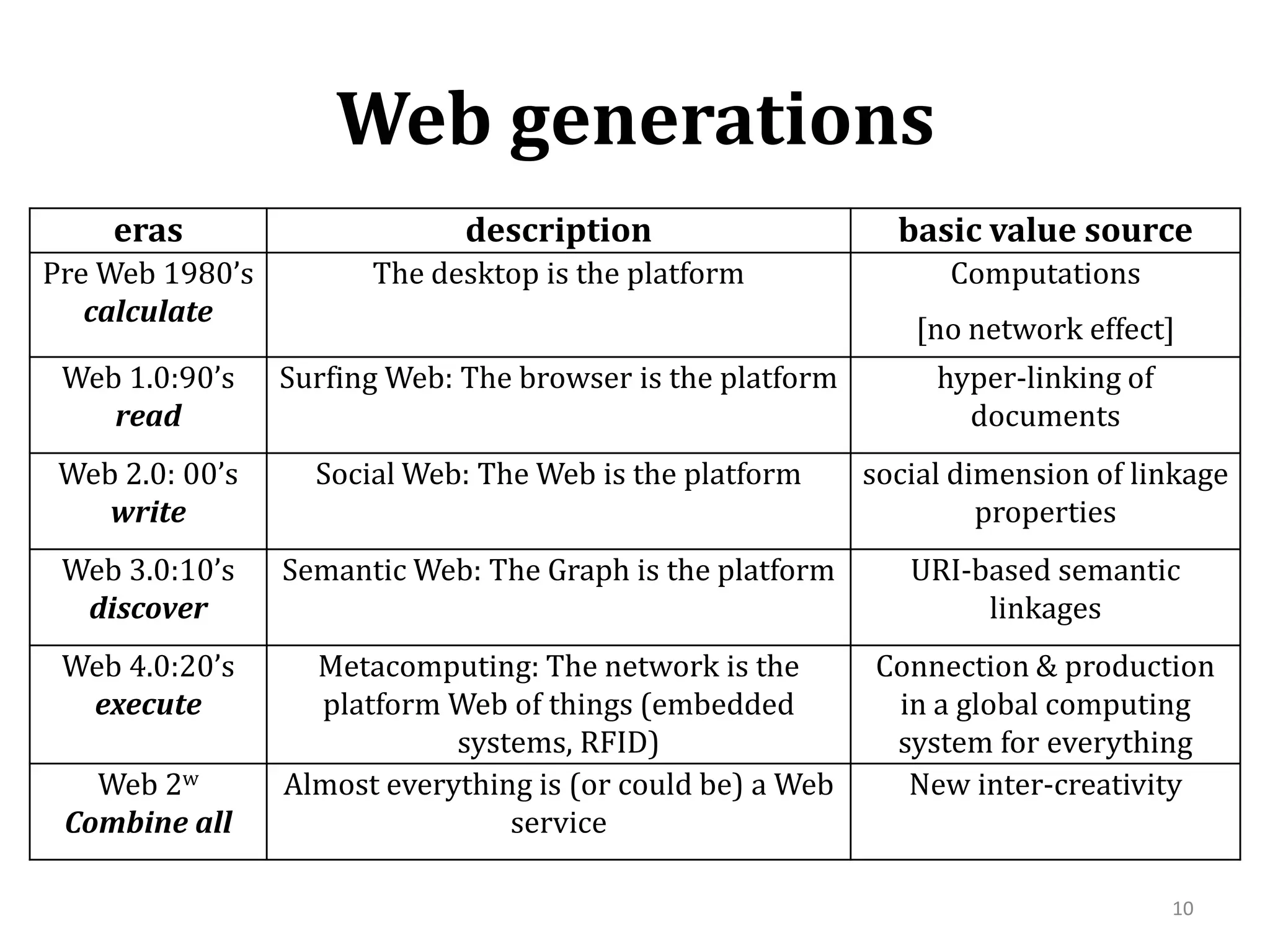
The document summarizes research on modeling the evolution of the World Wide Web as a complex system. It discusses the Web's structure as a directed graph and statistical properties like power law degree distributions and small world properties. It describes models of Web traffic and evolution that use concepts from statistical physics and complex networks. Game theoretic and query-based models are also summarized. The document focuses on a query-Web model that explains the Web's scale-free structure through the interaction of users, documents, and search engines.







