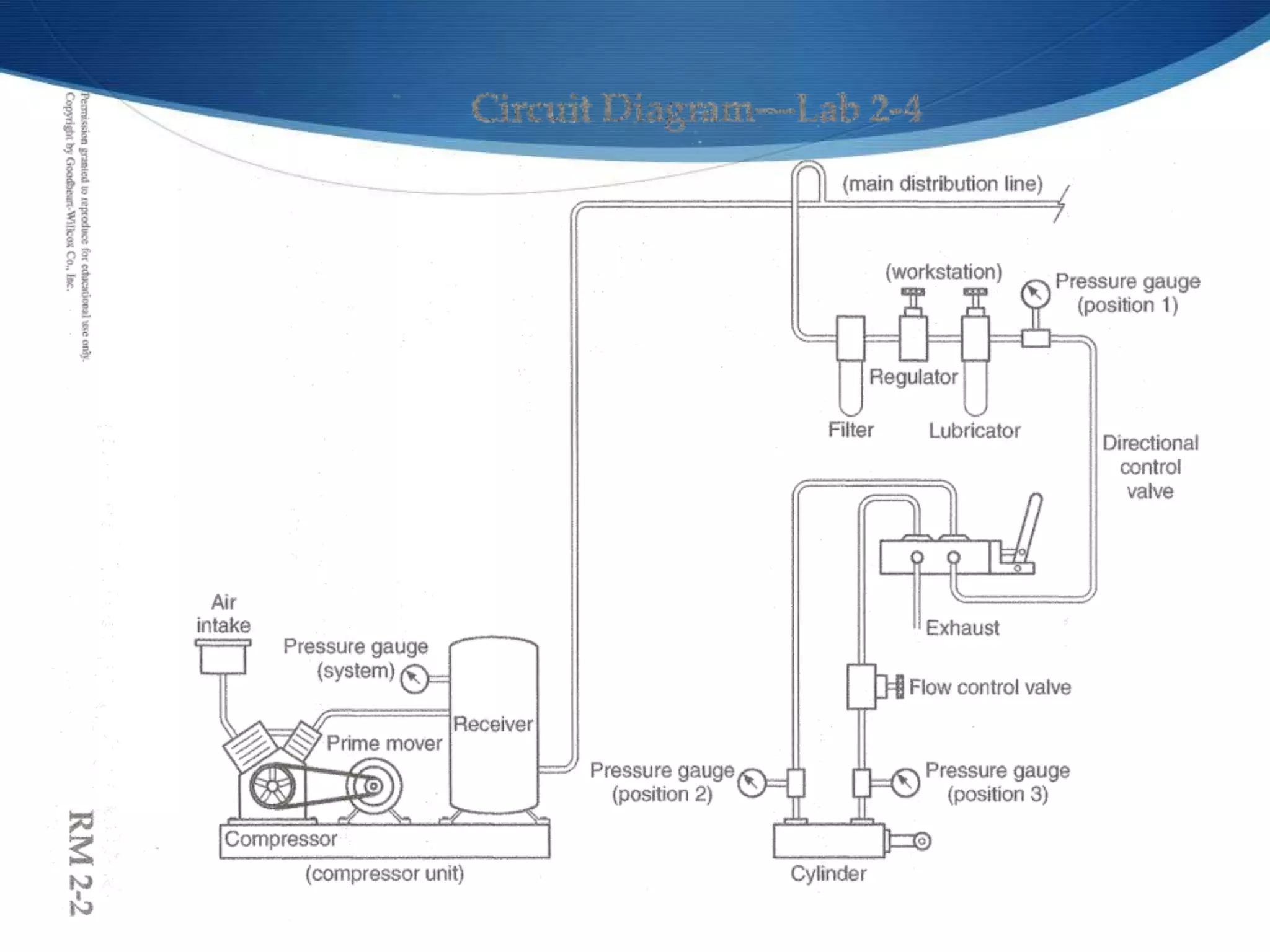
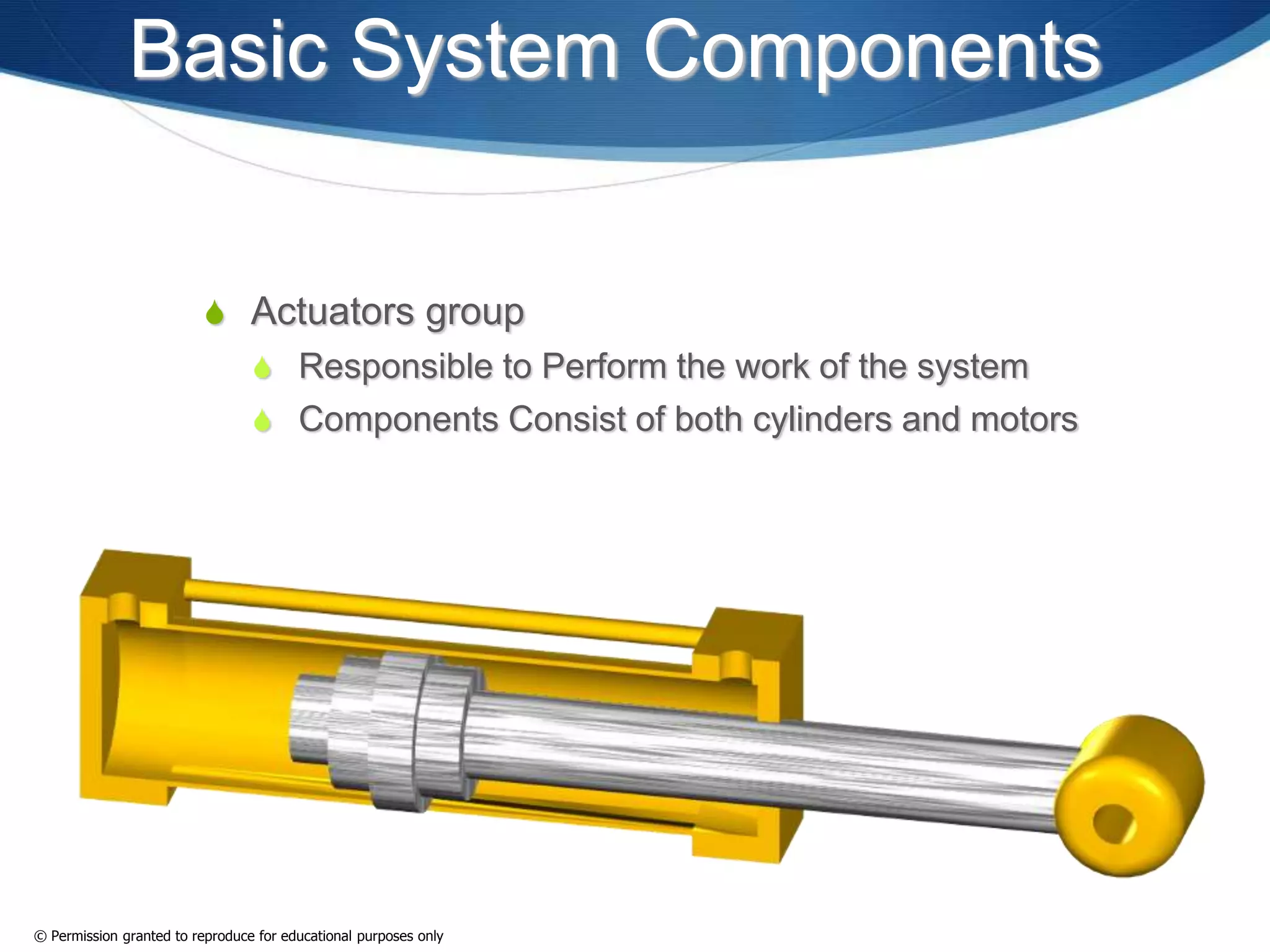
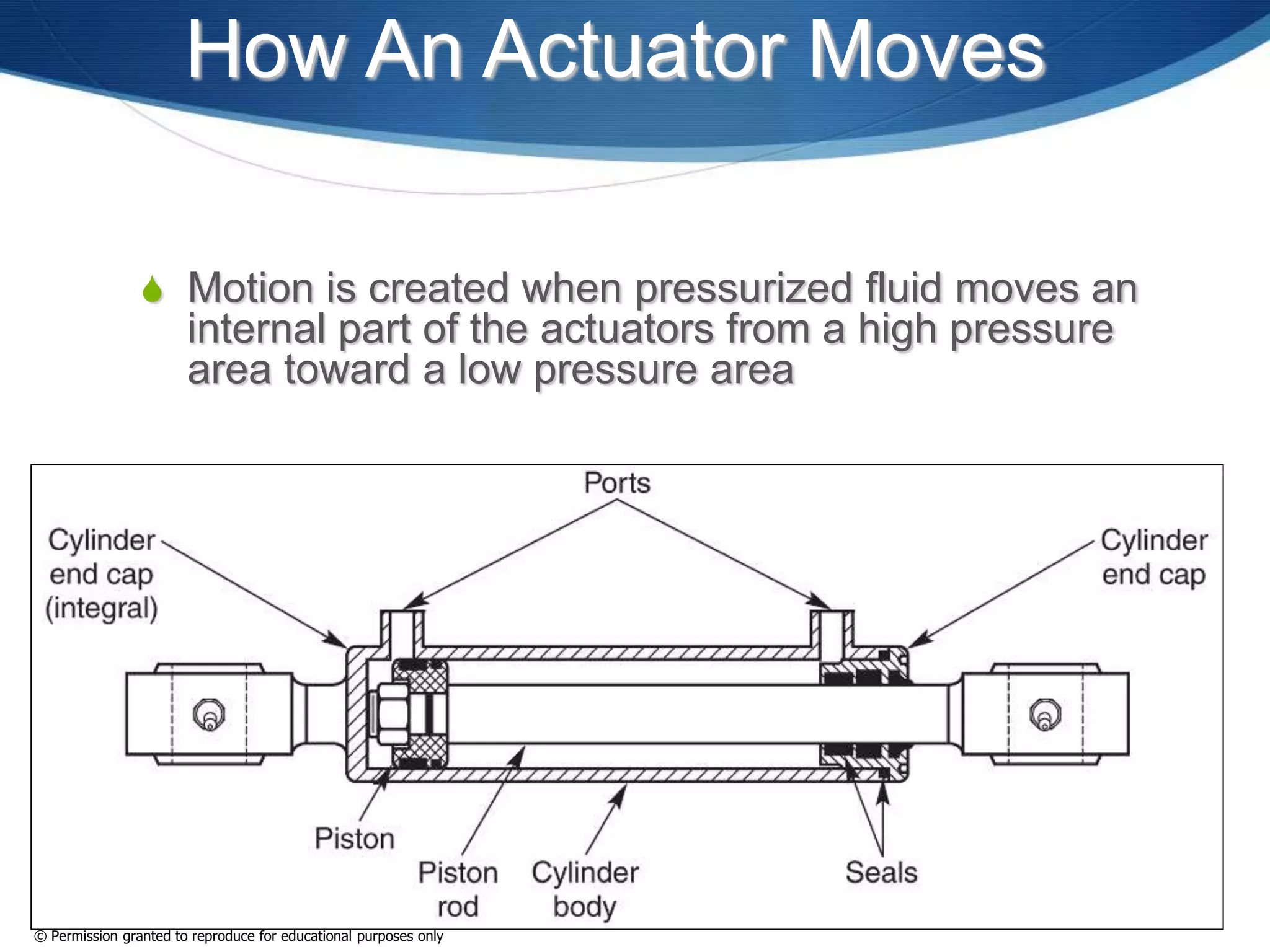
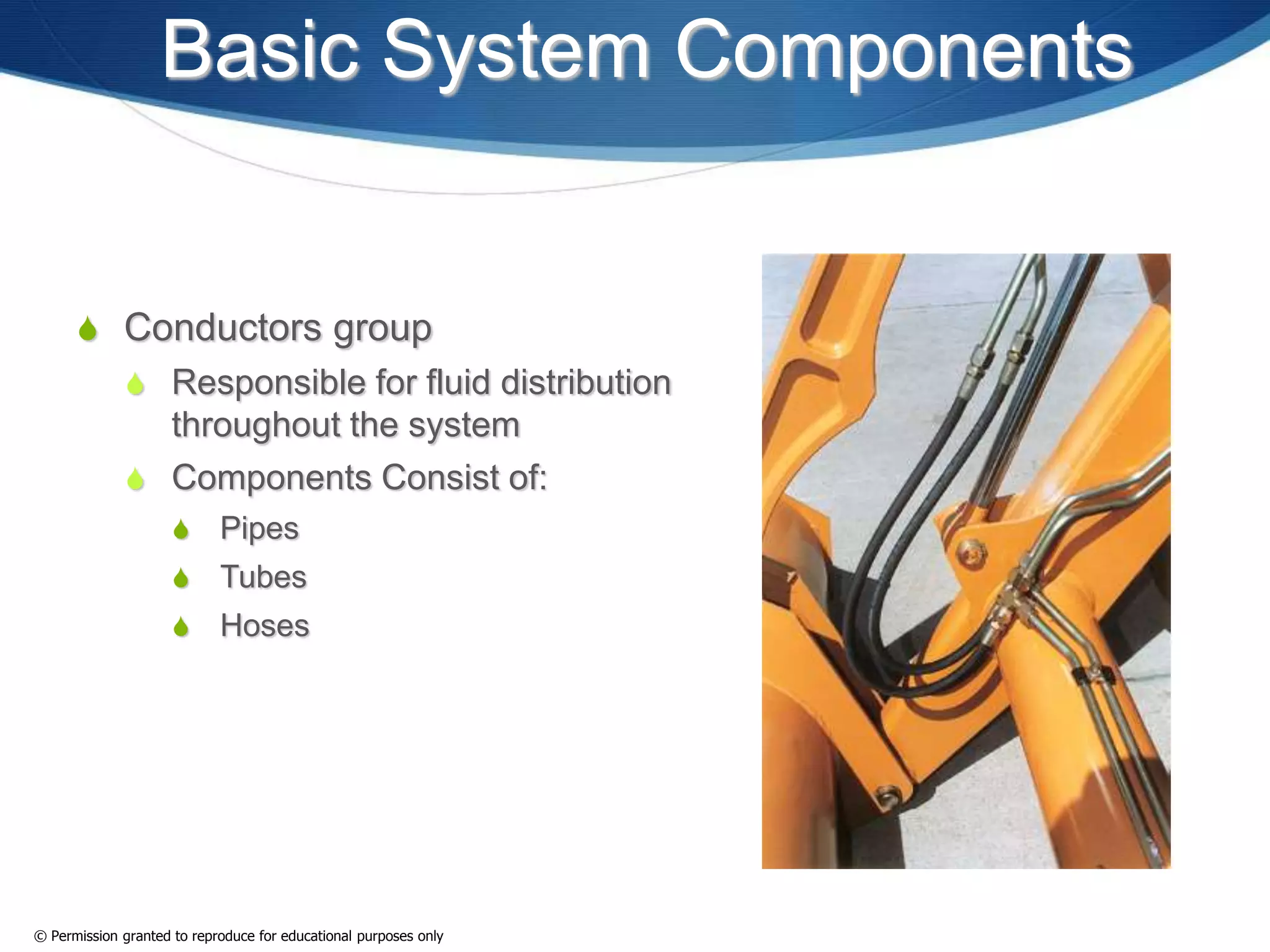
