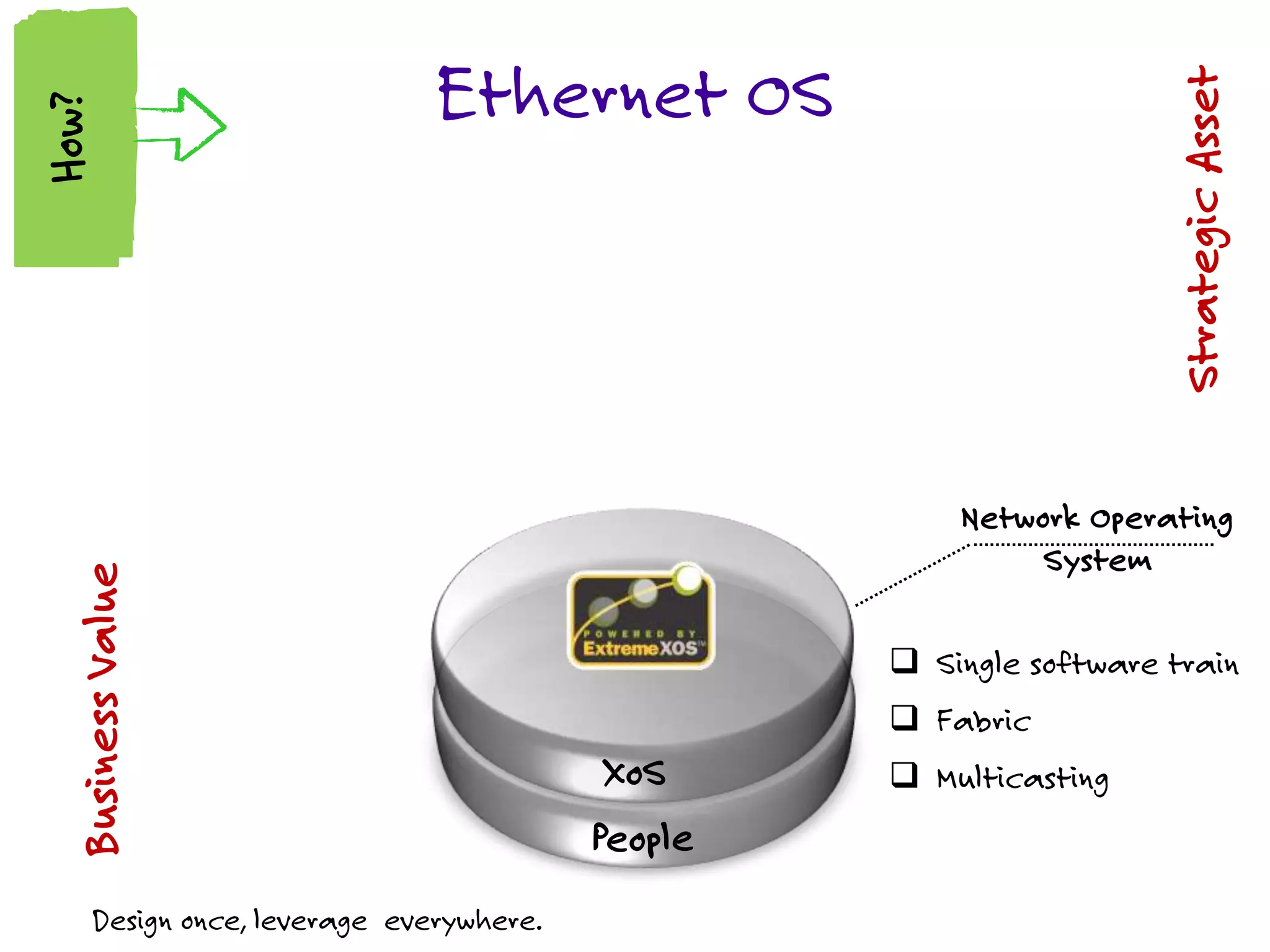
