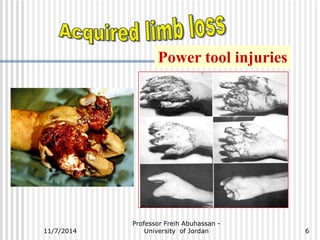
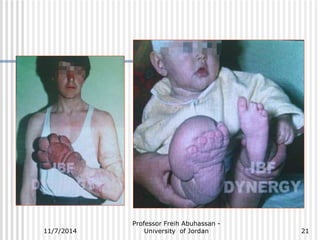
The document outlines various causes and management strategies for traumatic injuries and amputations, detailing conditions such as motor vehicle accidents, gunshot wounds, and birth trauma. It emphasizes techniques for preserving limb length and growth potential, particularly in pediatric cases, and discusses the psychological and functional considerations for juvenile amputees. Additionally, it highlights the importance of surgical approaches and prosthetic fitting to optimize outcomes for young patients.