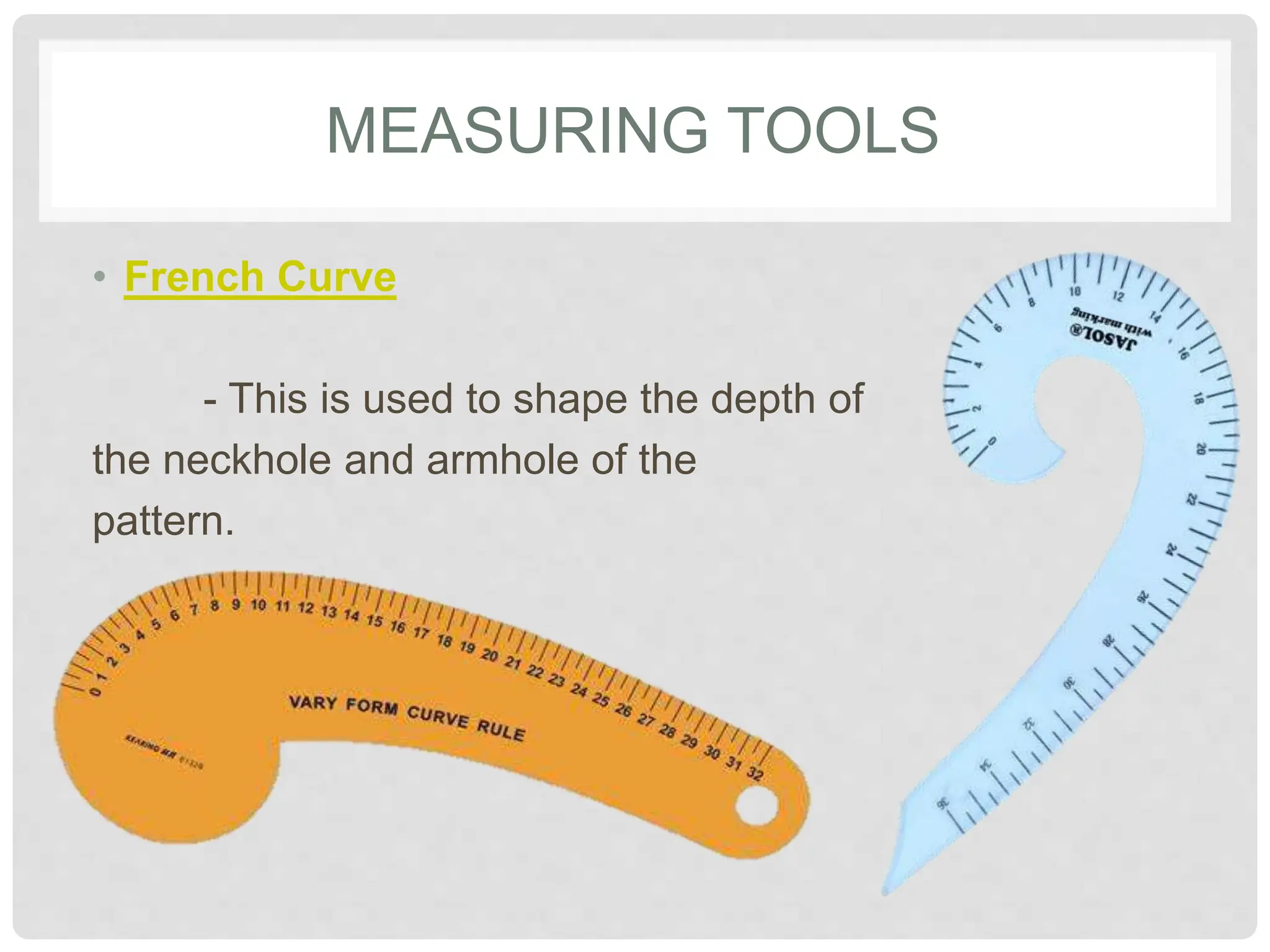
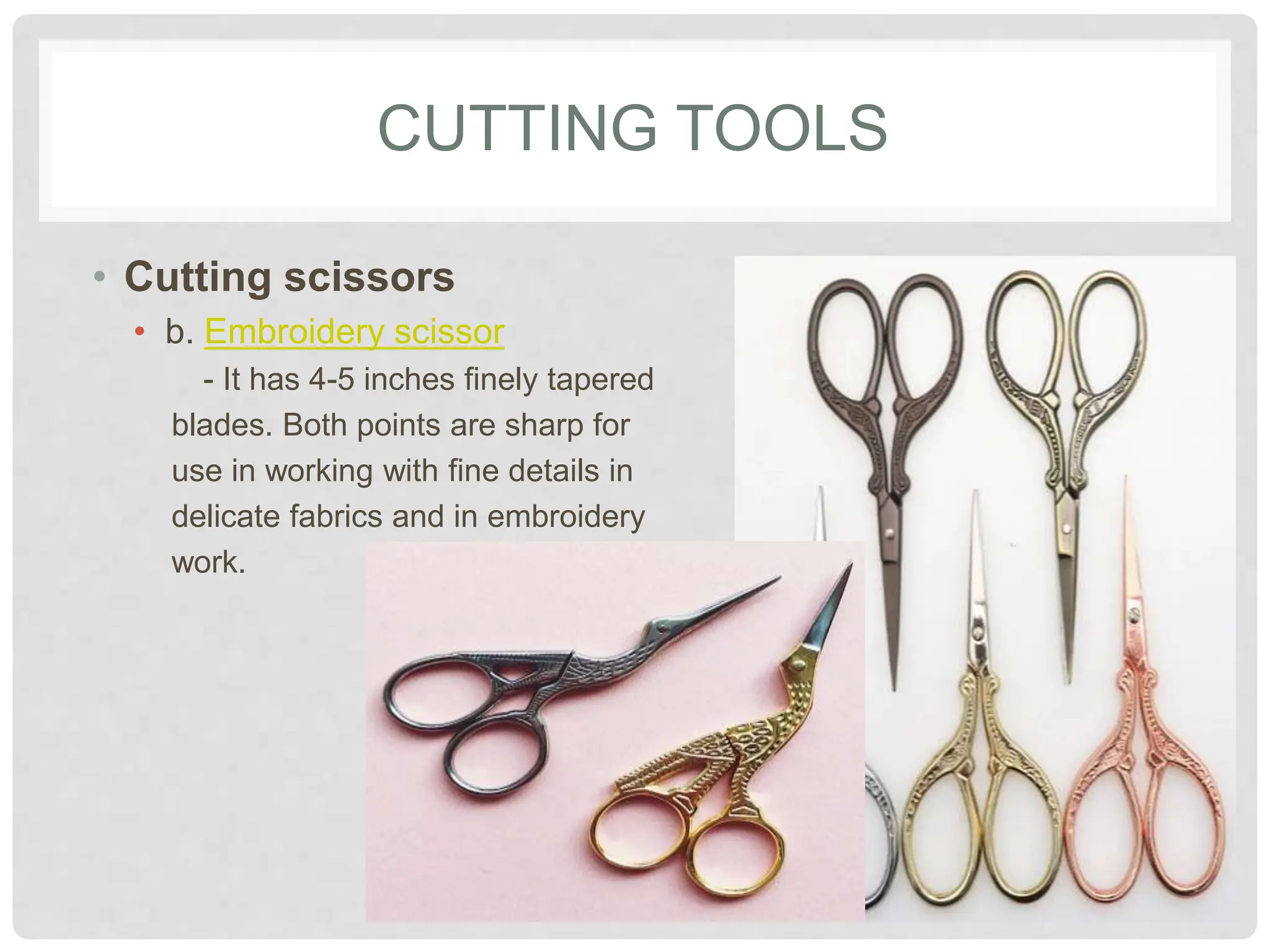
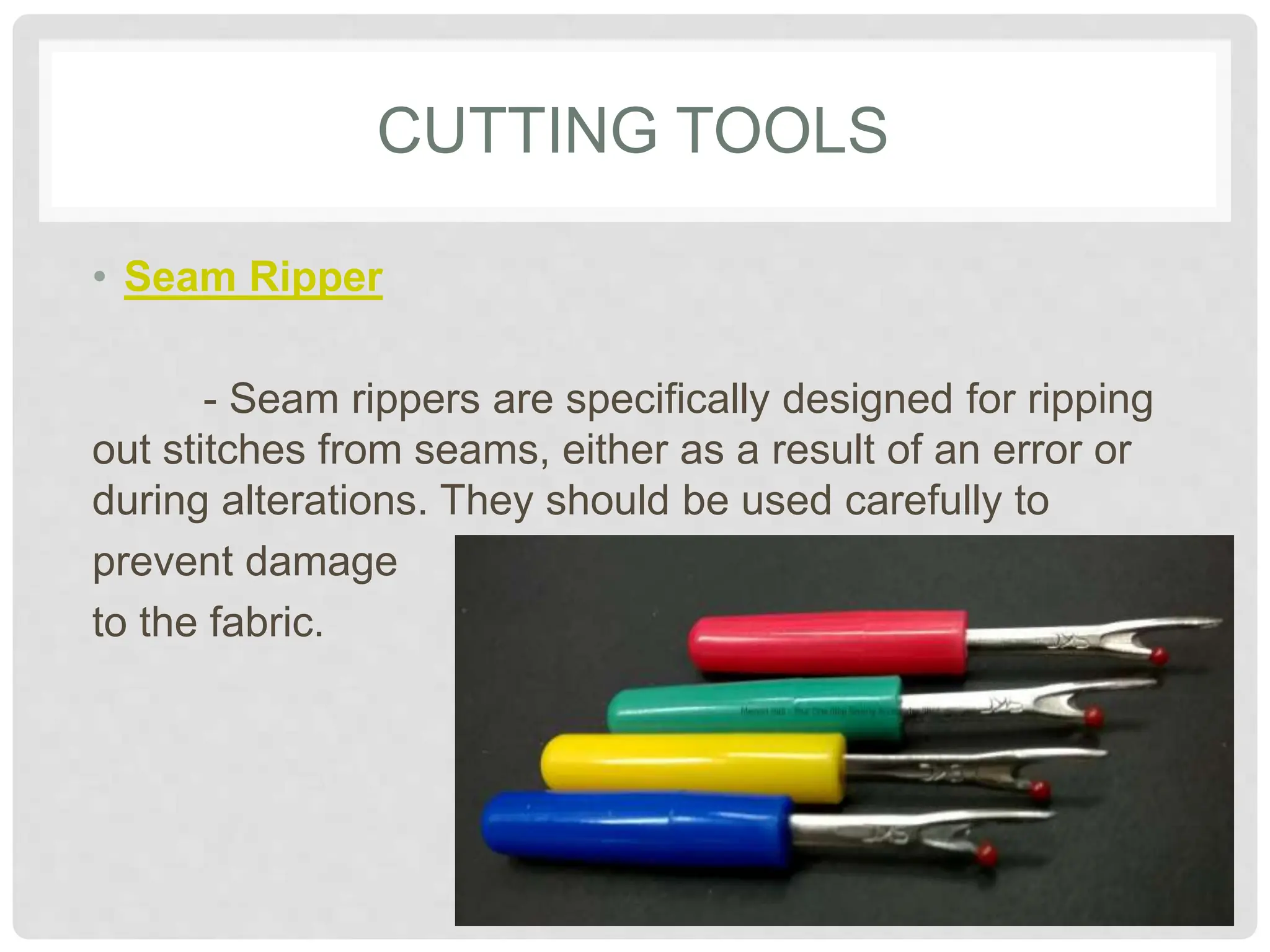