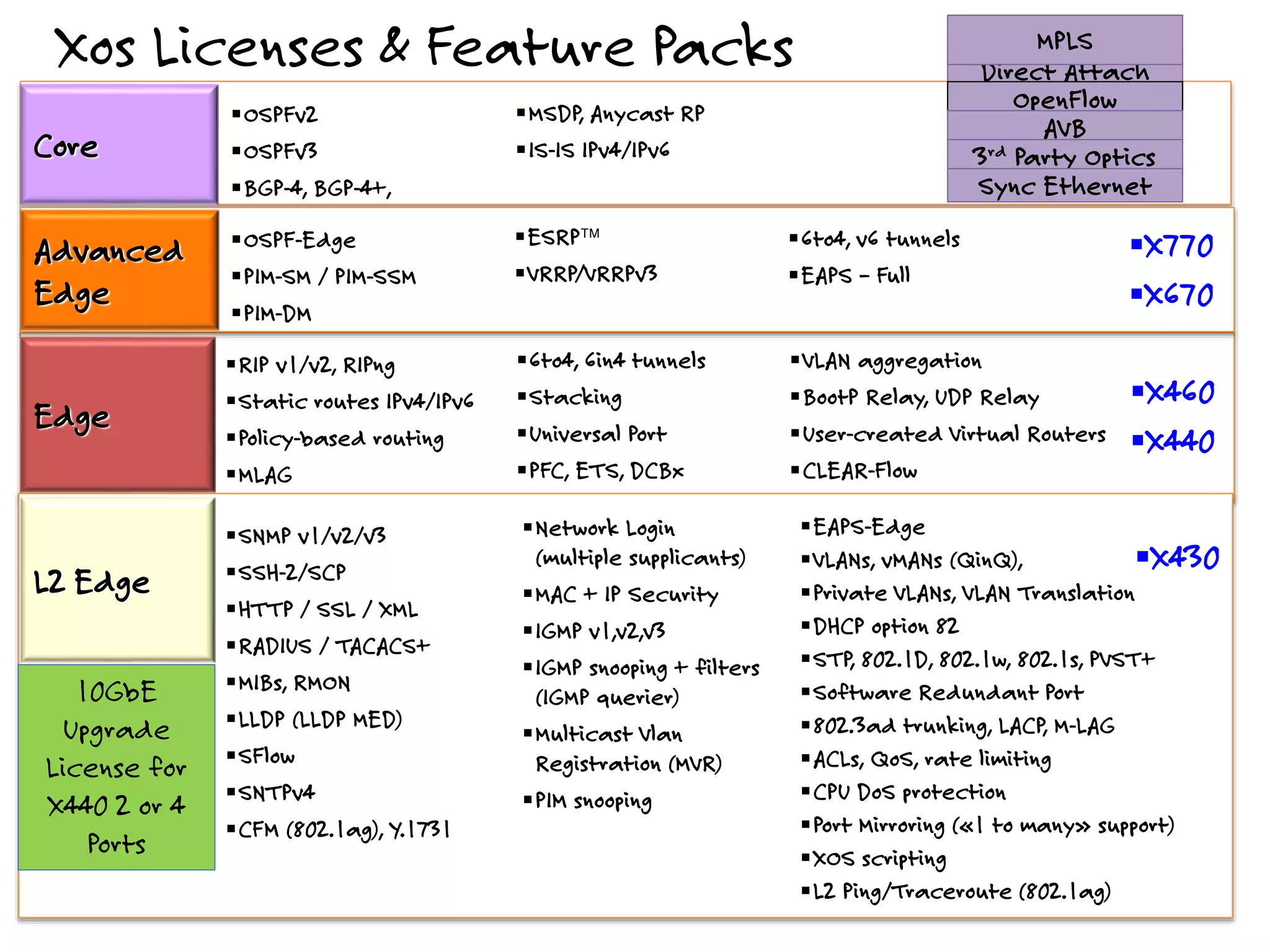
