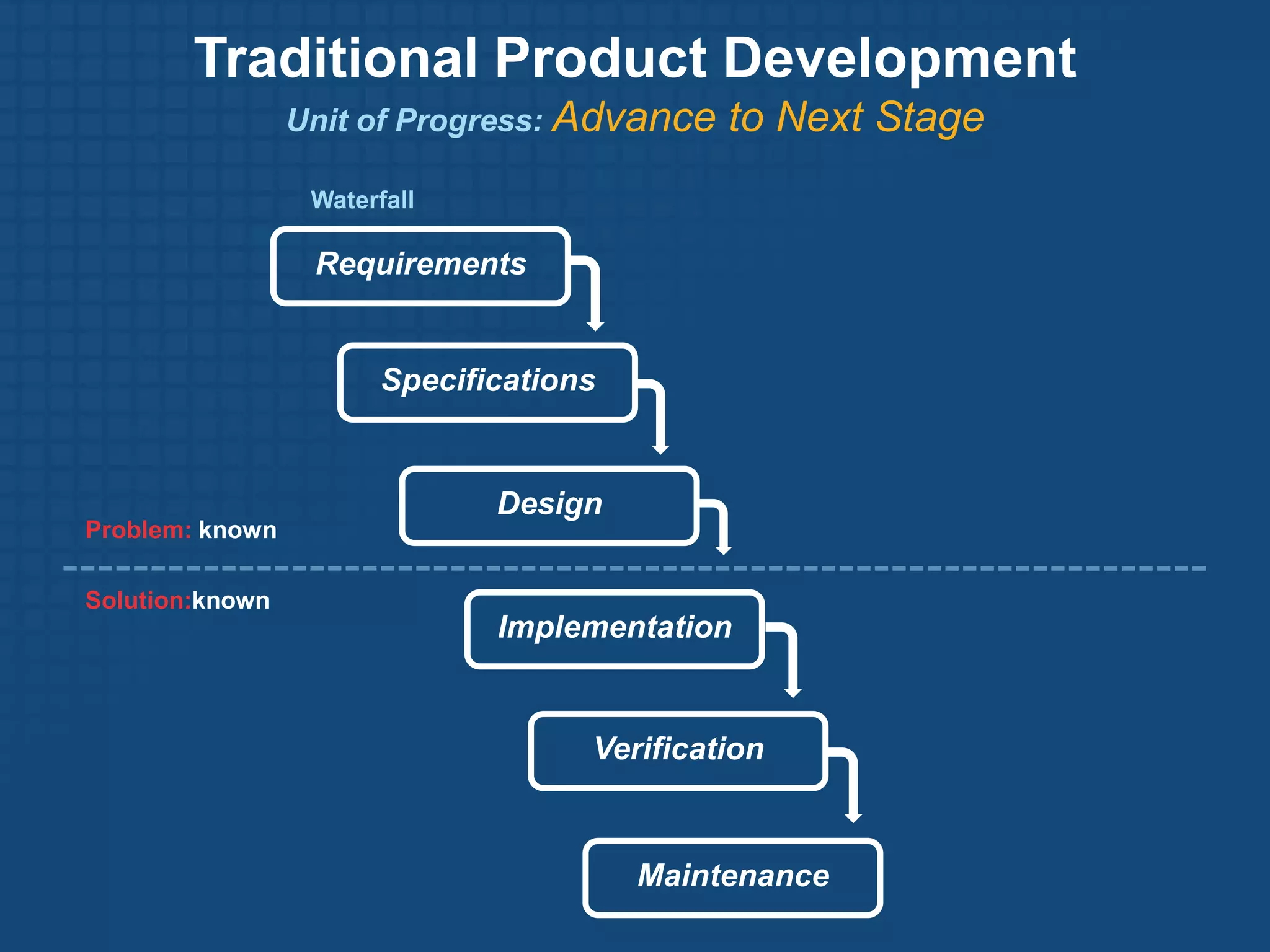
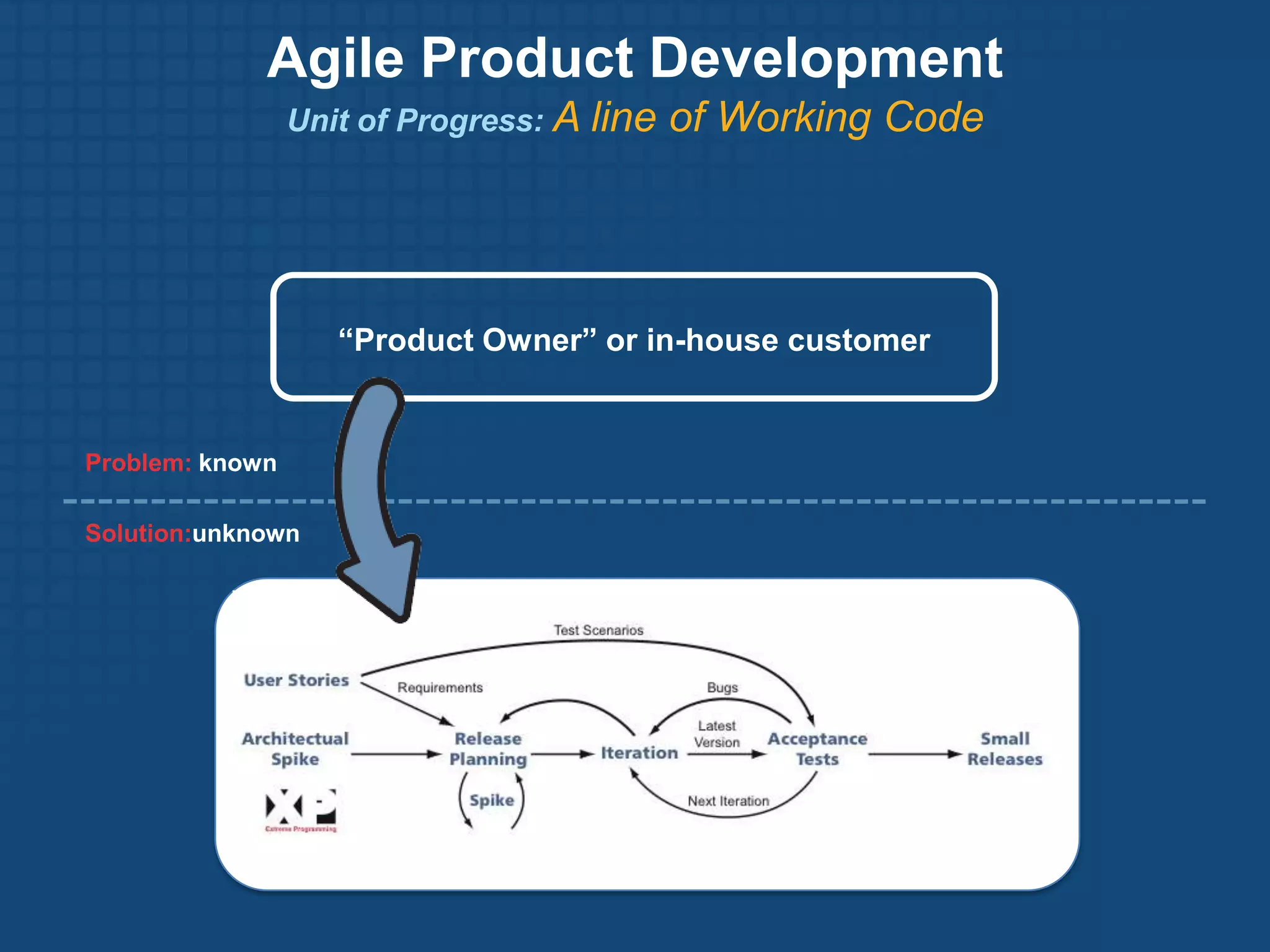
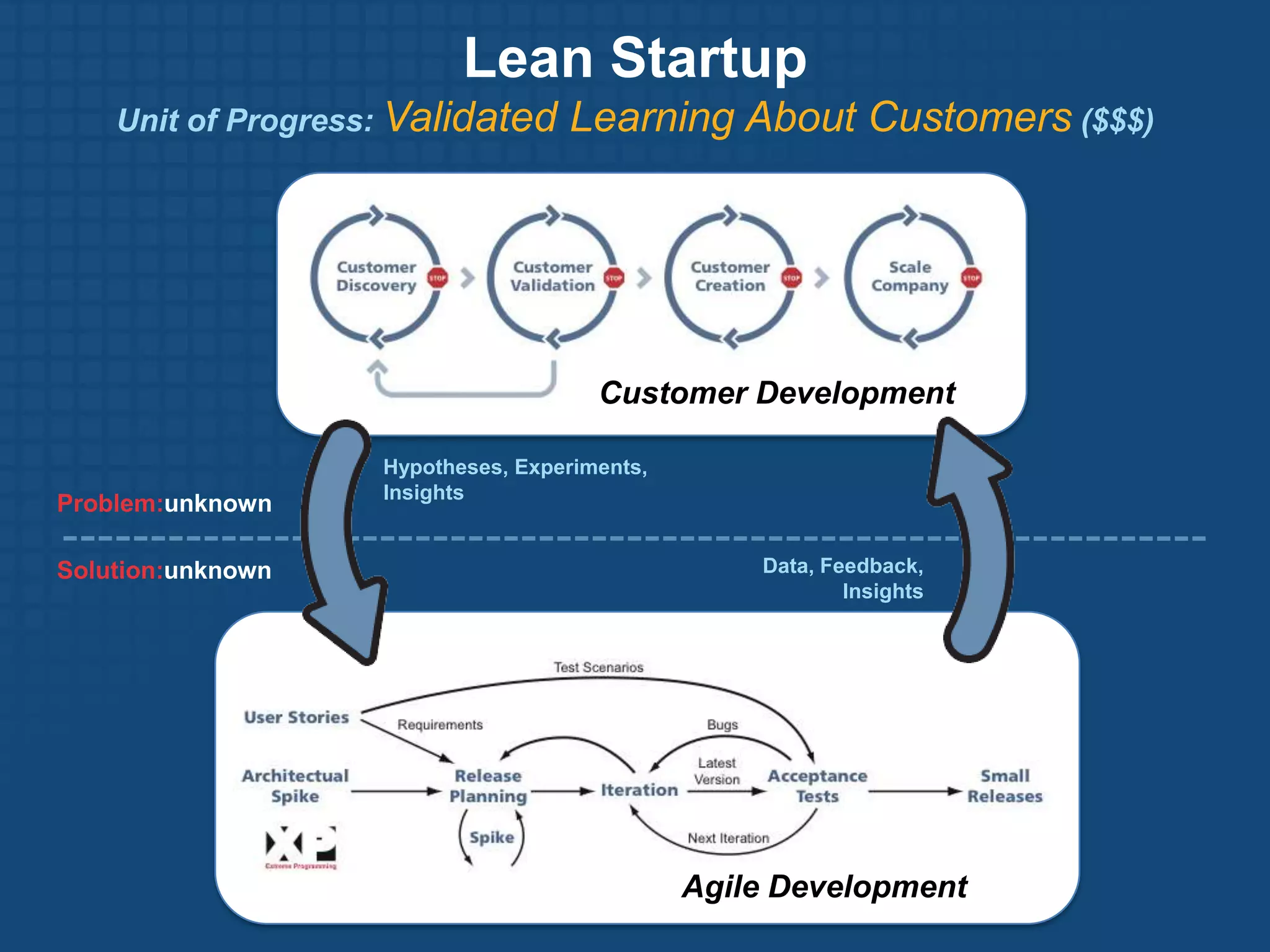