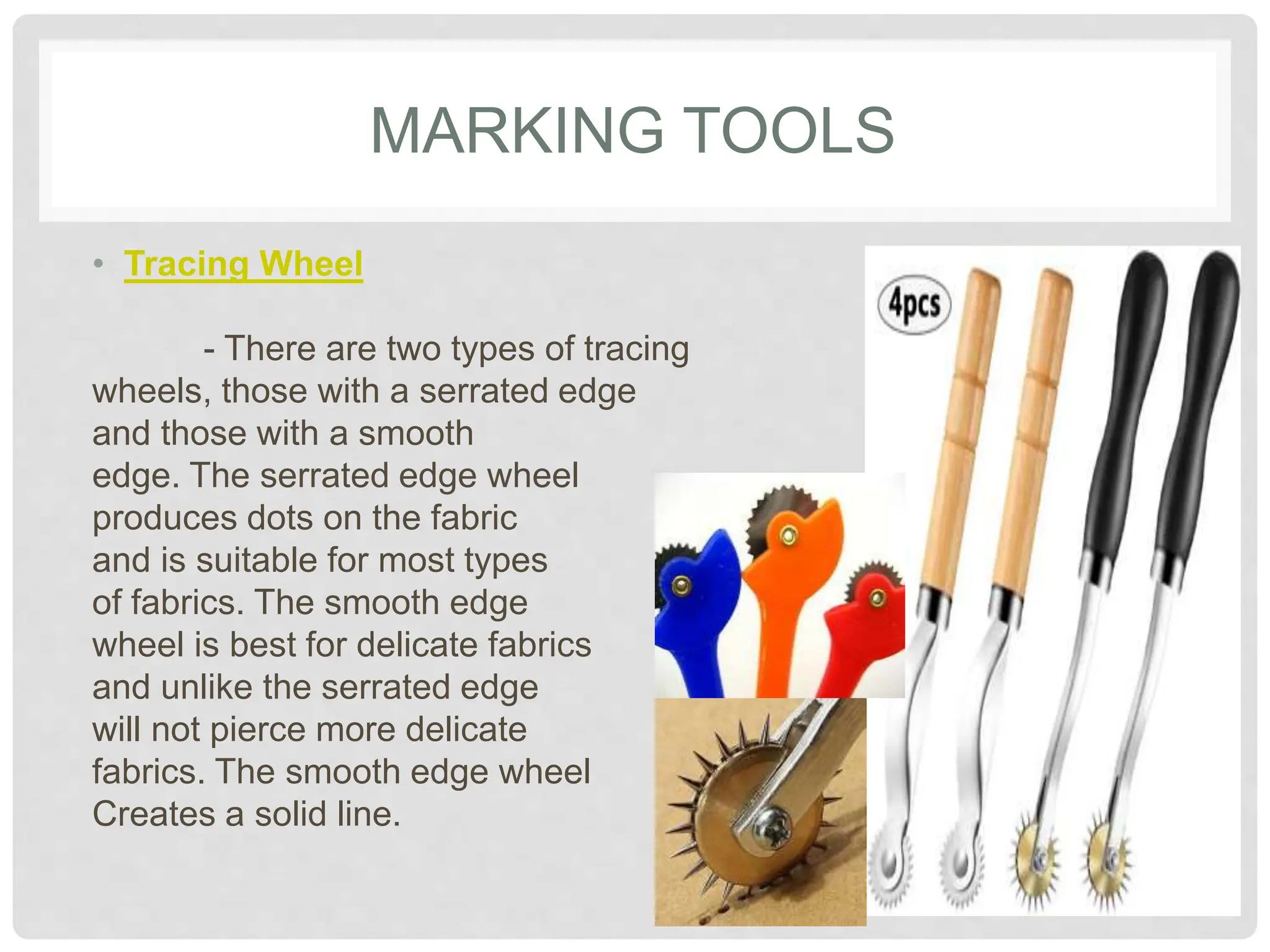
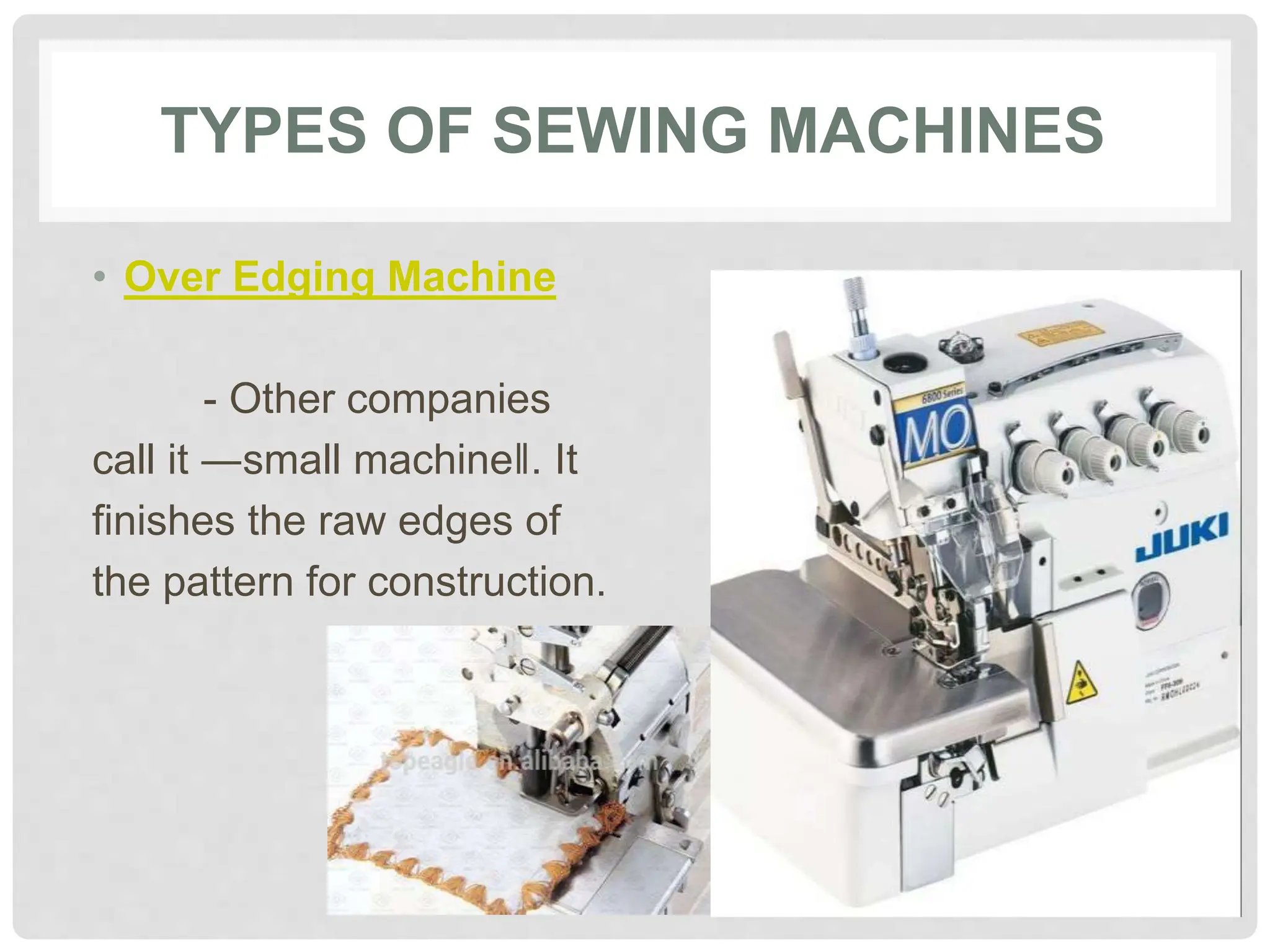