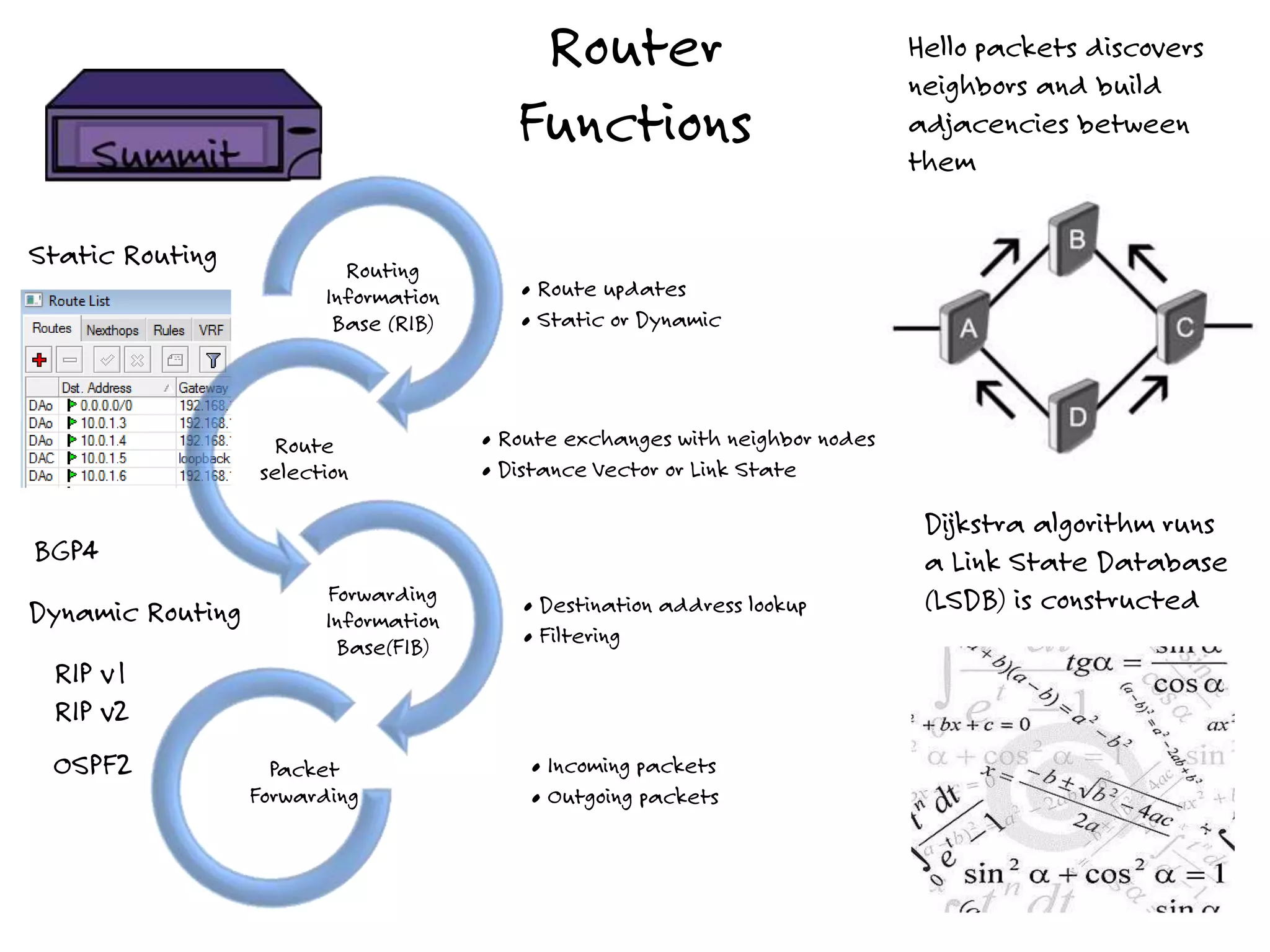
