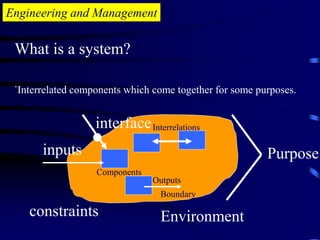
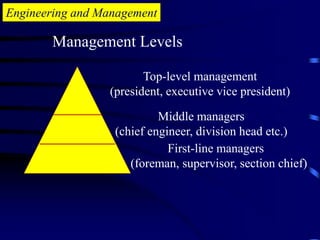
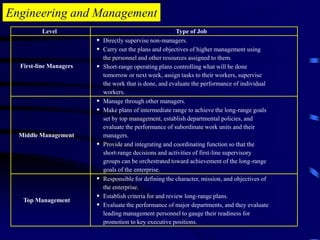
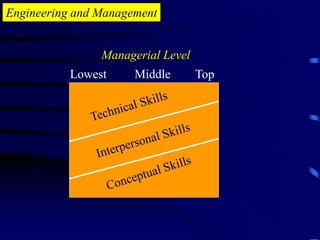
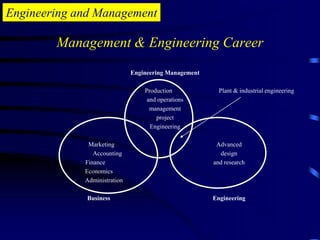
The document provides an introduction to engineering management. It defines engineering as applying scientific knowledge for the benefit of mankind, and management as directing group actions efficiently to achieve goals. The document outlines management levels from first-line to top management and necessary managerial skills. It also describes common managerial roles like interpersonal, informational, and decisional roles. Finally, it positions engineering management as requiring both engineering and management abilities to organize people and projects effectively.