![Web: the new continentOnline advertising spending in the UK has overtaken television expenditure for the first time [4 billion Euros/year] (30/9/2009, BBC)In US, spending on digital marketing will overtake that of print for the first time in 2010Amazon.com: 50 million daily visitors60 billion dollars market capitalization24.000 employess9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-08chaniastochasticwebmodelling-copy-110414014556-phpapp02/75/2010-06-08-chania-stochastic-web-modelling-copy-9-2048.jpg)



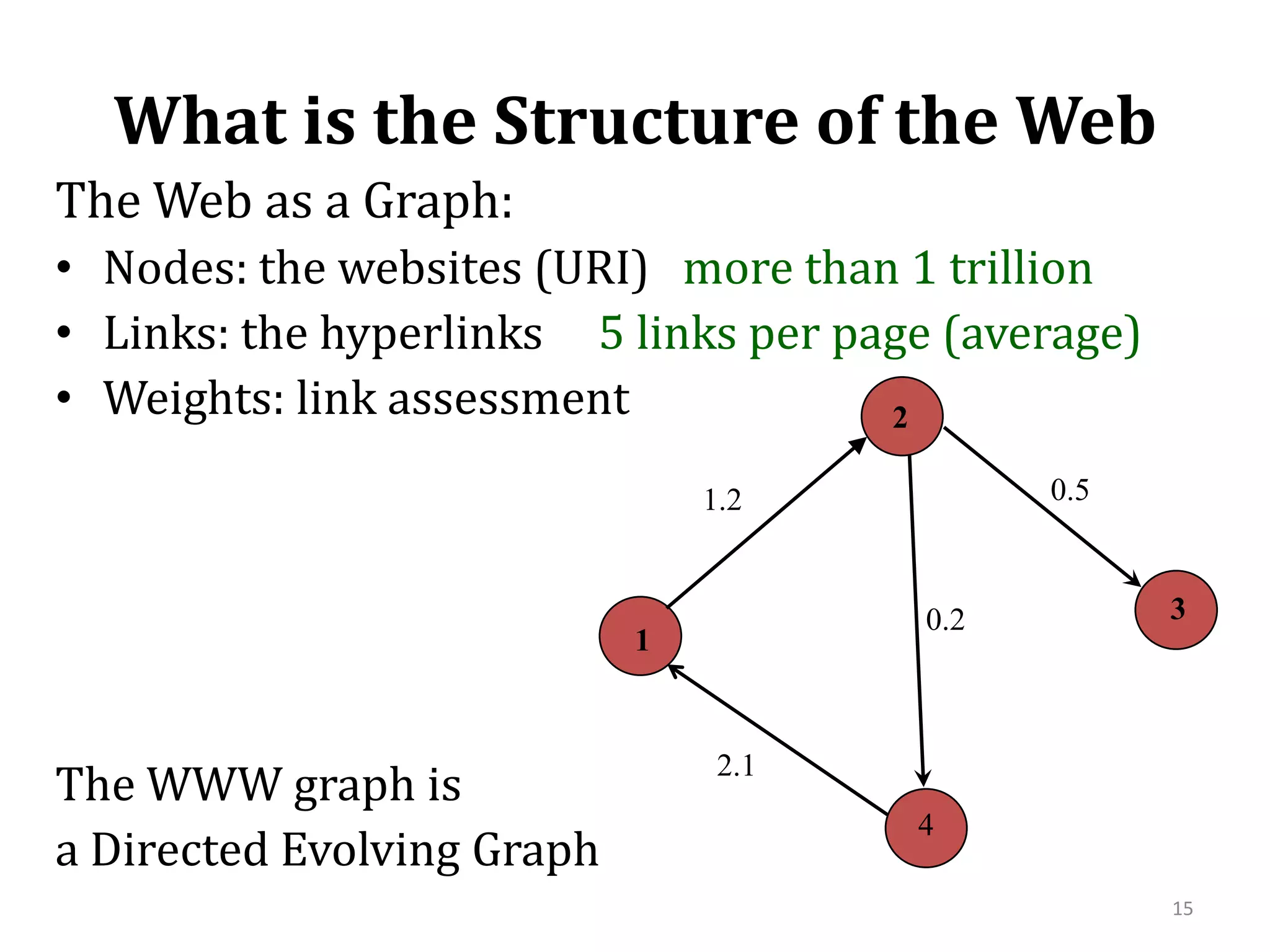
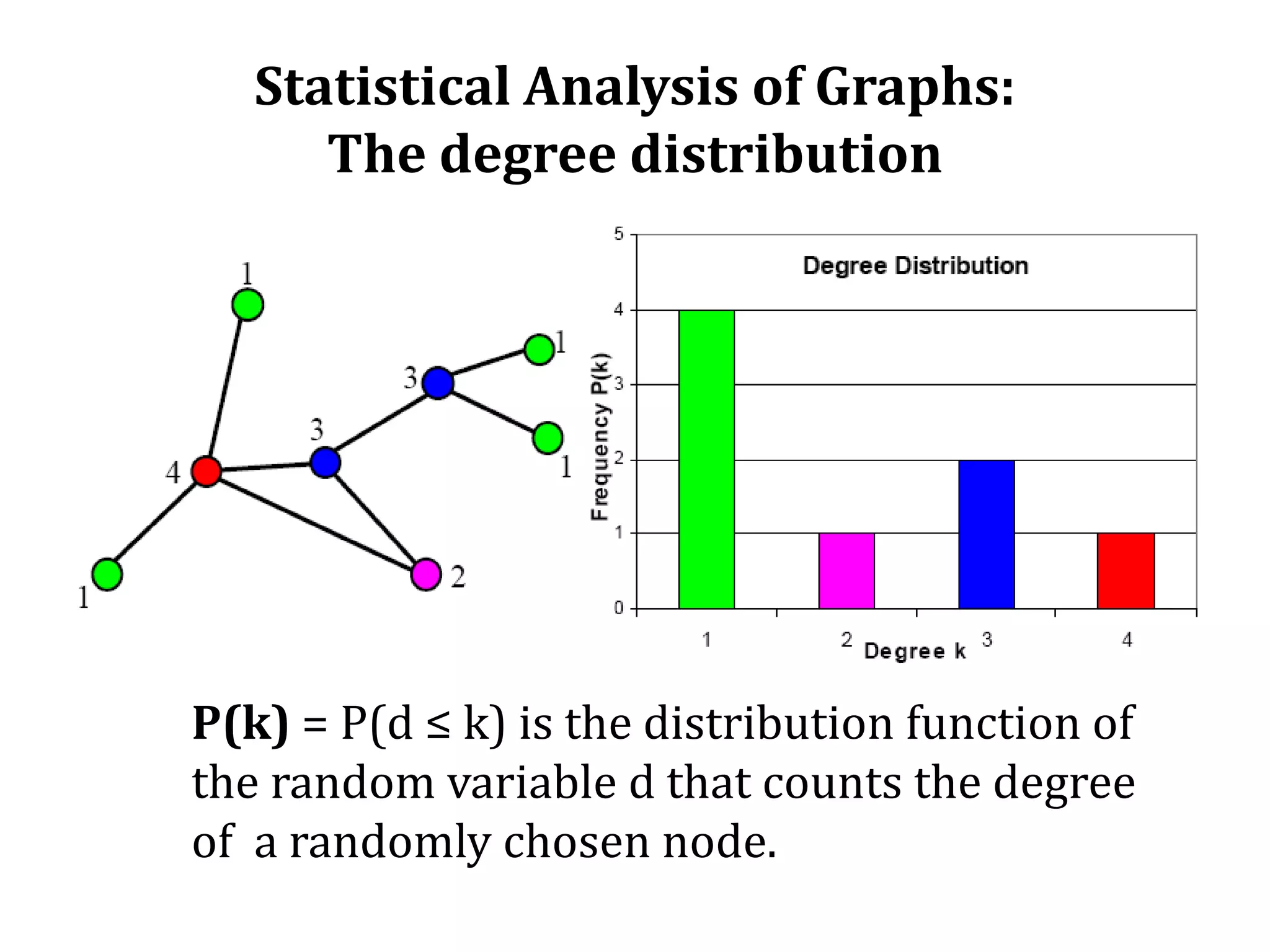
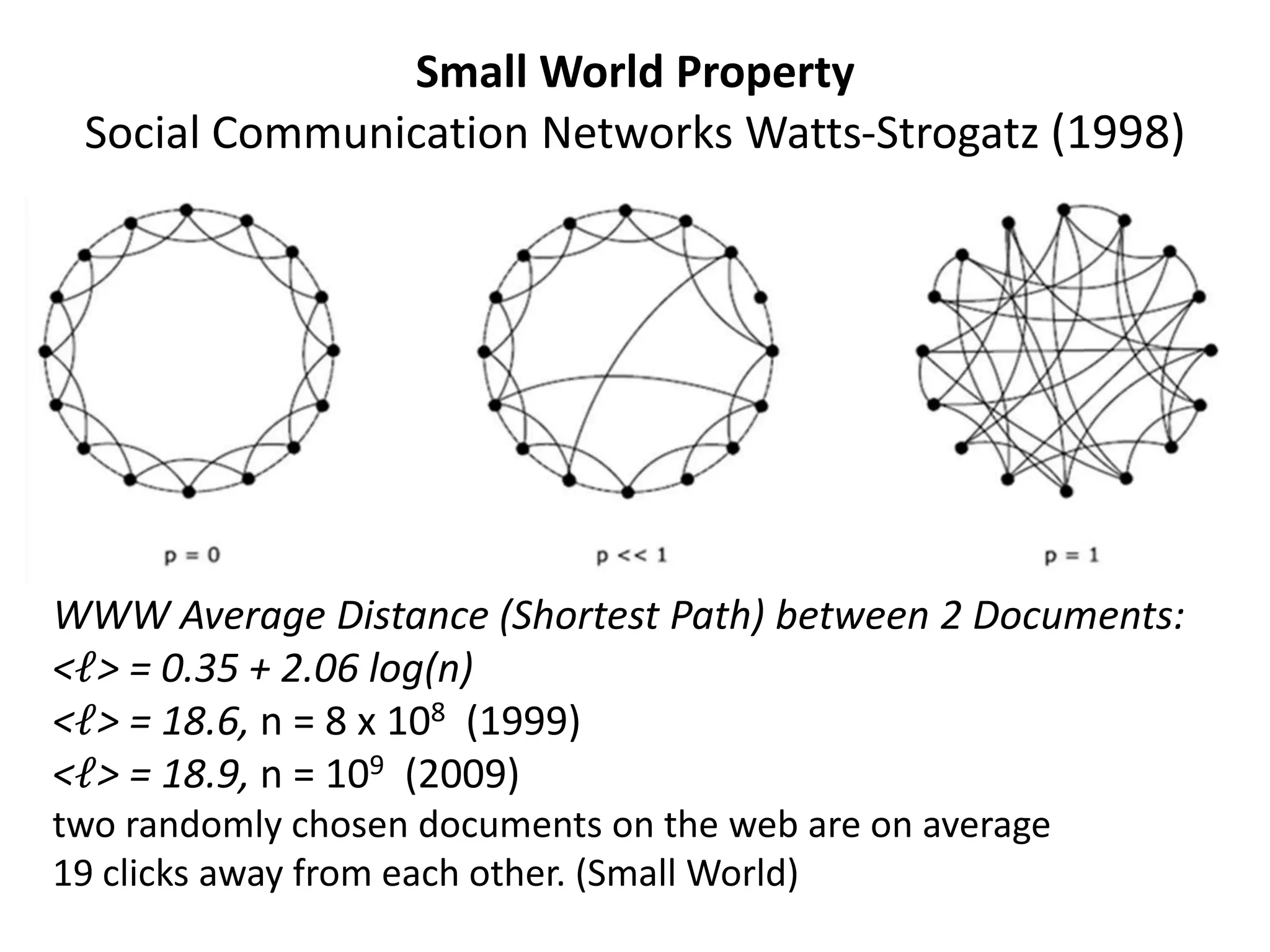