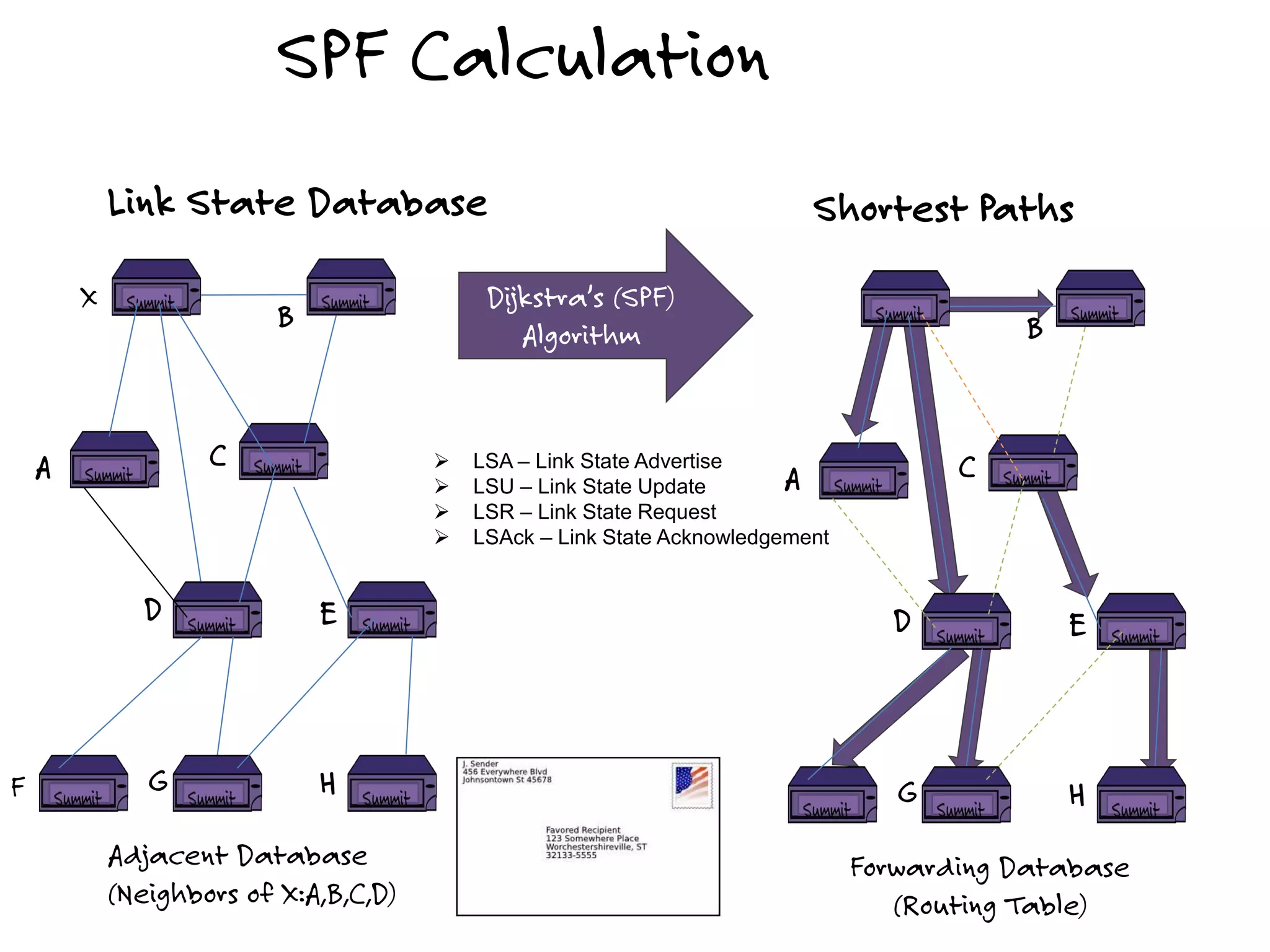
