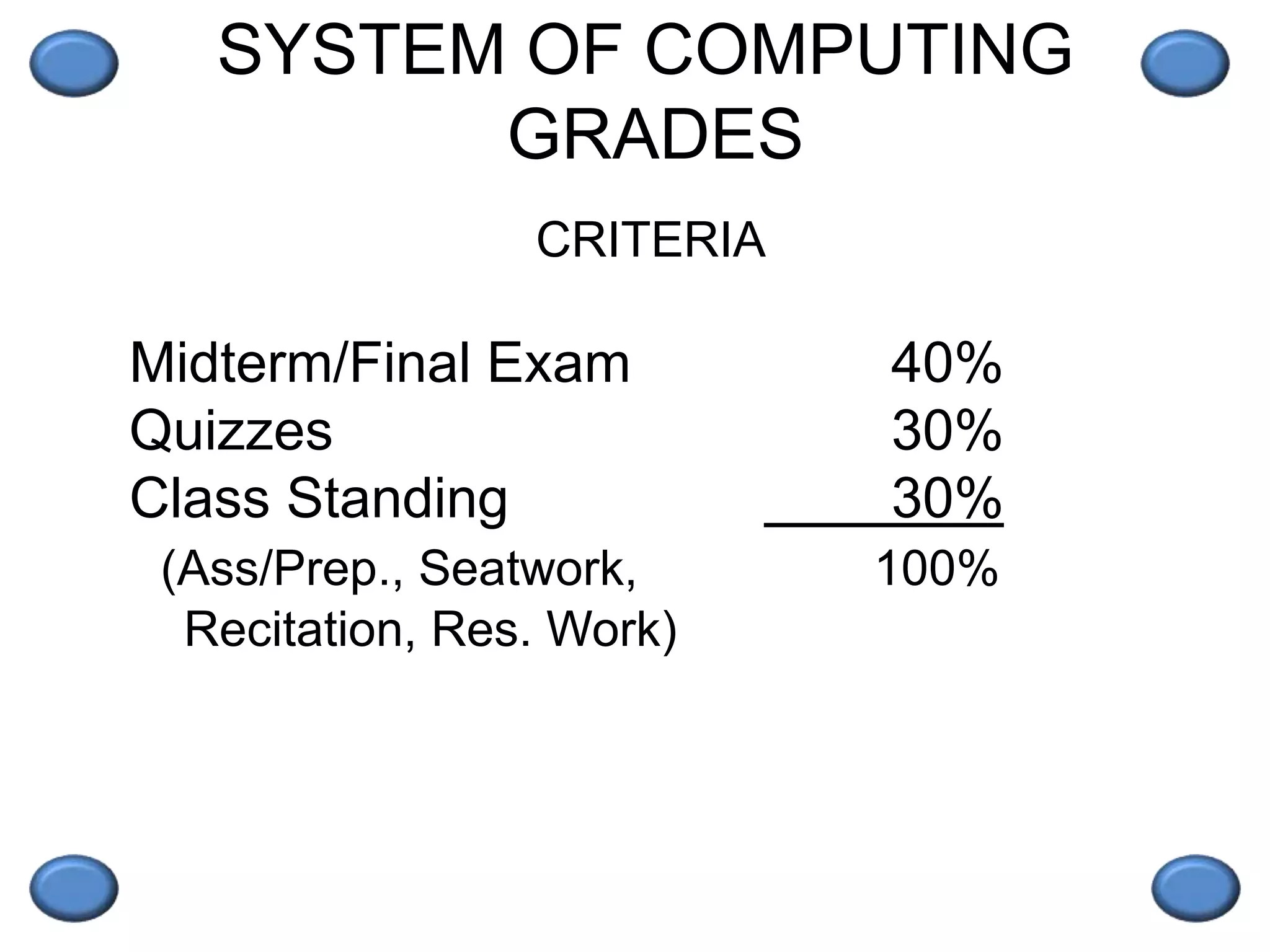
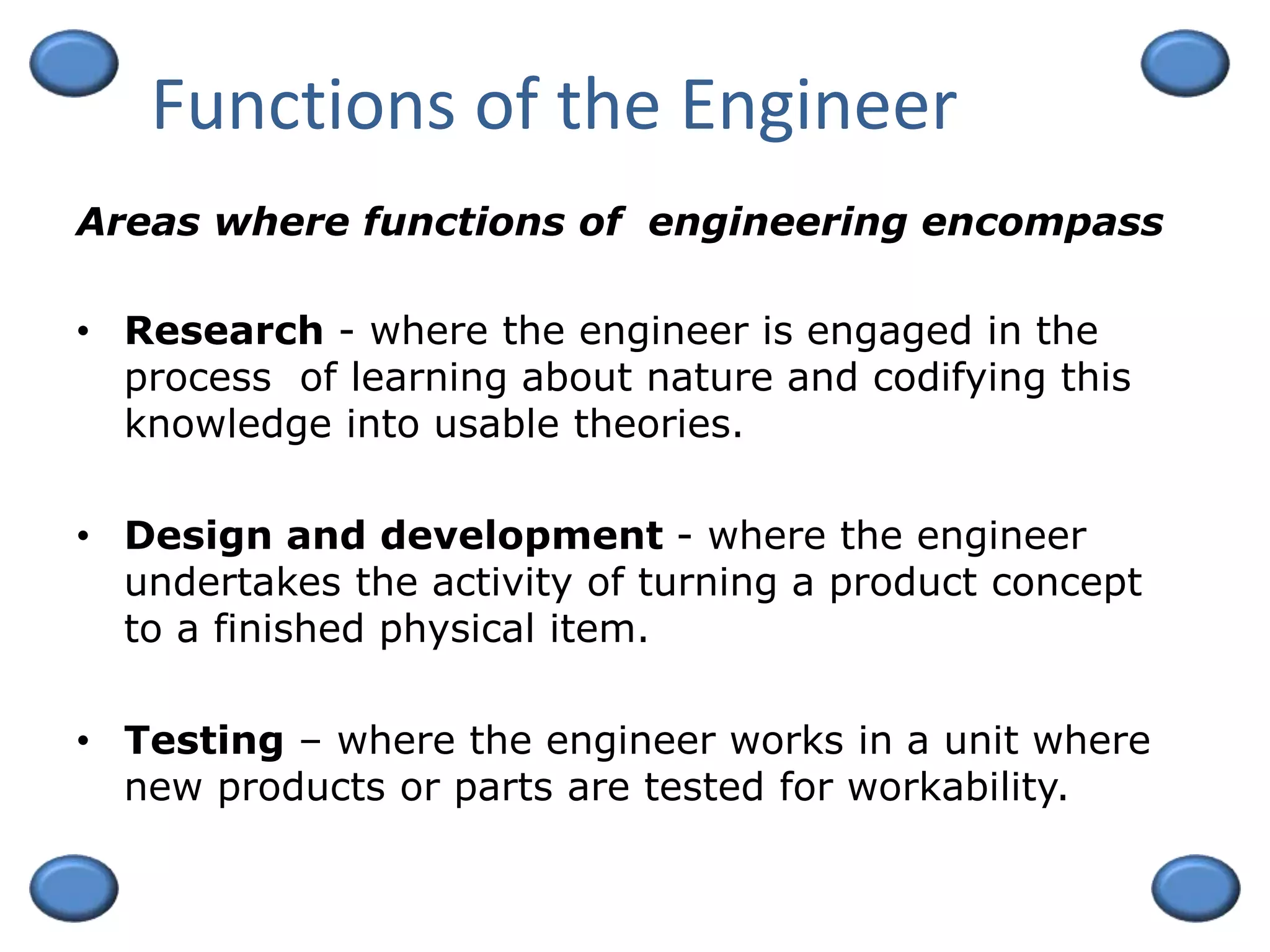
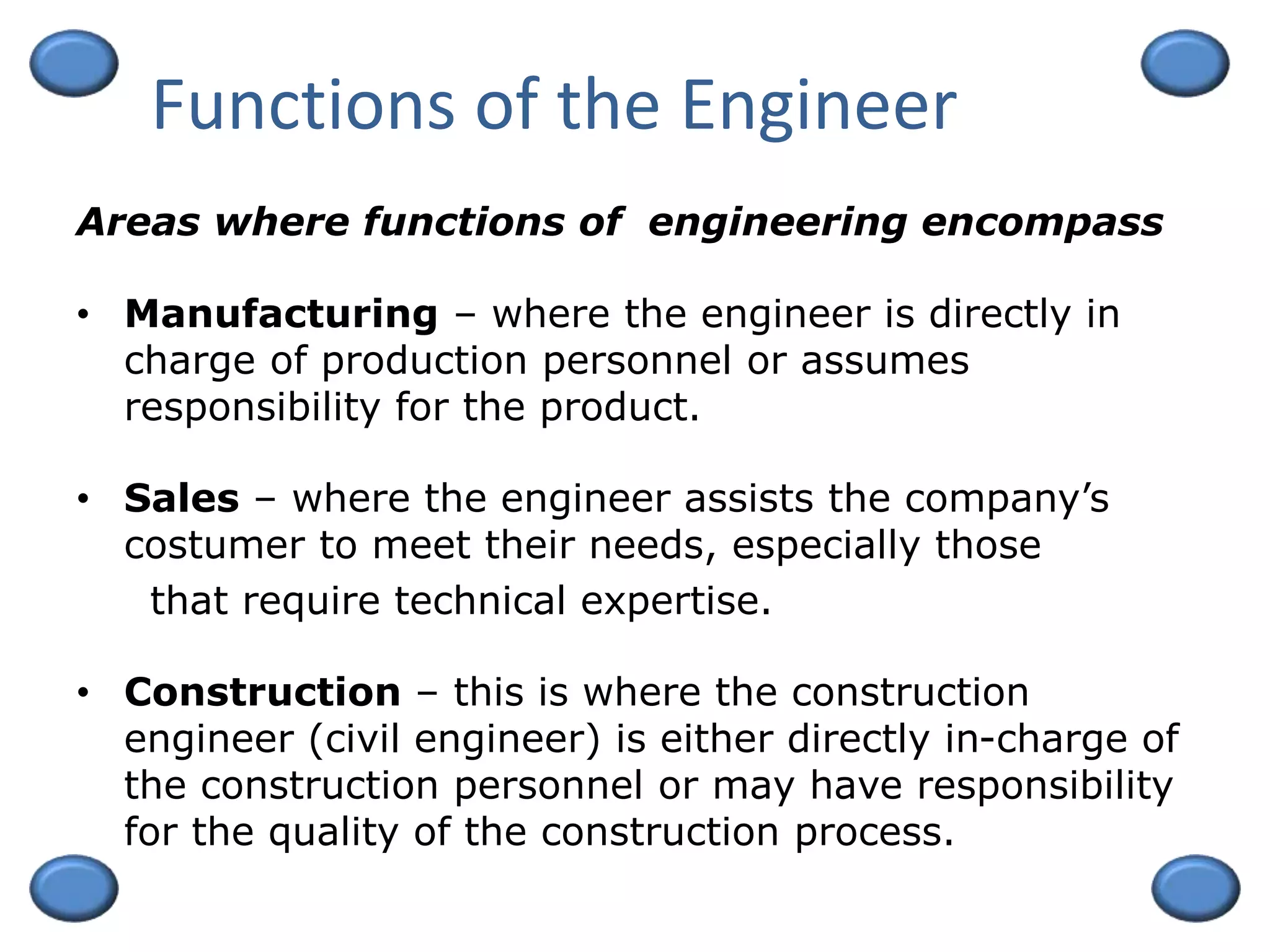
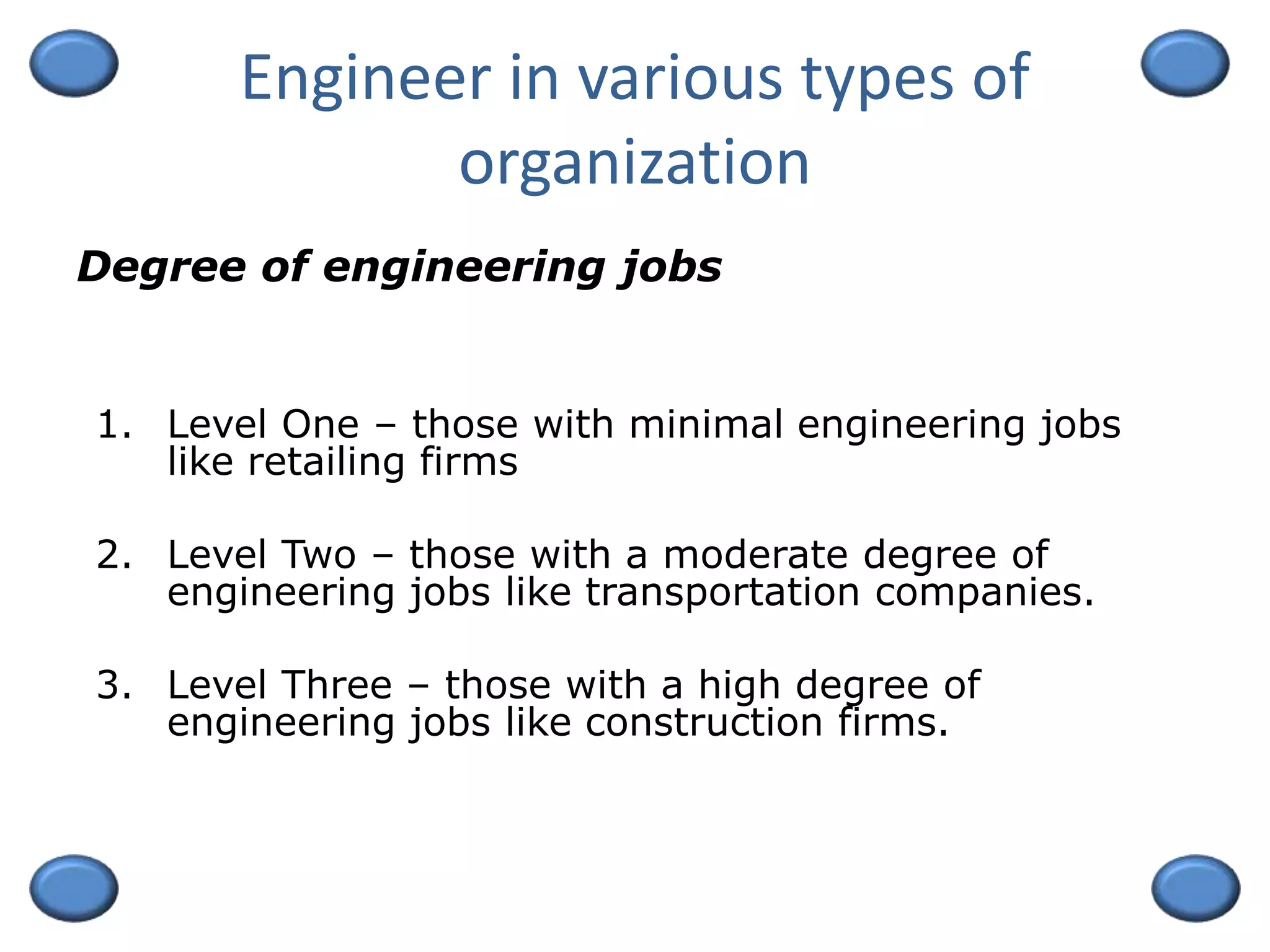
This document outlines an engineering management course. It discusses key topics like decision making, the functions of management including planning, organizing, staffing, and controlling. The course is 3 credit units and 54 hours in duration. Students must pass exams, submit assignments, and actively participate. Grades are based on exams, quizzes, and class participation. The document also provides an overview of engineering management as a field, discussing the skills and background needed for engineer managers including a degree in engineering and work experience. Successful engineer managers need ability, motivation to manage, and opportunities to take on managerial roles.