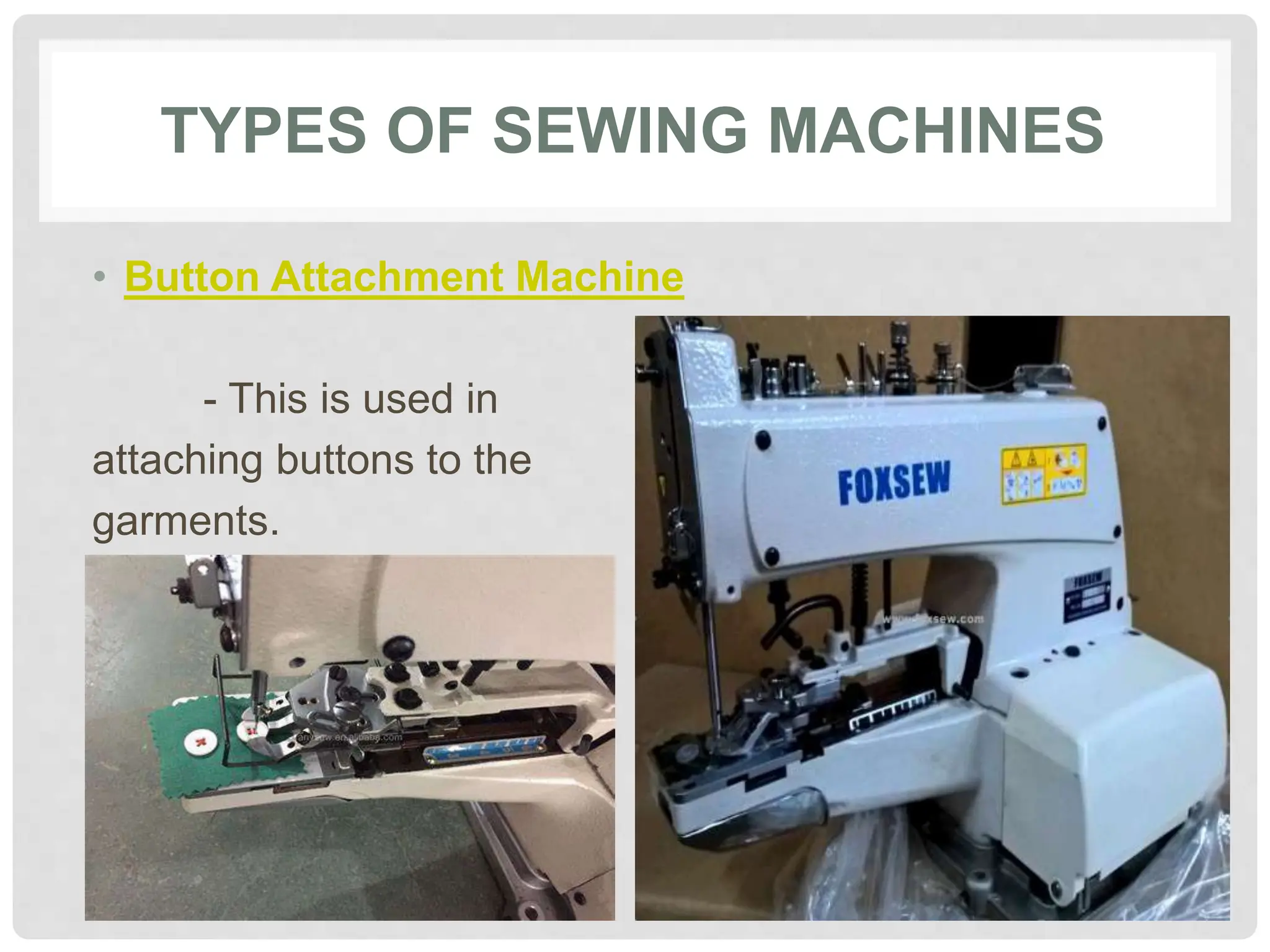
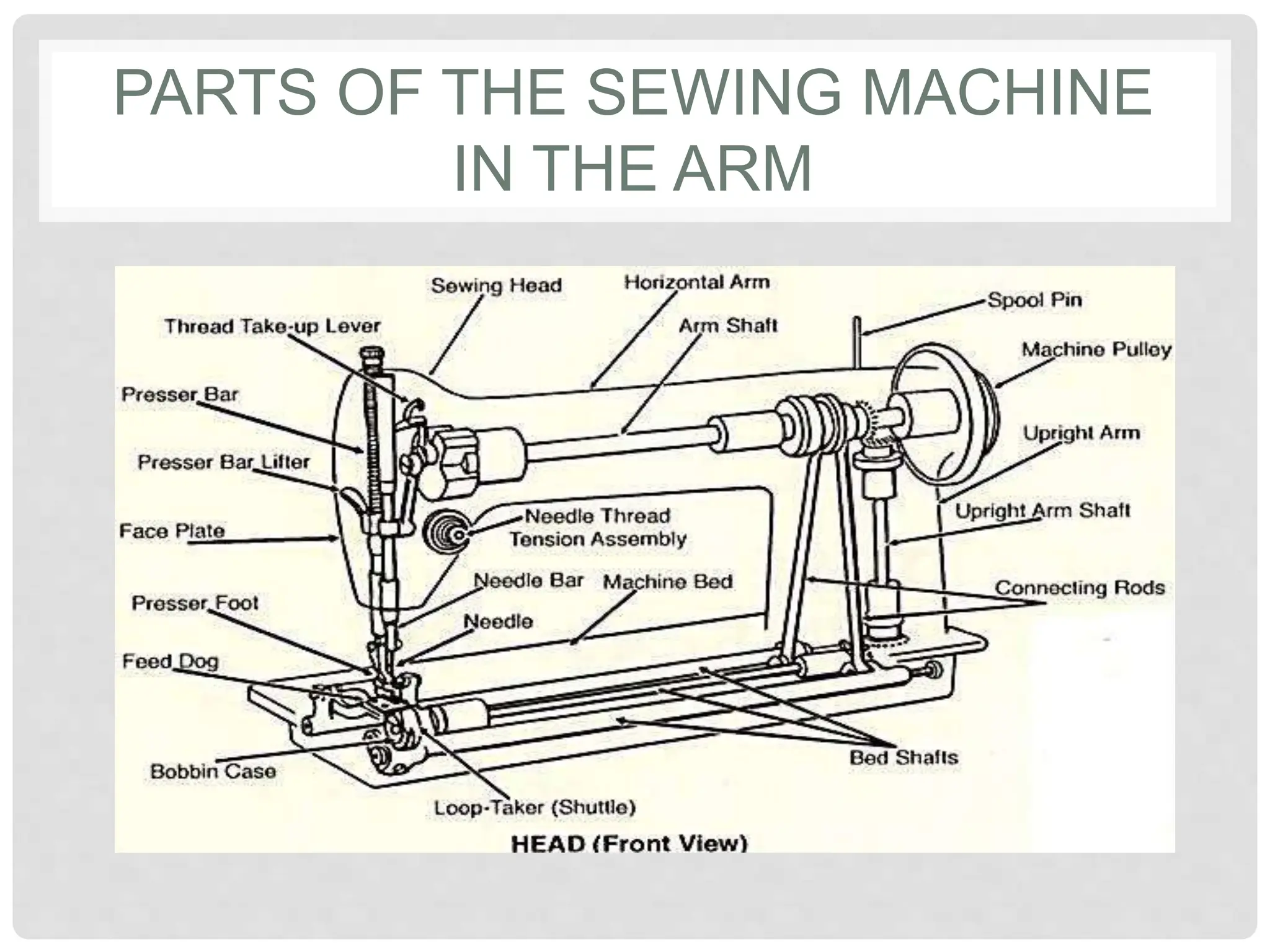
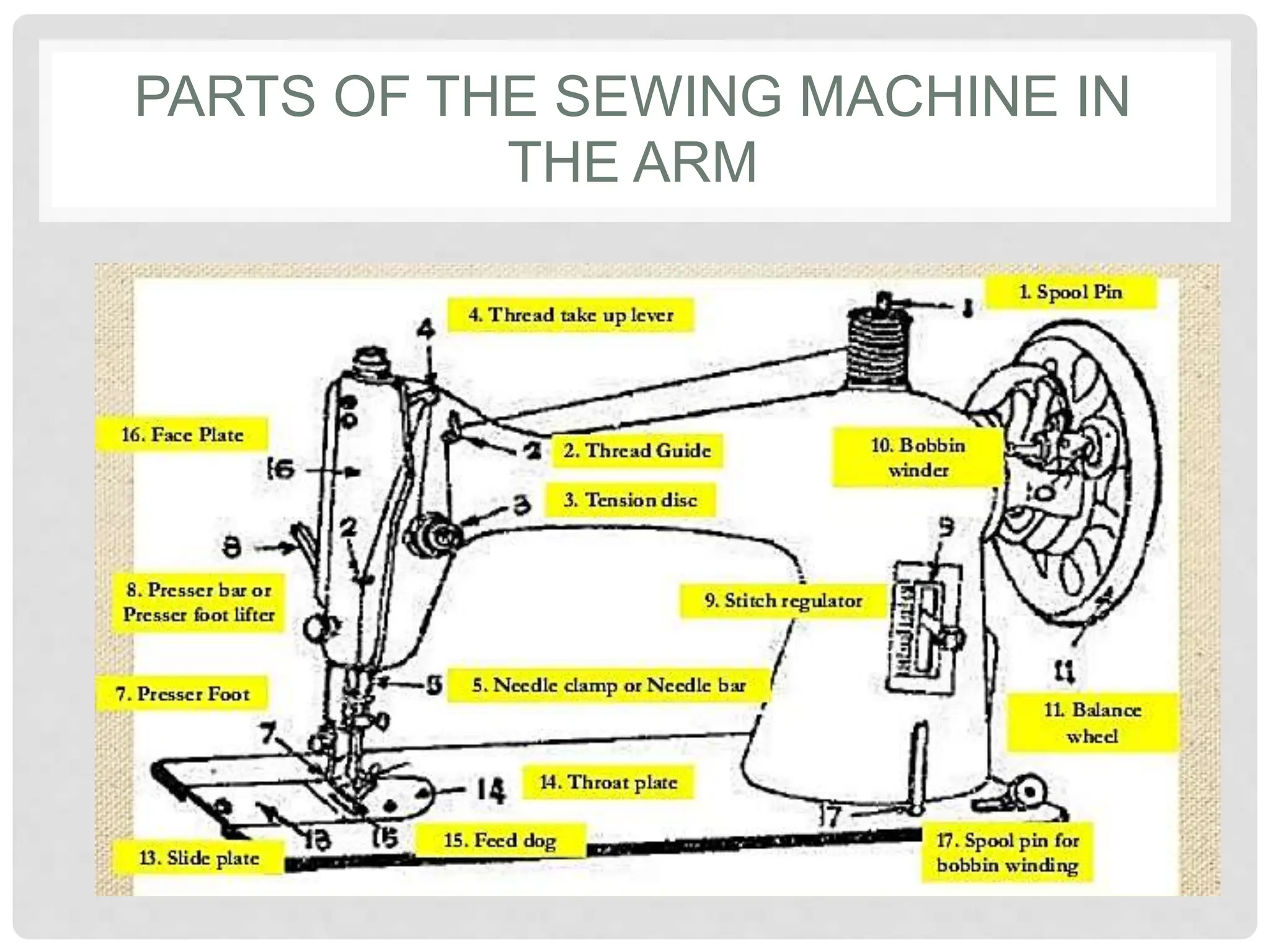