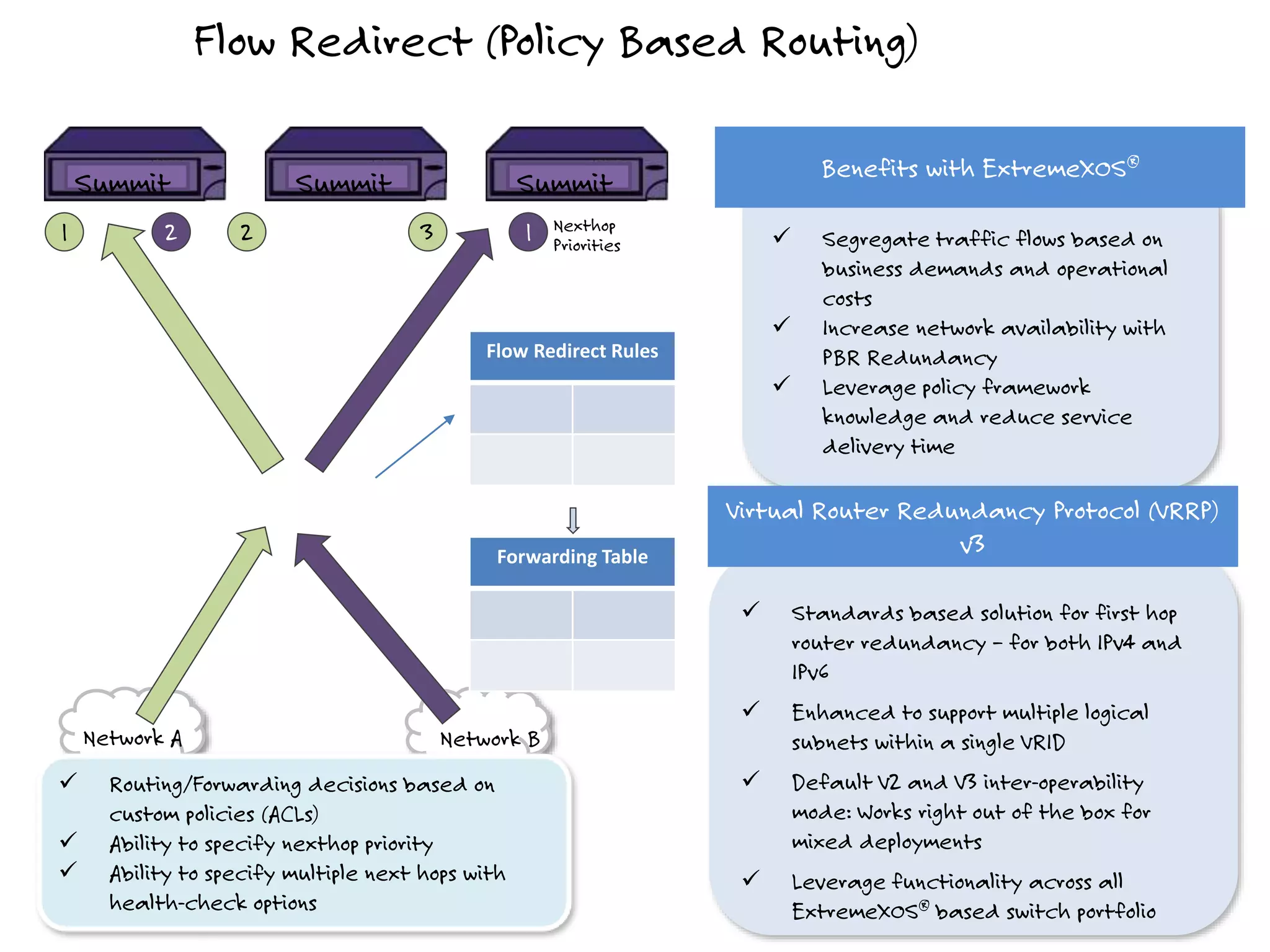
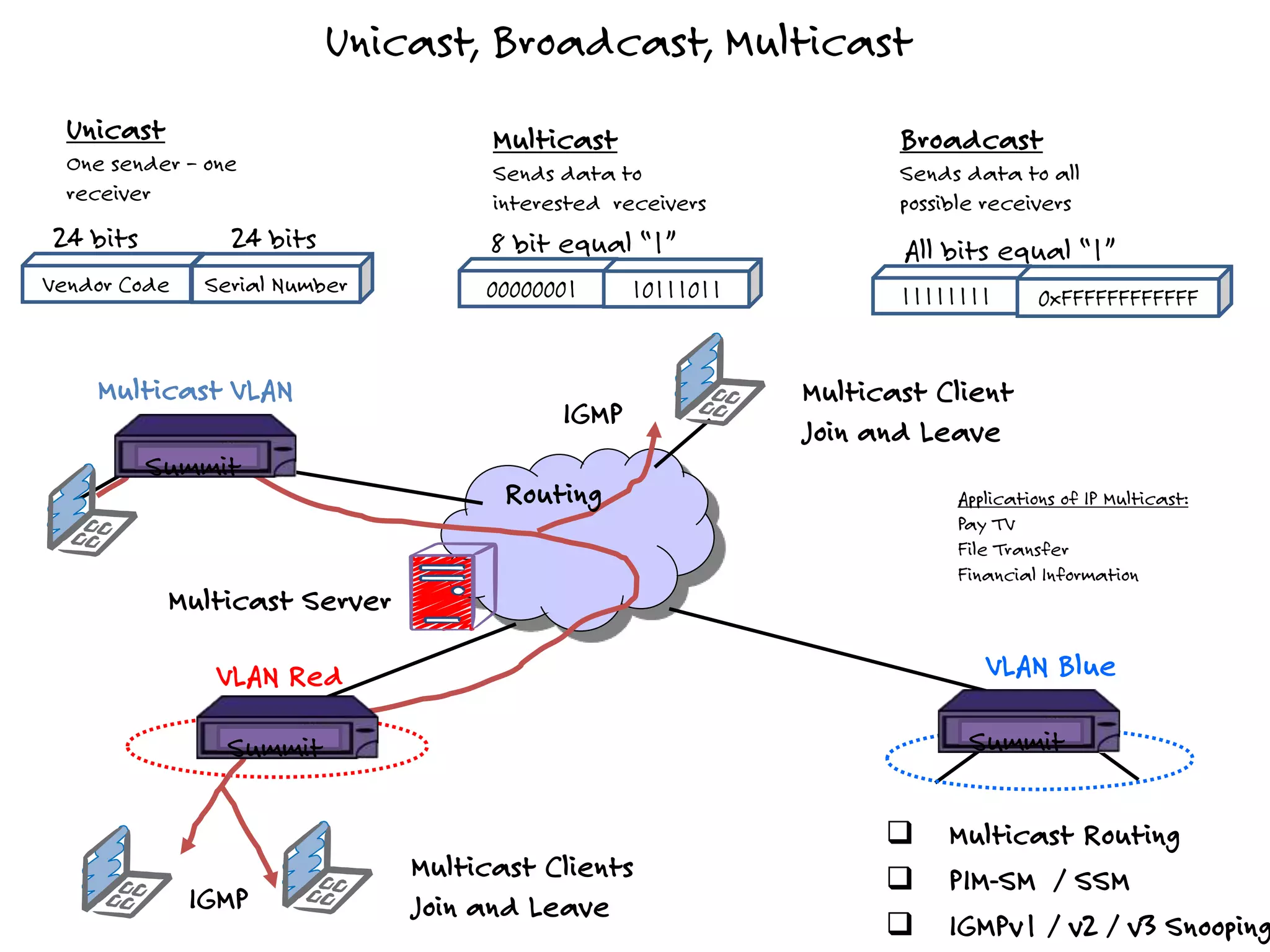
