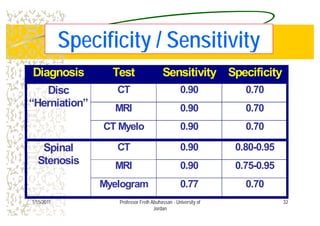
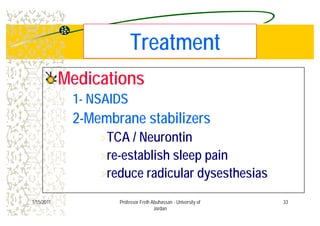
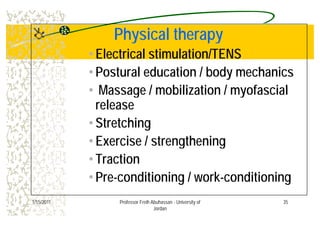
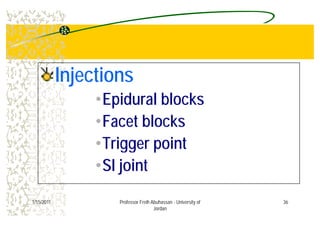
The document discusses low back pain (LBP) including its prevalence, causes, diagnostic considerations, and treatment options. It highlights that a significant percentage of LBP cases resolve without treatment and provides an overview of risk factors, differential diagnoses, and management strategies such as medications, physical therapy, and surgery. Key points include identifying red flags for serious conditions and the importance of patient-centered care in treatment.