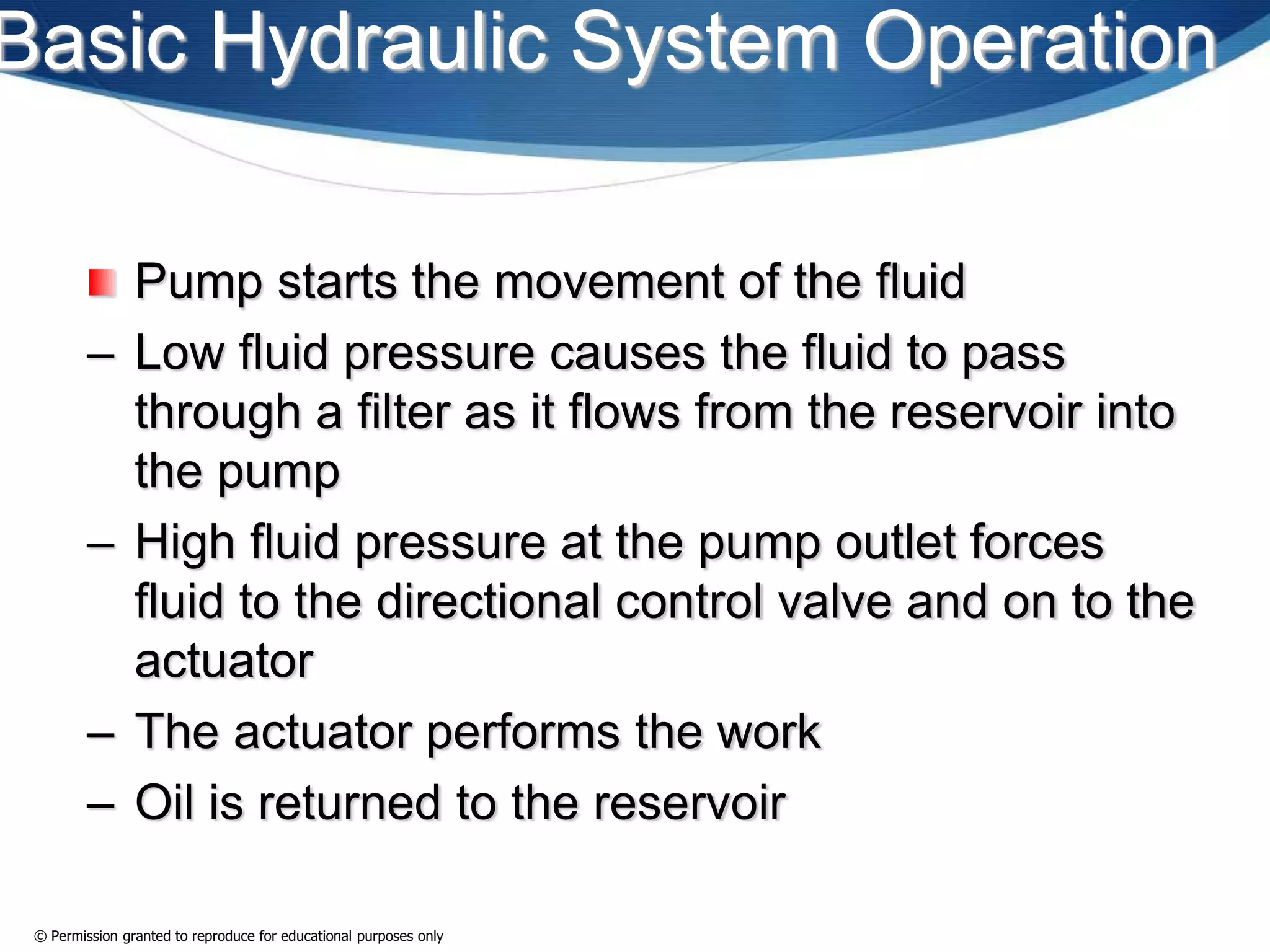
This document provides an overview of fluid power systems. It defines fluid power as any system that converts, transmits, or controls power through pressurized liquids or gases. The key components of fluid power systems include a prime mover, pump or compressor, transmission lines, and actuators. Fluid power systems are generally classified as hydraulic (using liquid) or pneumatic (using gas). The document then discusses the basic layout, functions, components and operation of hydraulic and pneumatic systems.