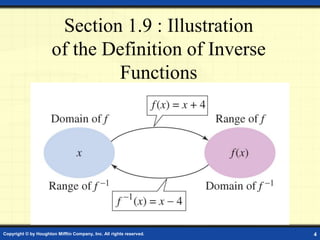
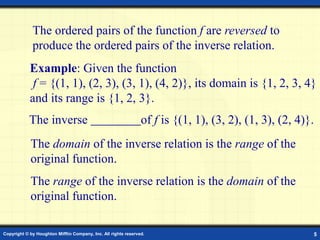
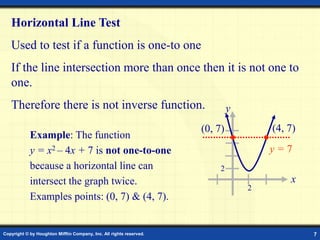
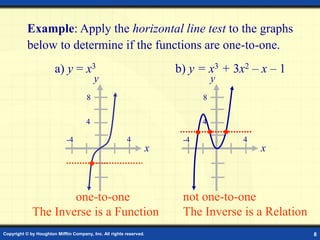
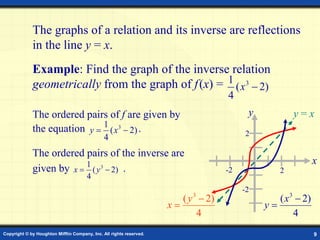
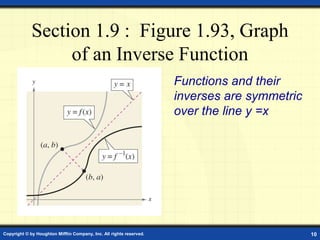
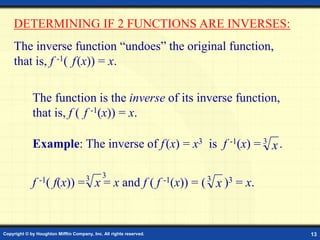
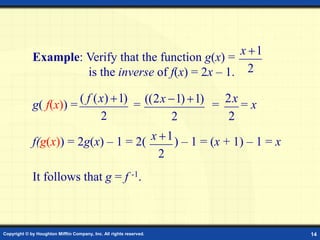
This document discusses one-to-one functions and inverse functions. It provides examples of functions and their inverses, and methods for finding the inverse of a function both graphically and algebraically. A key point is that a function must be one-to-one to have an inverse function, while non one-to-one relations only have an inverse relation. The inverse of a function "undoes" the original function. Functions and their inverses are reflections over the line y = x.