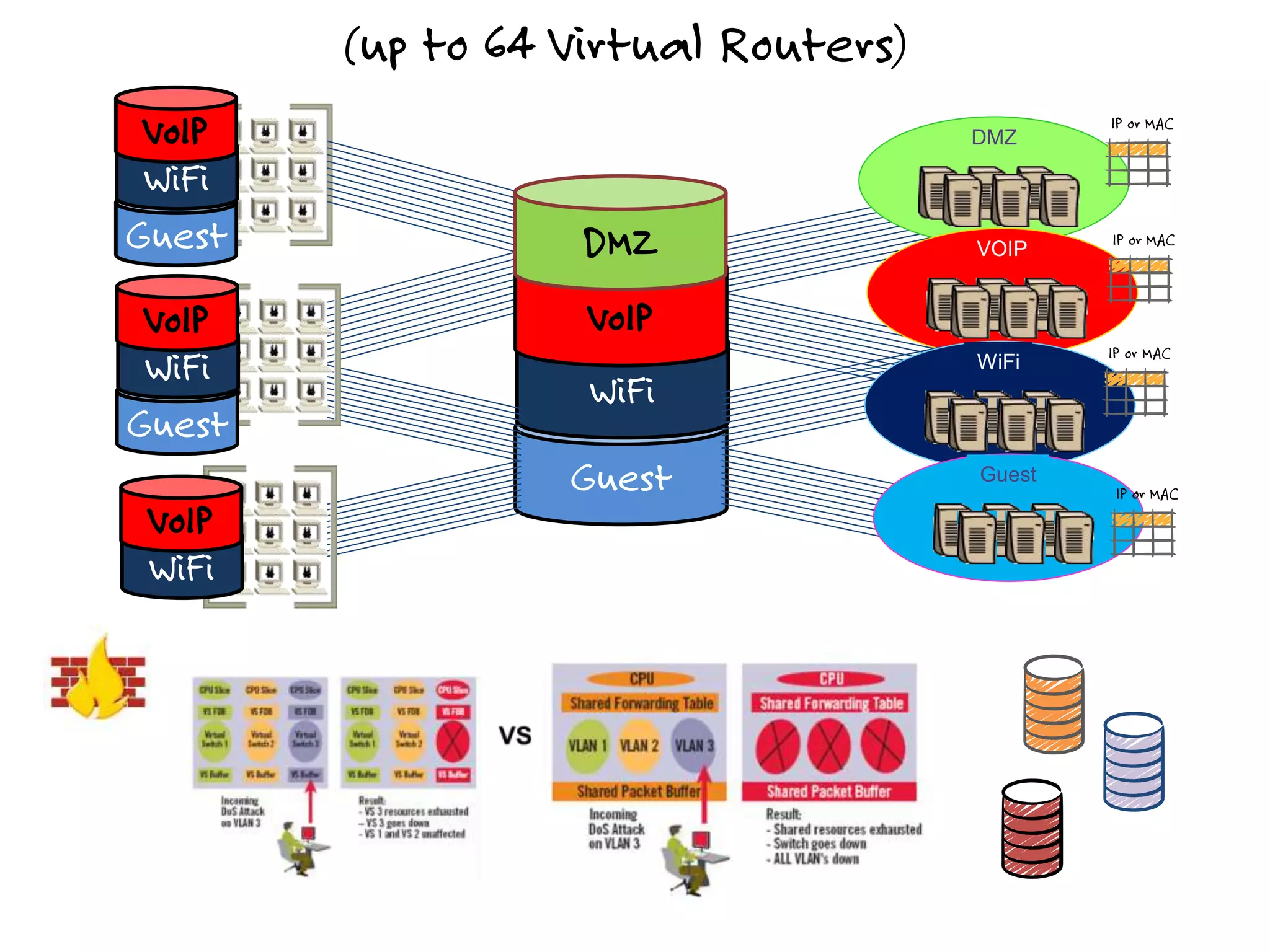