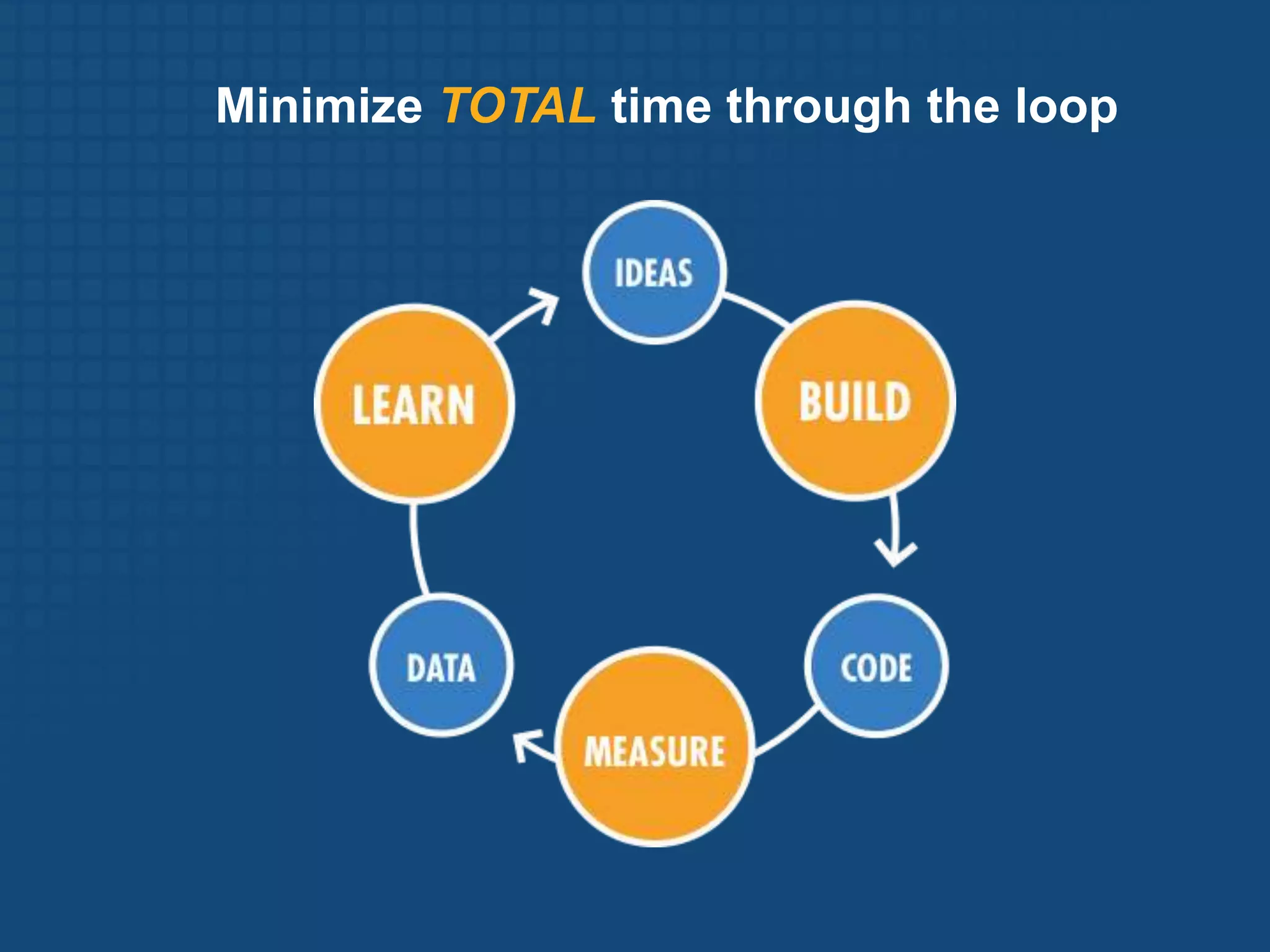
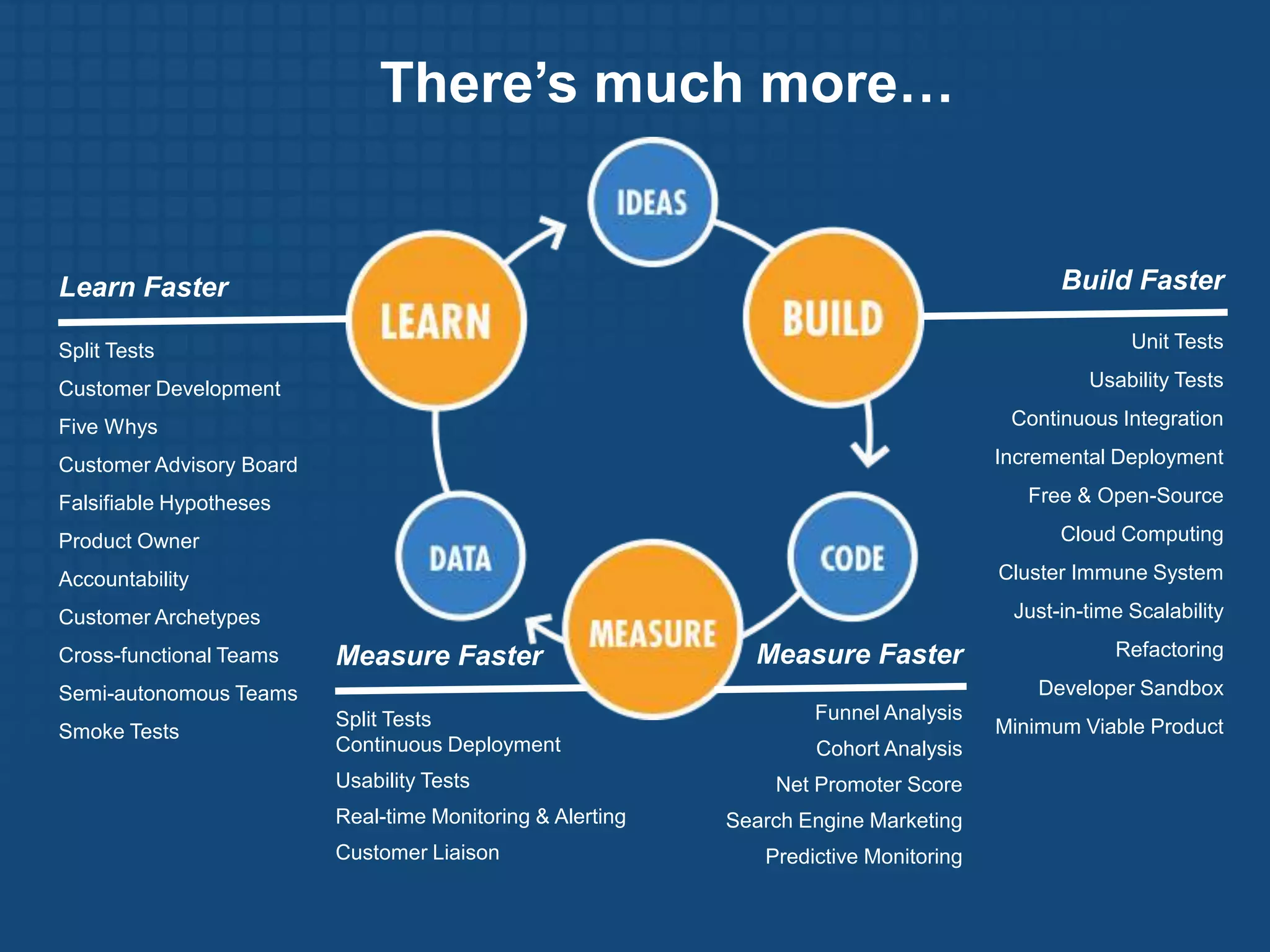
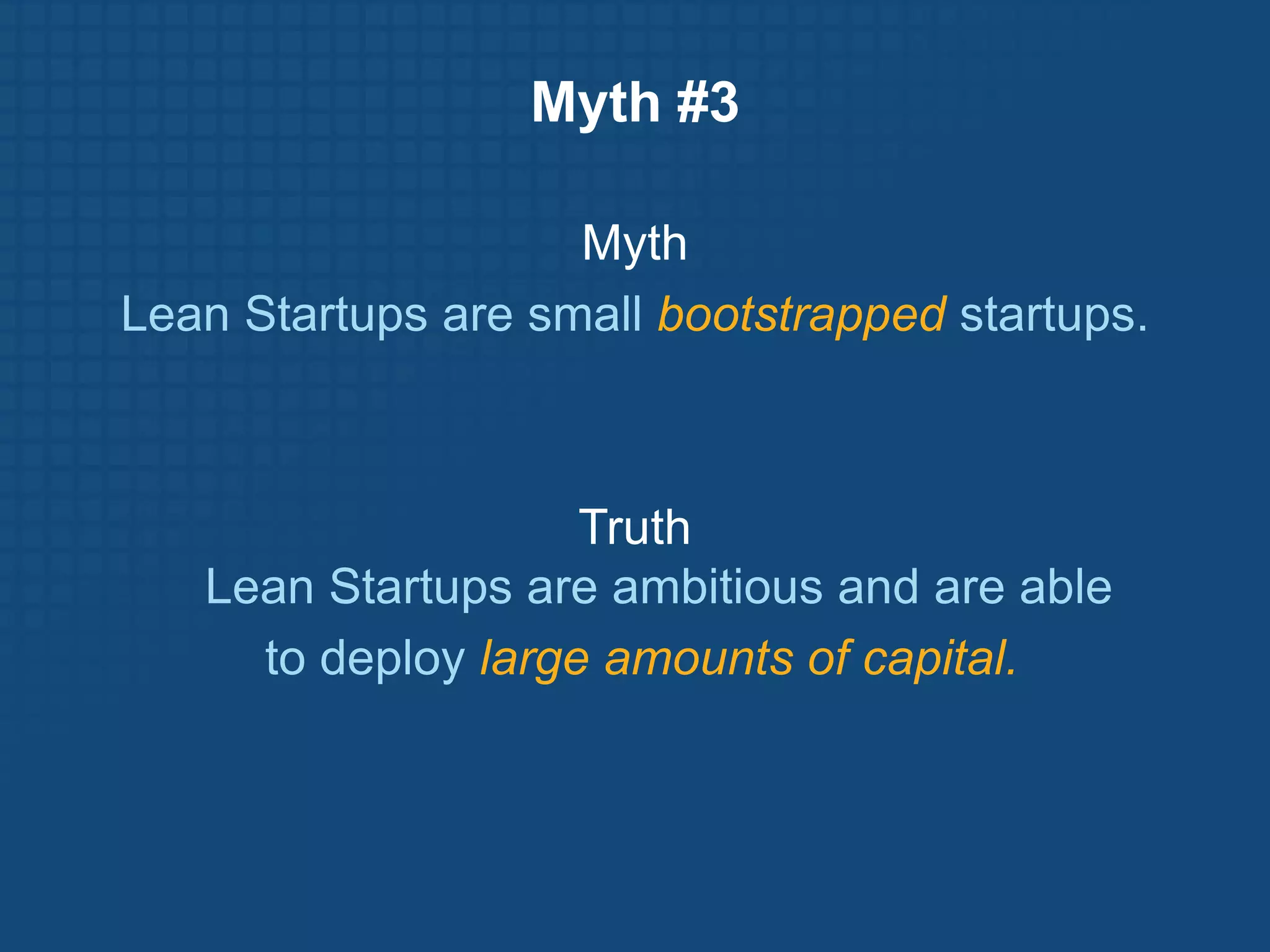
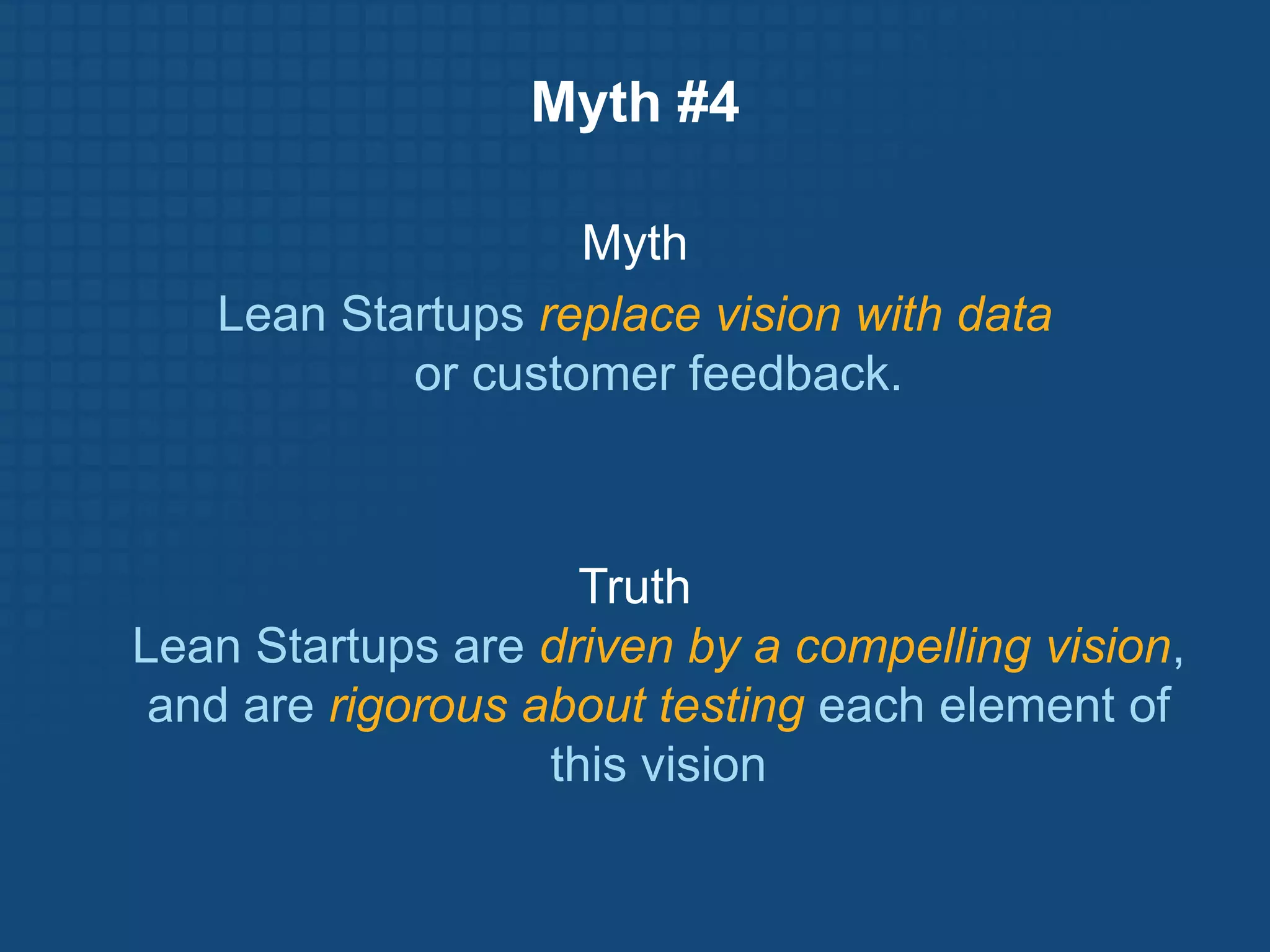