![Distribution of links on the World-Wide Web P(k)∼ k−γ power law a, Outgoing links (URLs found on an HTML document); b, Incoming links Web.c, Average of the shortest path between two documents as a function of system size [Barabasi,ea 1999]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-08chaniastochasticwebmodelling-copy-110414014556-phpapp02/75/2010-06-08-chania-stochastic-web-modelling-copy-18-2048.jpg)


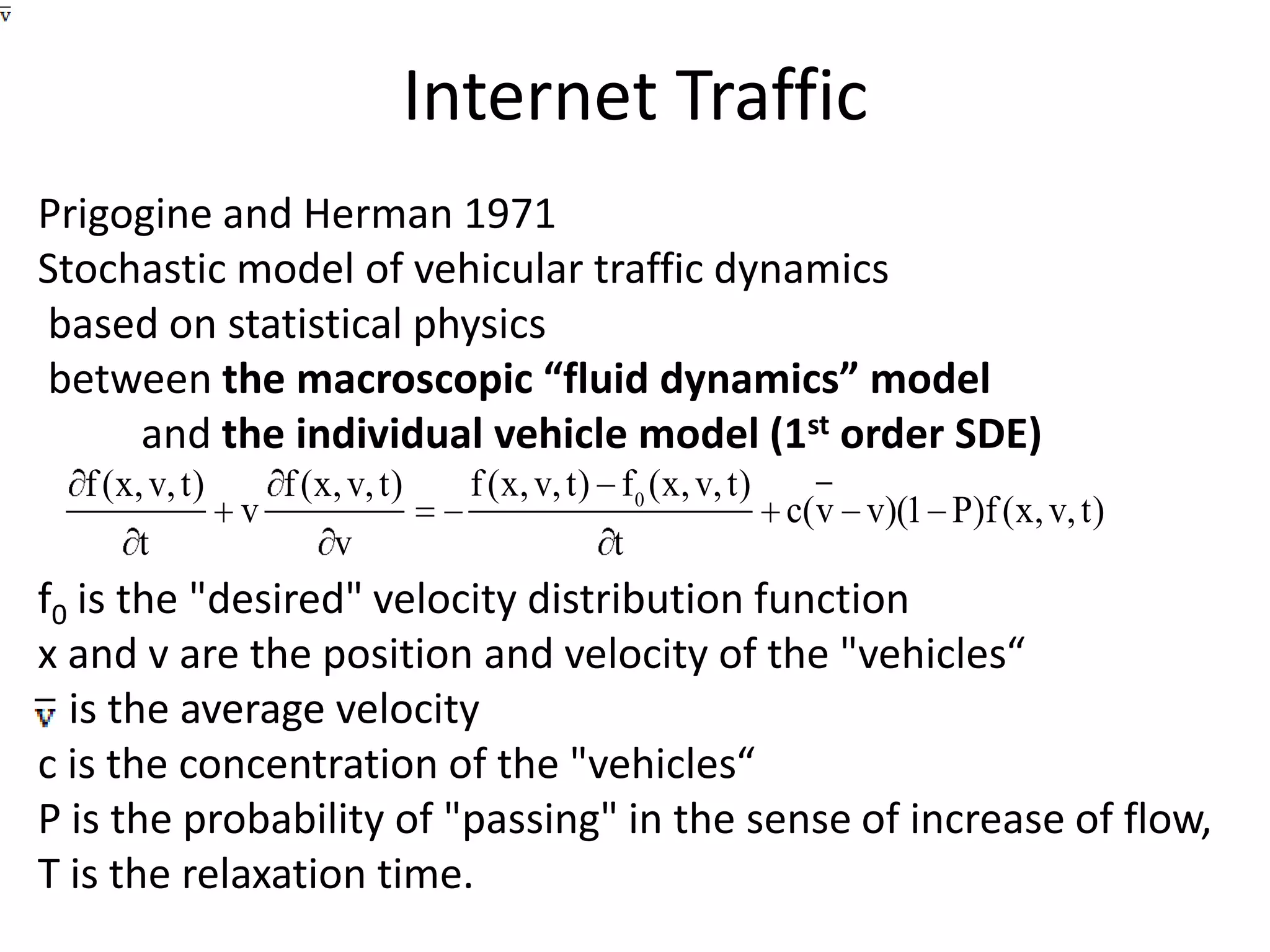
![Adaptation of the Prigogine - Hermann Model for the Internet Traffic [Antoniou, Ivanov 2002,2003]Vehicles = the Information PackagesStatistics of Information Packages: Log-Normal Distribution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-08chaniastochasticwebmodelling-copy-110414014556-phpapp02/75/2010-06-08-chania-stochastic-web-modelling-copy-24-2048.jpg)
