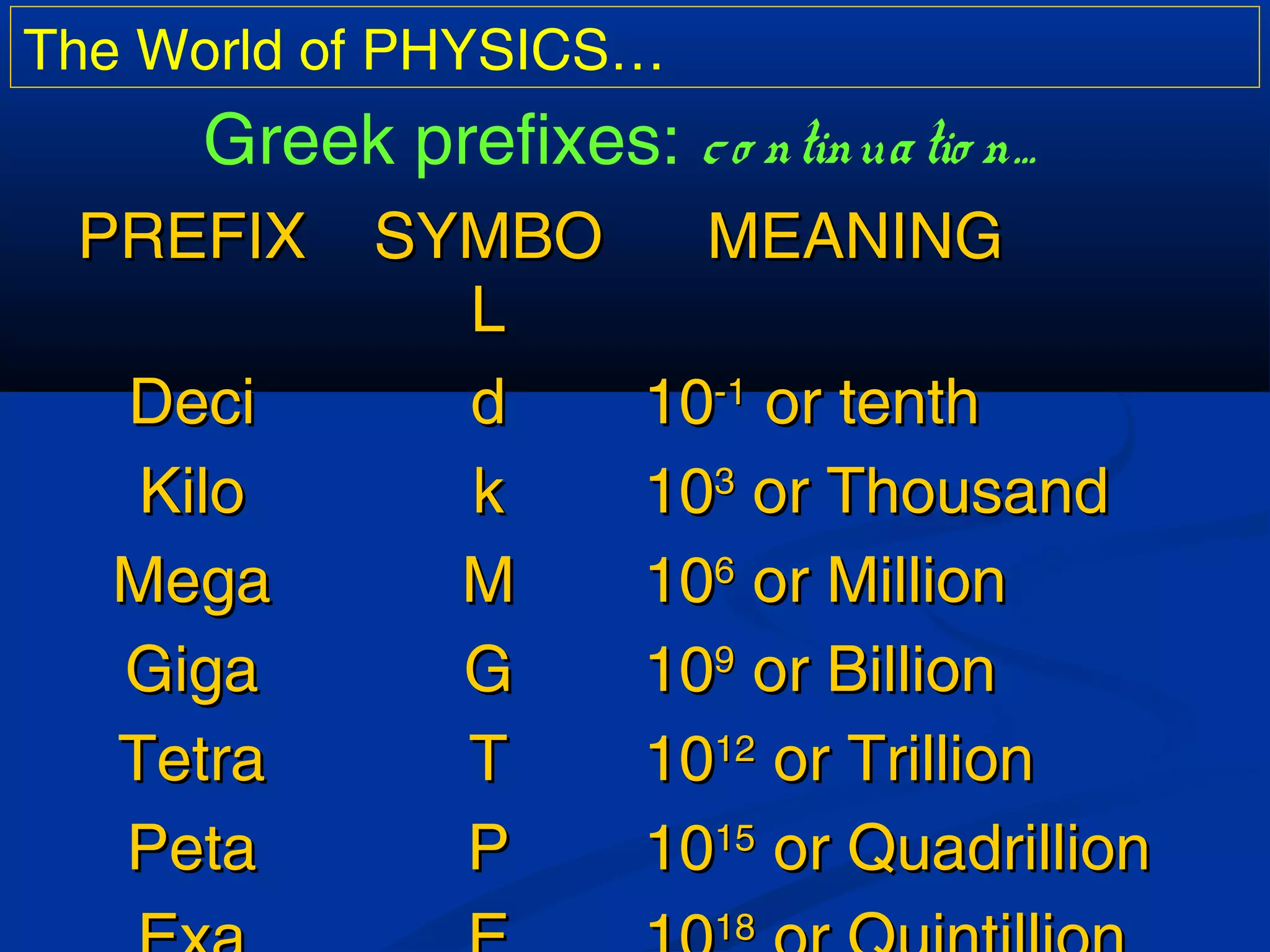
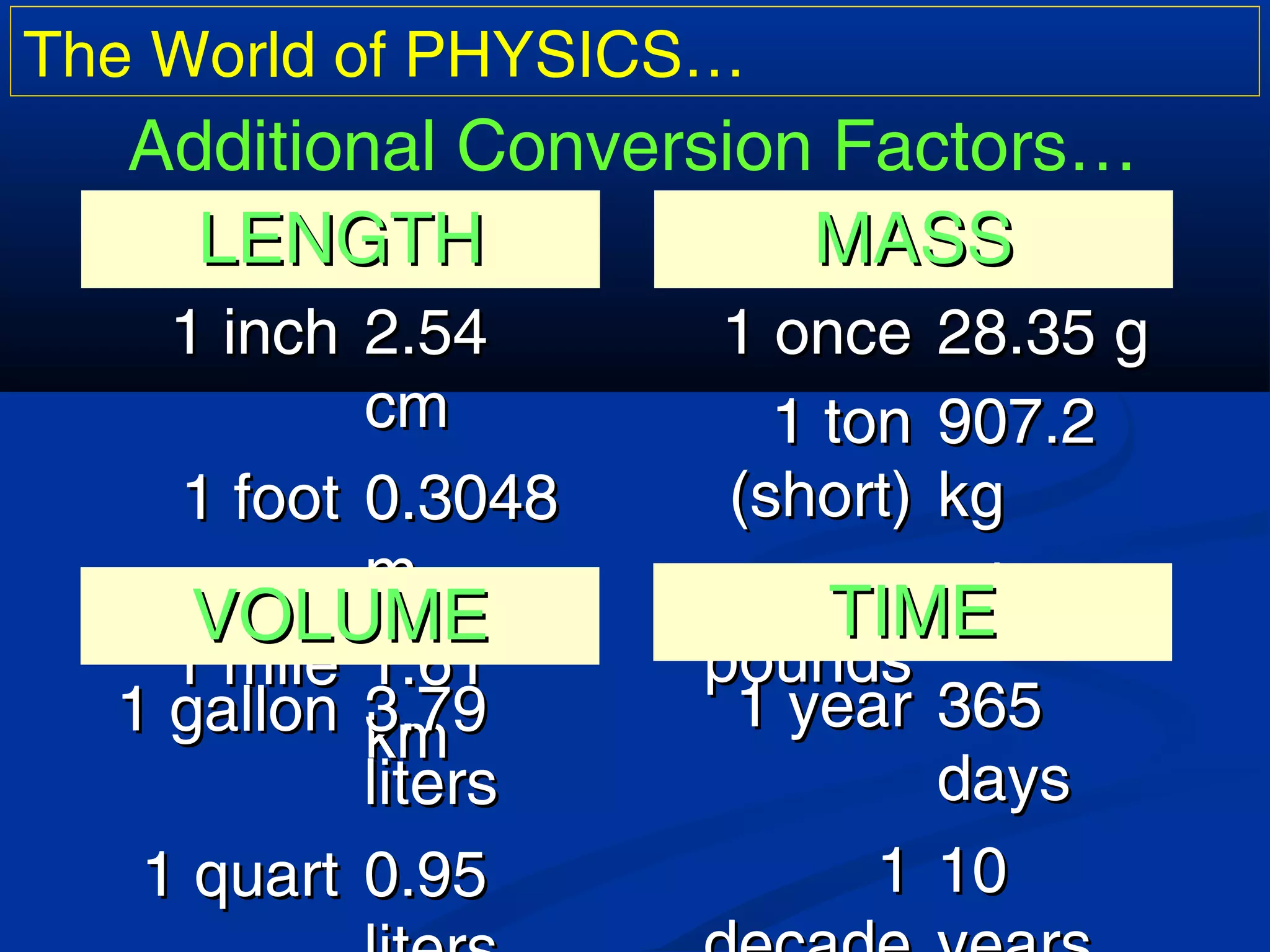
Scientific notation is a way to write large and small numbers using powers of 10. It involves writing a number as the product of a constant term and a power of 10. Some examples of scientific notation given are the Earth's diameter of 1.276 x 107 meters and the wavelength of red light being 6.5 x 10-5 cm. Greek prefixes are also sometimes used to denote powers of 10, with examples like giga for 10^9 and pico for 10^-12. Common conversion factors between units like meters and kilometers or kilograms and grams are also presented.