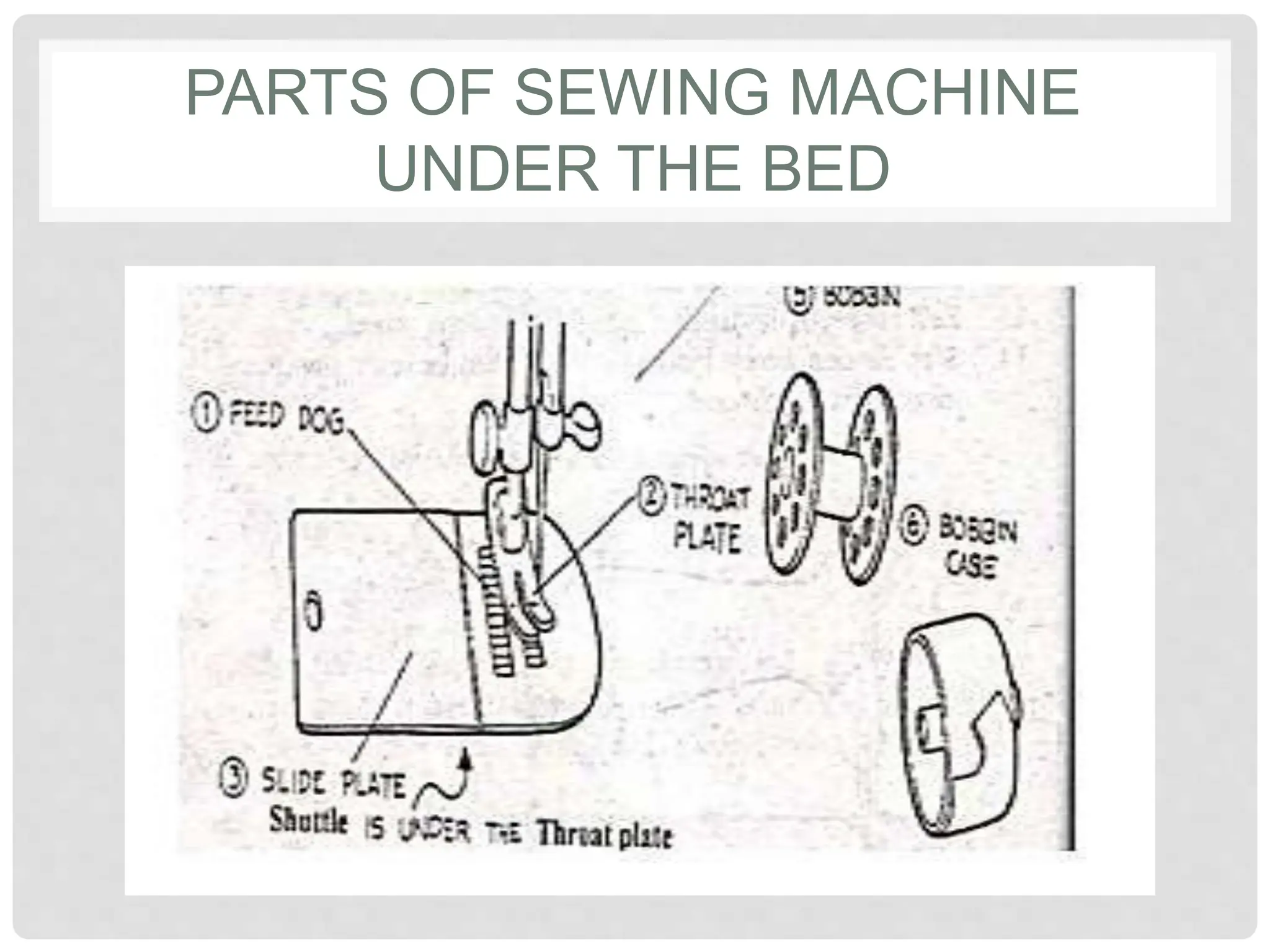
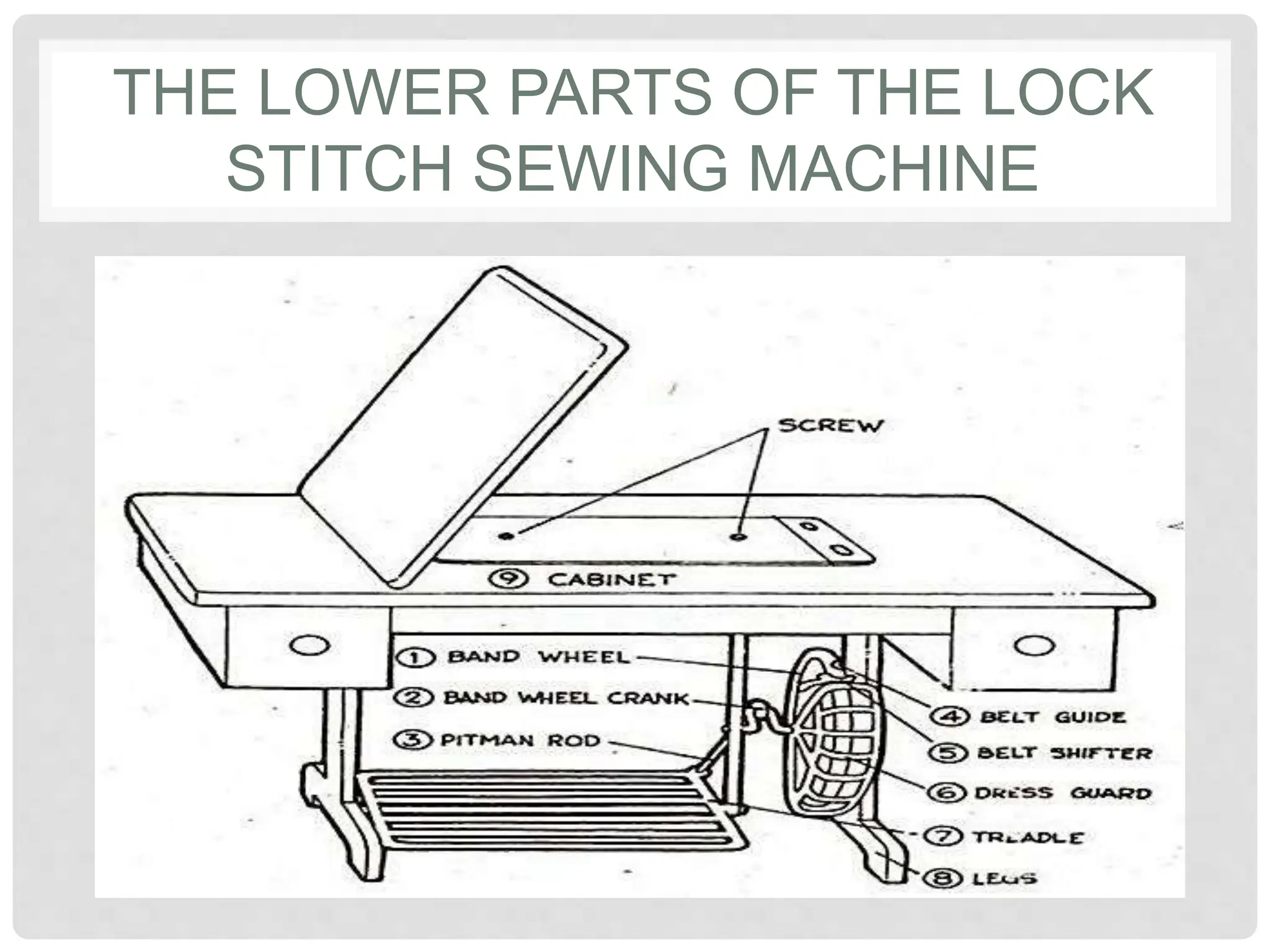
This document provides information on various tools and equipment used for dressmaking. It discusses measuring tools like tape measures, sewing gauges, and rulers. It also outlines cutting tools such as shears, pinking shears, and scissors. Additionally, it details marking tools including chalk pencils, pens, and tailor's chalk. The document also mentions pinning and sewing tools as well as materials used for dressmaking and different types of sewing machines.