![The Origin of Power Law in Network Structure and Network TrafficKolmogorov 1941, The local structure of the turbulence in incompressibleviscous fluid for very large Reynolds numbers, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 30, 301.The origin of Self-Similar Stochastic Processes Model of the homogeneous fragmentationApplying a variant the central limit theorem, Kolmogorov found that the logarithms of the grain sizes are normally distributedBefore Fractals and Modern scale-free models, Wavelet Analysis of data [Antoniou, Ivanov 2002]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-08chaniastochasticwebmodelling-copy-110414014556-phpapp02/75/2010-06-08-chania-stochastic-web-modelling-copy-25-2048.jpg)
![Evolution: Graph GeneratorsErdős-Rényi (ER)model [Erdős, Rényi ‘60]Small-world model [Watts, Strogatz ‘98]Preferential Attachment [Barabási, Albert ‘99]EdgeCopying models [Kumar et al.’99], [Kleinberg et al.’99],Forest Fire model [Leskovec, Faloutsos ‘05]Kroneckergraphs [Leskovec, Chakrabarti, Kleinberg, Faloutsos ‘07]Optimization-based models [Carlson,Doyle,’00] [Fabrikant et al. ’02]26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-08chaniastochasticwebmodelling-copy-110414014556-phpapp02/75/2010-06-08-chania-stochastic-web-modelling-copy-26-2048.jpg)

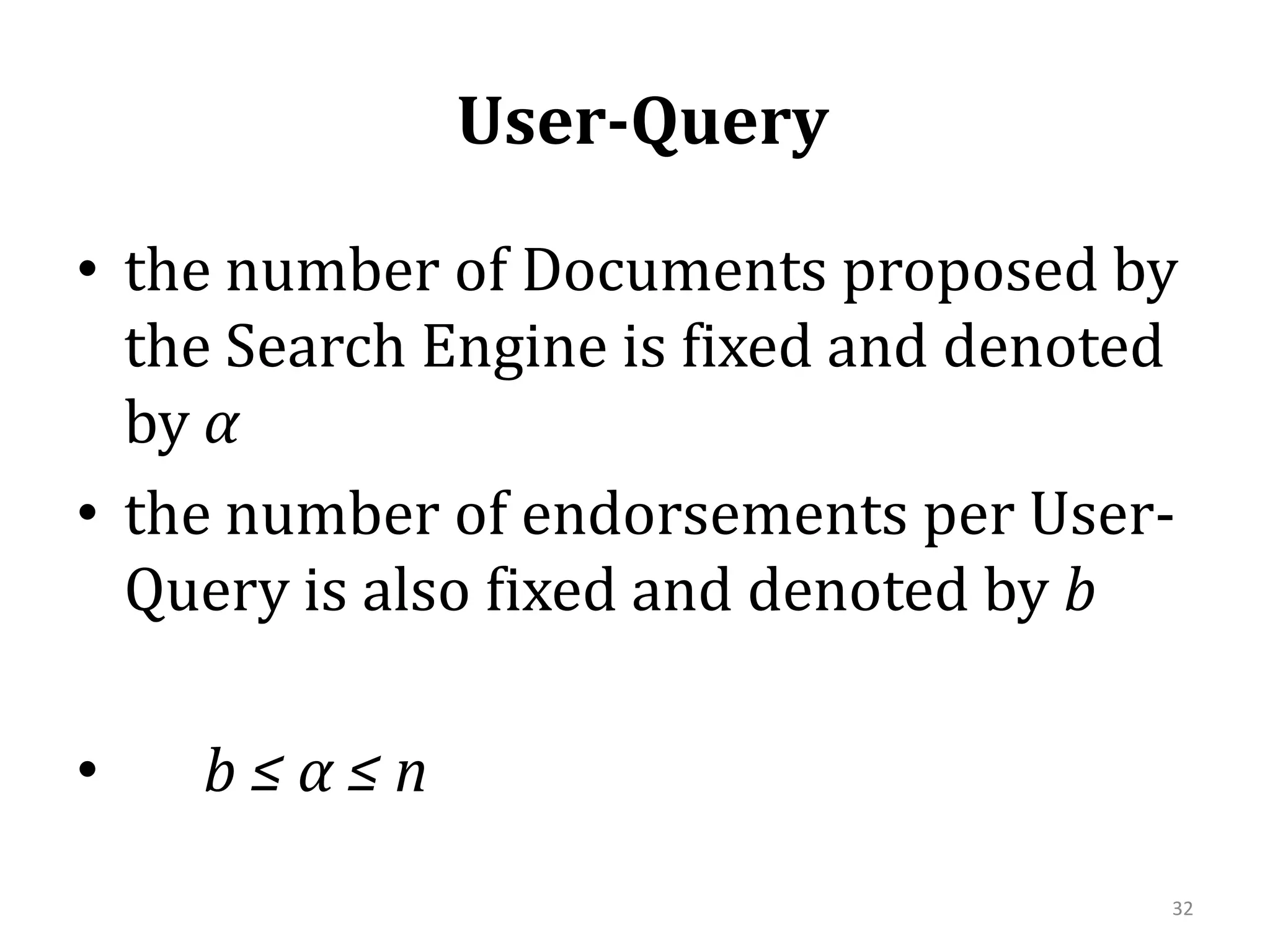
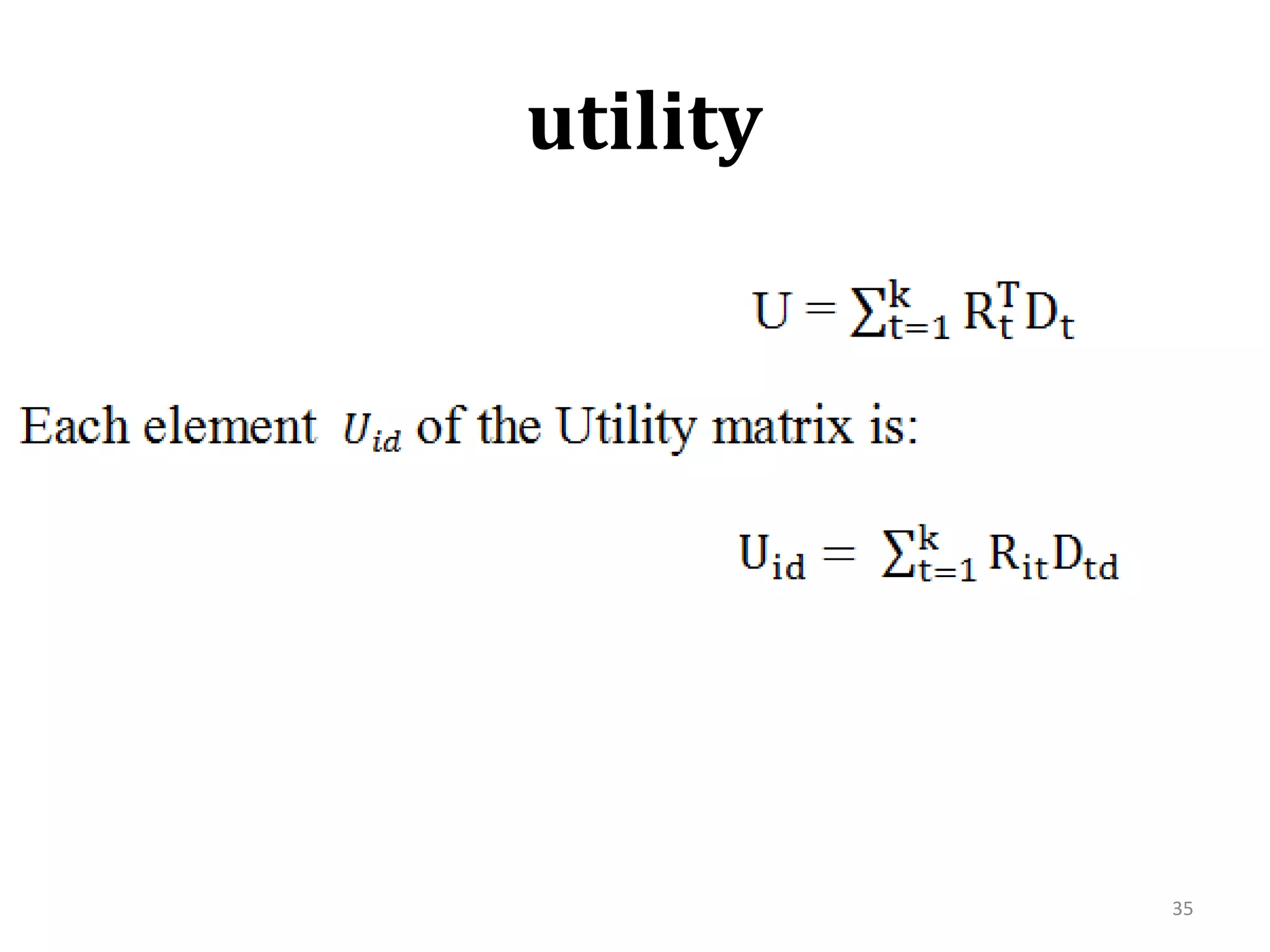
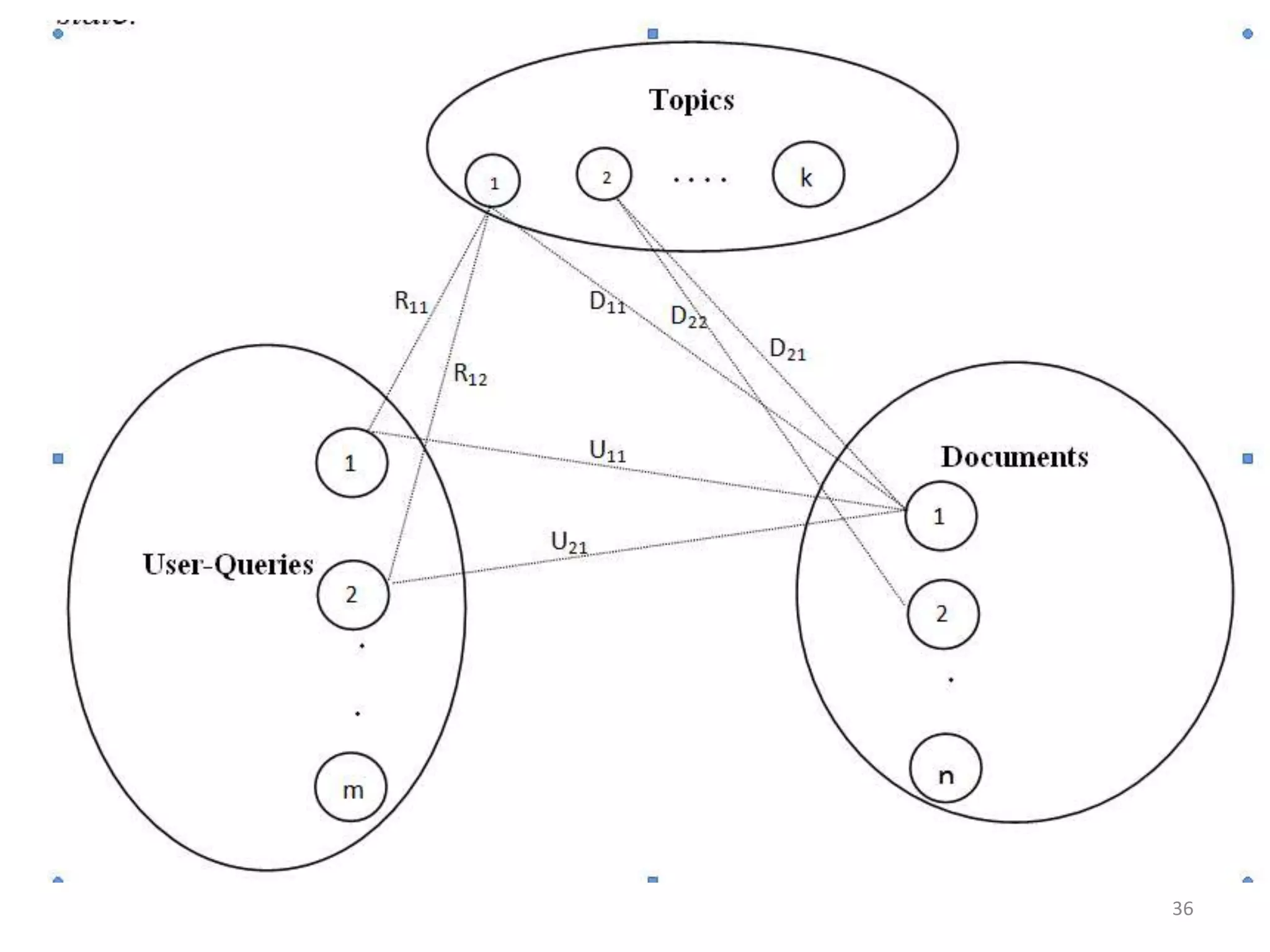