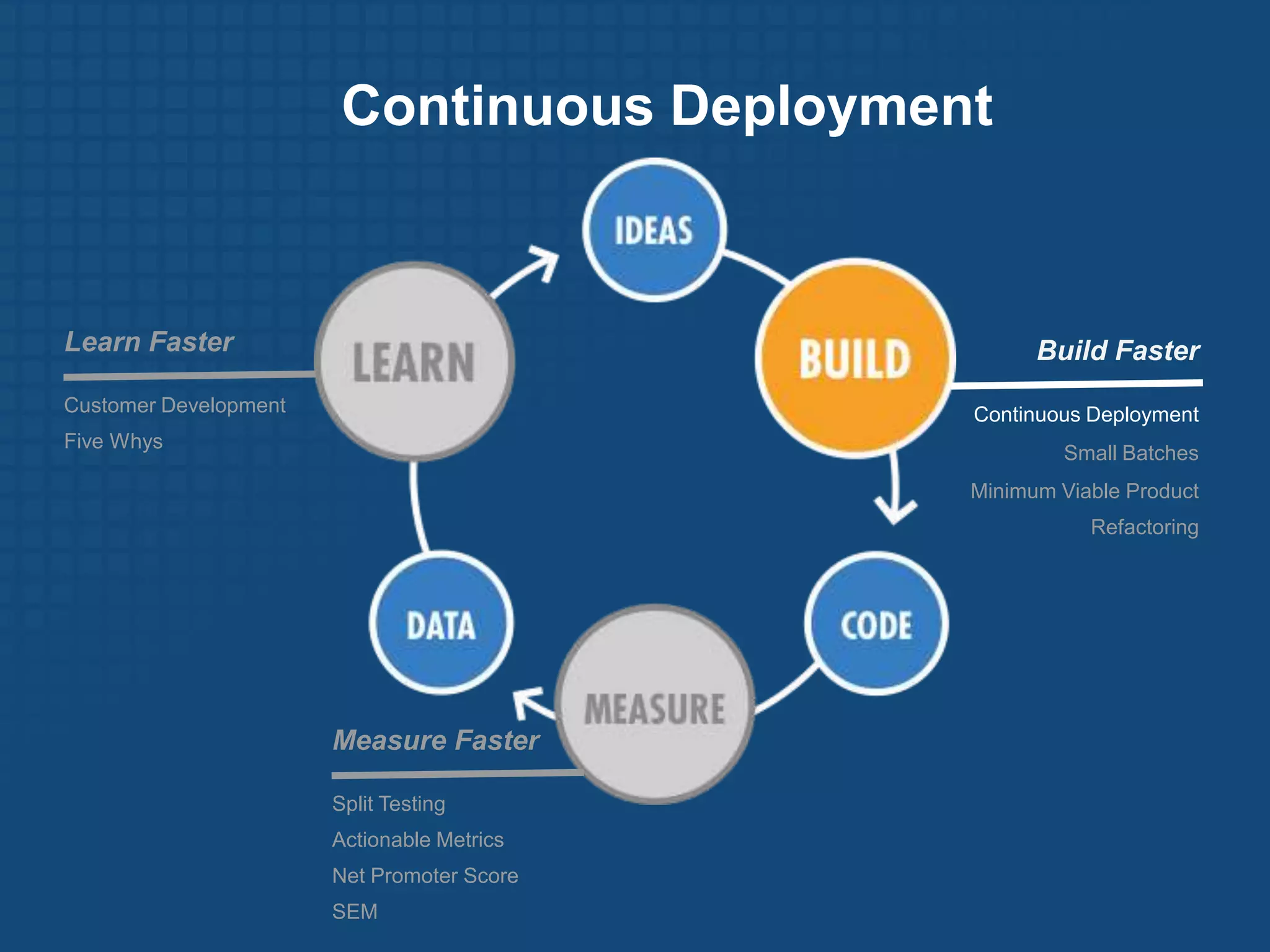
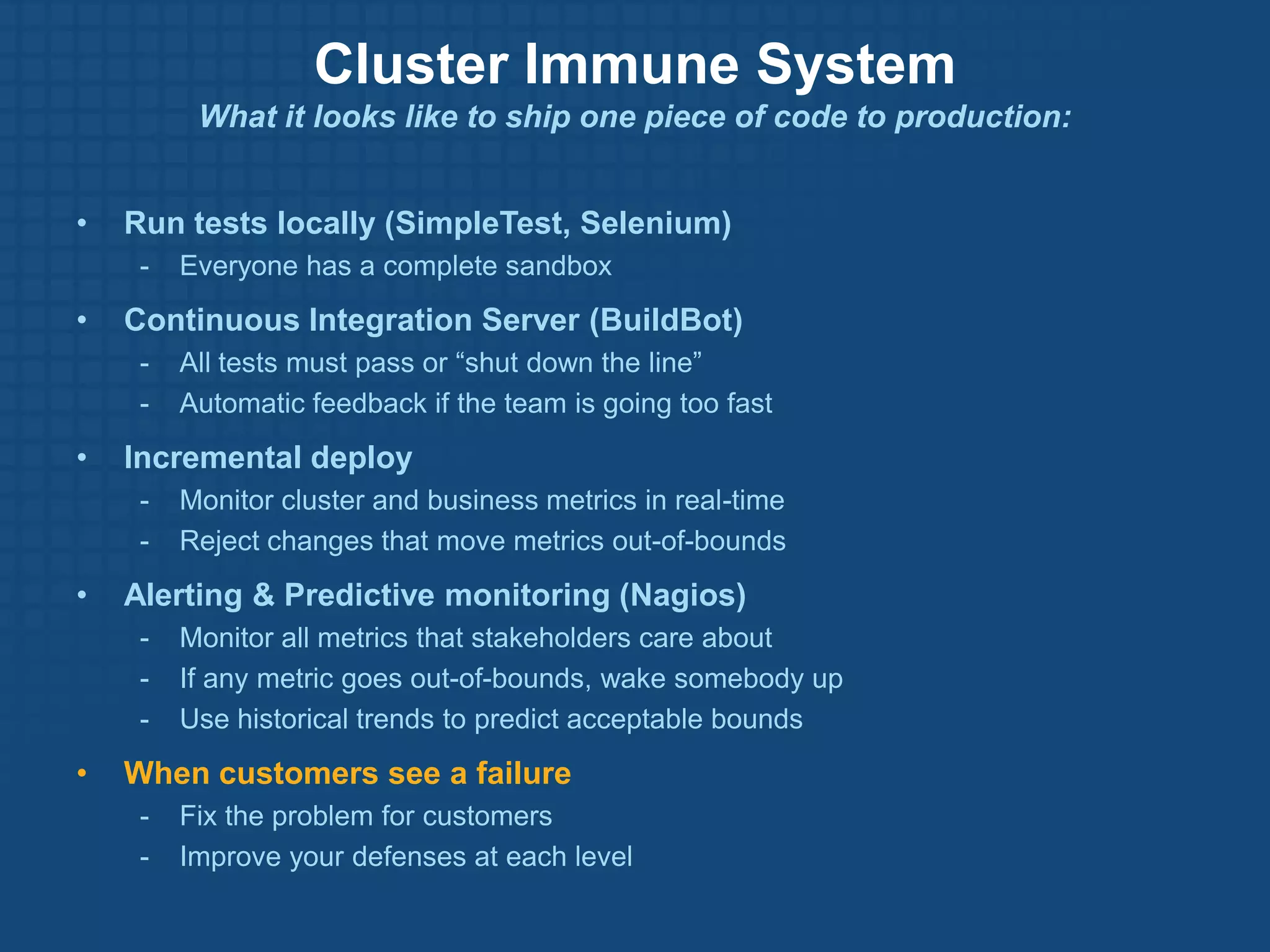
The document discusses the Lean Startup methodology for developing products under conditions of extreme uncertainty. It advocates for minimizing the time between product iterations or "pivots" through rapid experimentation and validated learning about customers. This is achieved by adopting practices like continuous integration, deployment and testing to get fast feedback; measuring key metrics through techniques like A/B testing and cohort analysis; and employing customer development processes to gain insights. The document debunks some myths about Lean Startups and provides examples of how companies have implemented continuous deployment and a "cluster immune system" to learn quickly from customers.