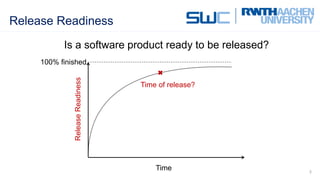
Defect Tracking, Software Readiness Index (SRI), and ShipIt were compared as methods to measure software release readiness. Defect Tracking focuses only on reliability using defect metrics but is the simplest. SRI takes a more holistic quality-based approach, considering multiple criteria, but is more complex. ShipIt measures overall project progress across requirements, design, testing, and quality, making it the most comprehensive but also most complex approach. The document recommends combining metrics for reliability, quality, and progress to provide a holistic view of release readiness.