![Evolution: Queries- Search Engine -Web Kouroupas, Koutsoupias, Papadimitriou, SideriKKPS 2005Economic-inspired model (utility)Explains scale-free behaviorIn the Web three types of entities exist:Documents-i.e. web pages, created by authors [n] Users [m]Topics [k]k≤m≤n28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-08chaniastochasticwebmodelling-copy-110414014556-phpapp02/75/2010-06-08-chania-stochastic-web-modelling-copy-28-2048.jpg)



![the algorithm Step 1: A User-Query,for a specific Topic, isentered in the Search EngineStep 2: The Search Engine recommends αrelevant Documents. The listing order is defined by a rule. In the very first operation of the Search Engine the Documents the rule is random listing according to some probability distributionStep 3: Among the α recommended Documents, bareendorsed on the basis of highest Utility. In this way, the bipartite graph S= ([m], [n], L) of Document endorsements is formed. Compute the in-degree of the Documents from the endorsements 33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-08chaniastochasticwebmodelling-copy-110414014556-phpapp02/75/2010-06-08-chania-stochastic-web-modelling-copy-33-2048.jpg)



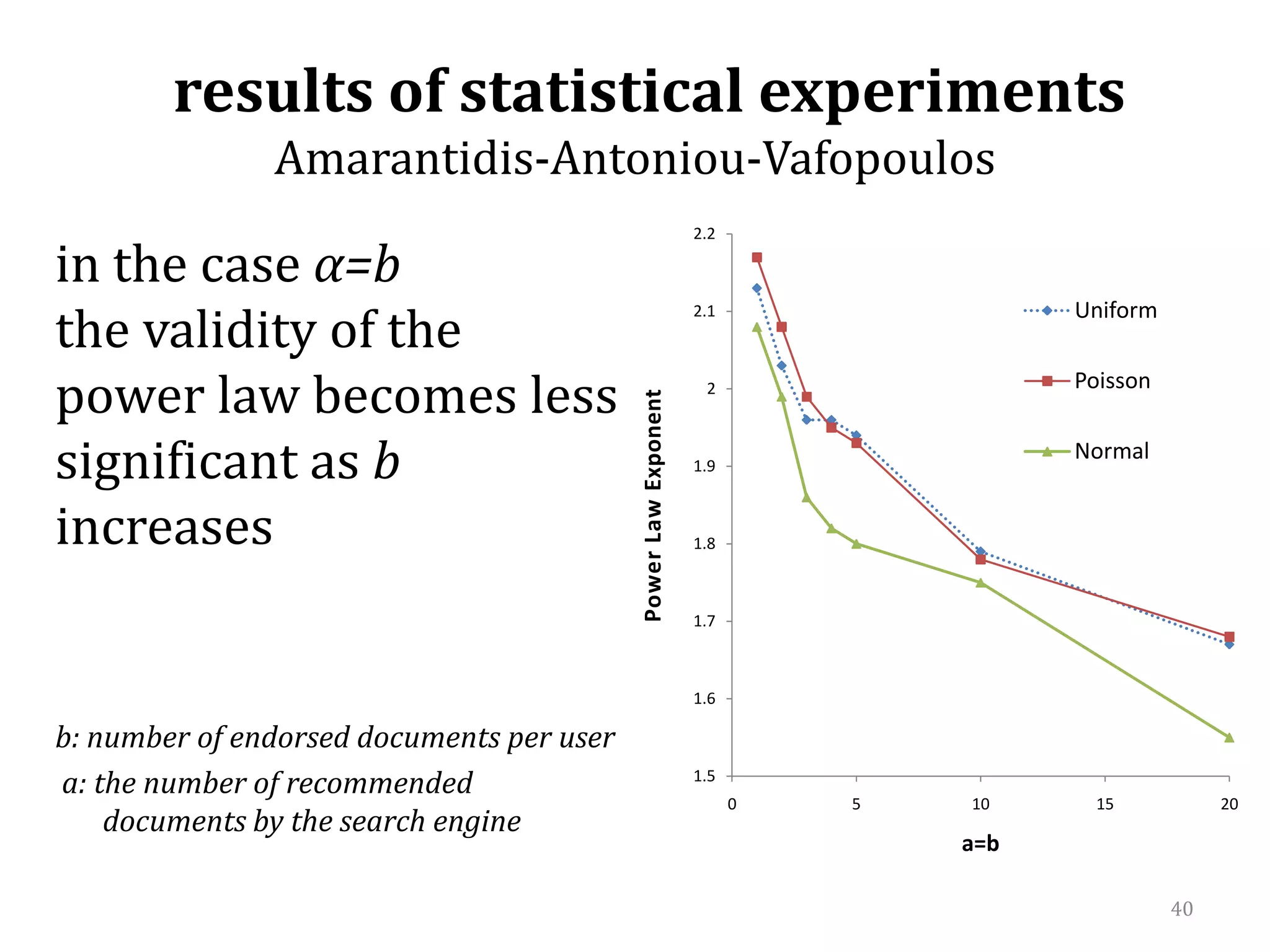
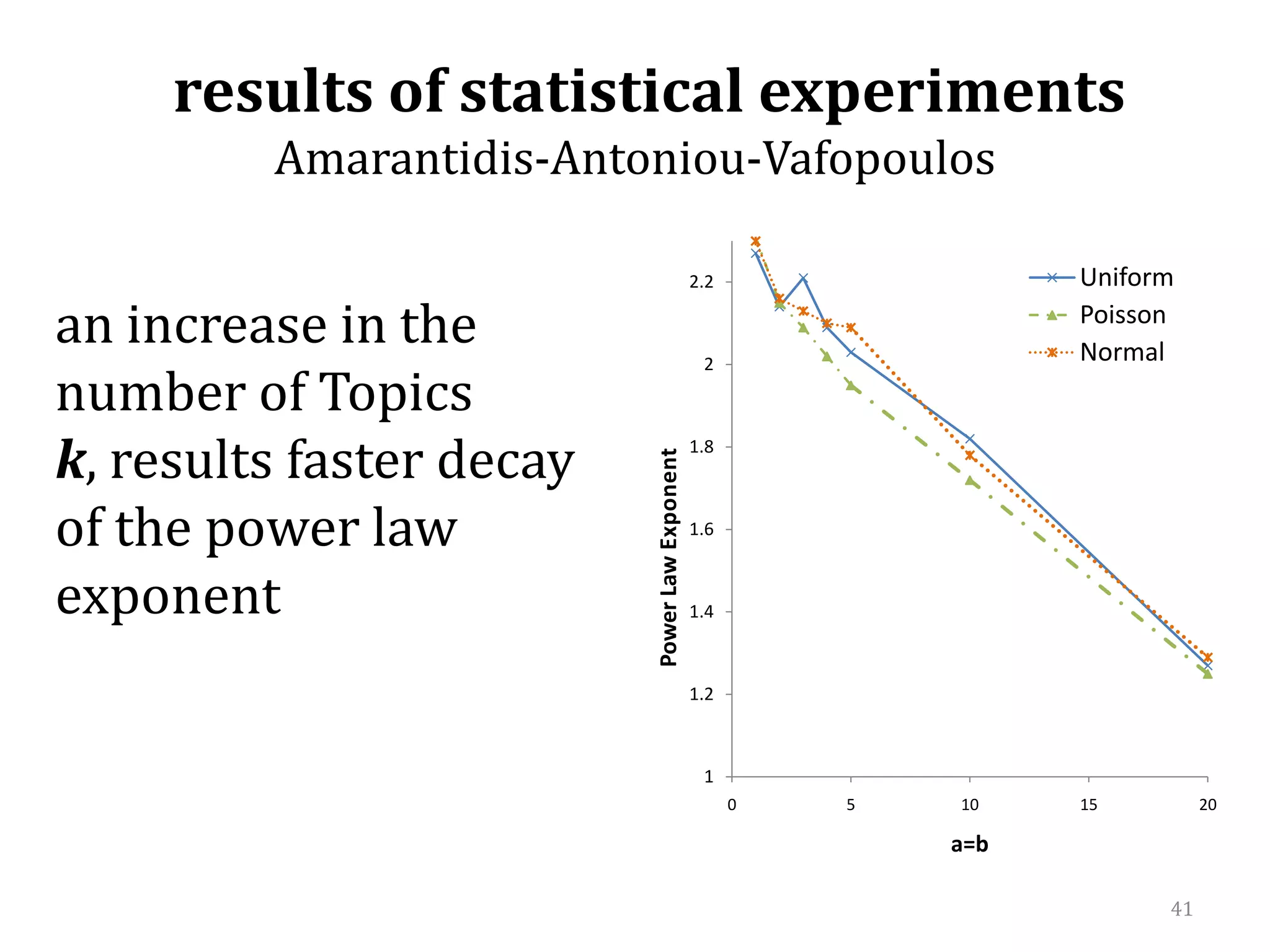
![efficiency of the search algorithm α=befficiency of the search algorithm increases when the number of topics k increases[confirmation of KKPS results]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-08chaniastochasticwebmodelling-copy-110414014556-phpapp02/75/2010-06-08-chania-stochastic-web-modelling-copy-43-2048.jpg)