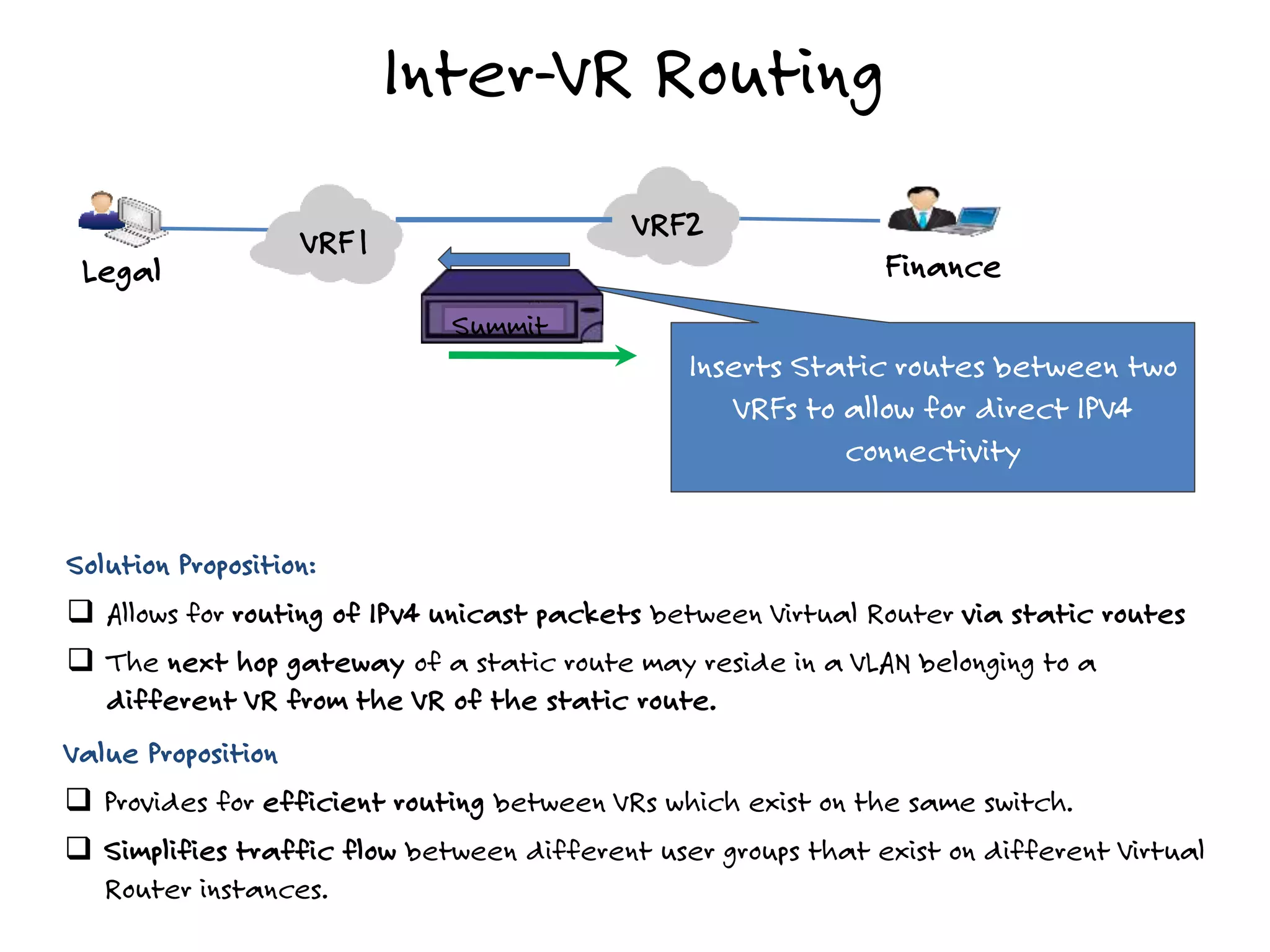