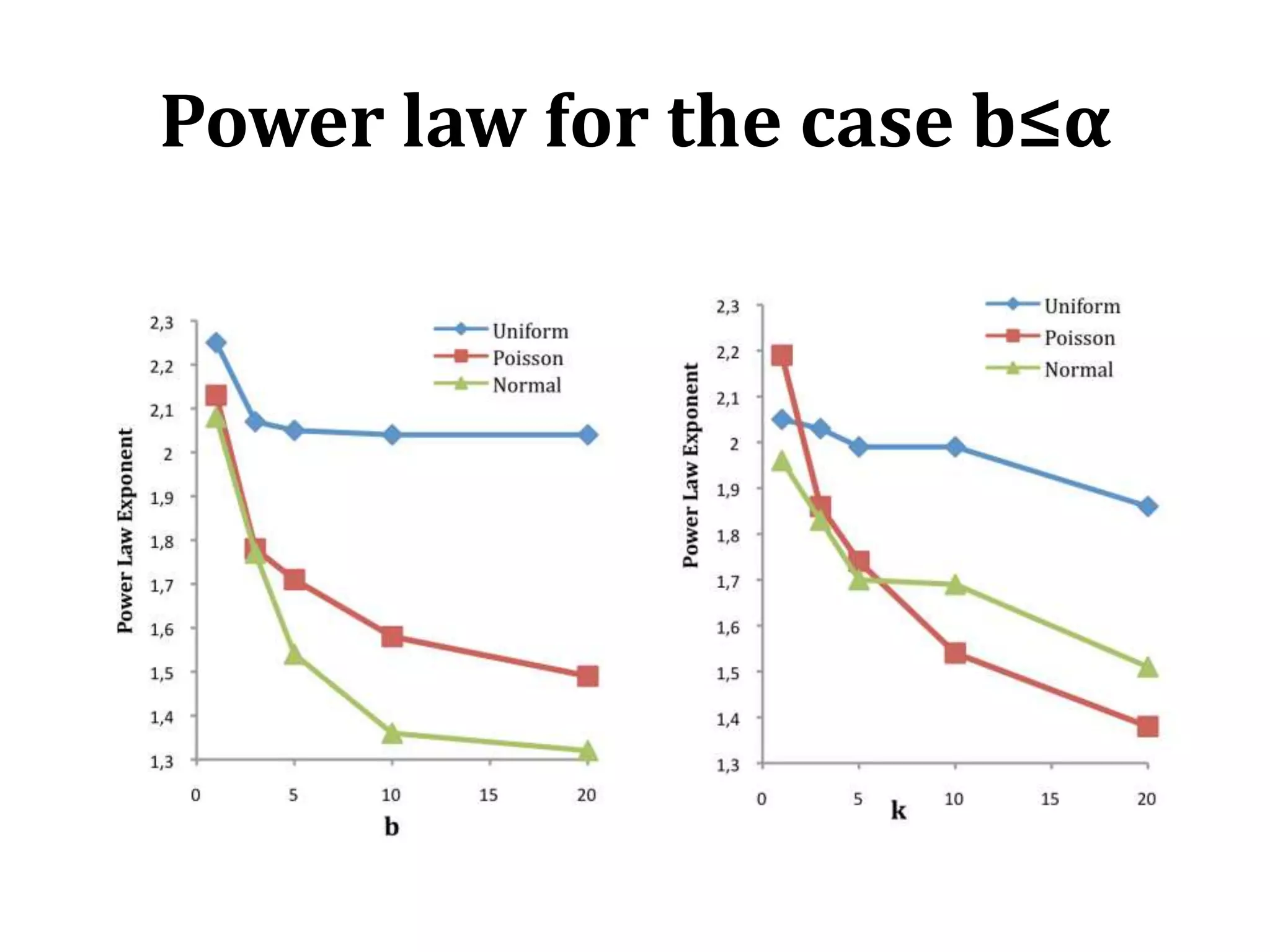
![efficiency of the search algorithm in the case b≤α efficiency of the search algorithm increases when the number of recommended Documents by the Search Engine α increases[confirmation of KKPS results]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-08chaniastochasticwebmodelling-copy-110414014556-phpapp02/75/2010-06-08-chania-stochastic-web-modelling-copy-44-2048.jpg)
![efficiency of the search algorithm b≤αefficiency of the search algorithm increases when the number of bof endorsed Documents per User-Query increases[KKPS results not confirmed]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-08chaniastochasticwebmodelling-copy-110414014556-phpapp02/75/2010-06-08-chania-stochastic-web-modelling-copy-45-2048.jpg)