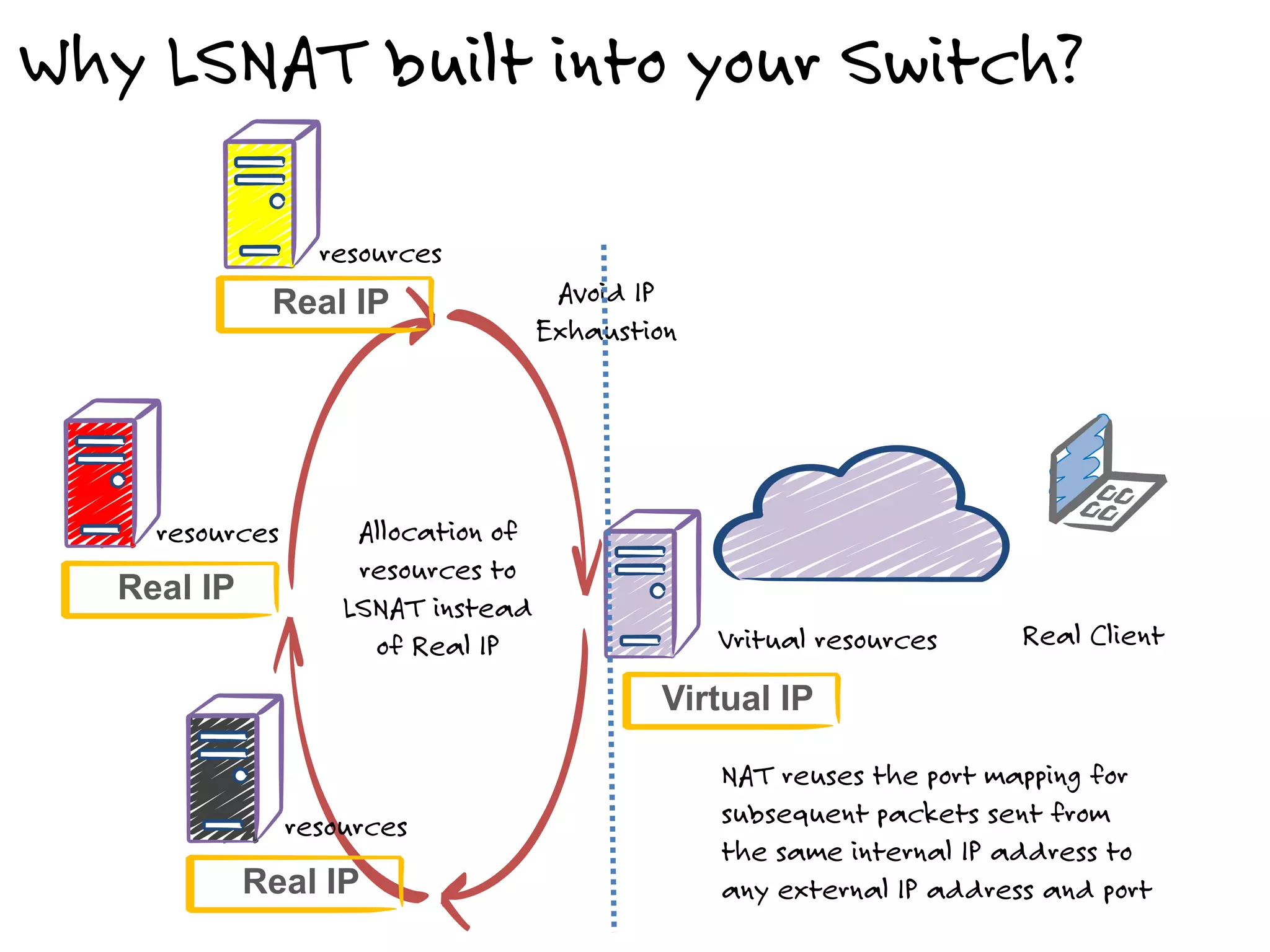
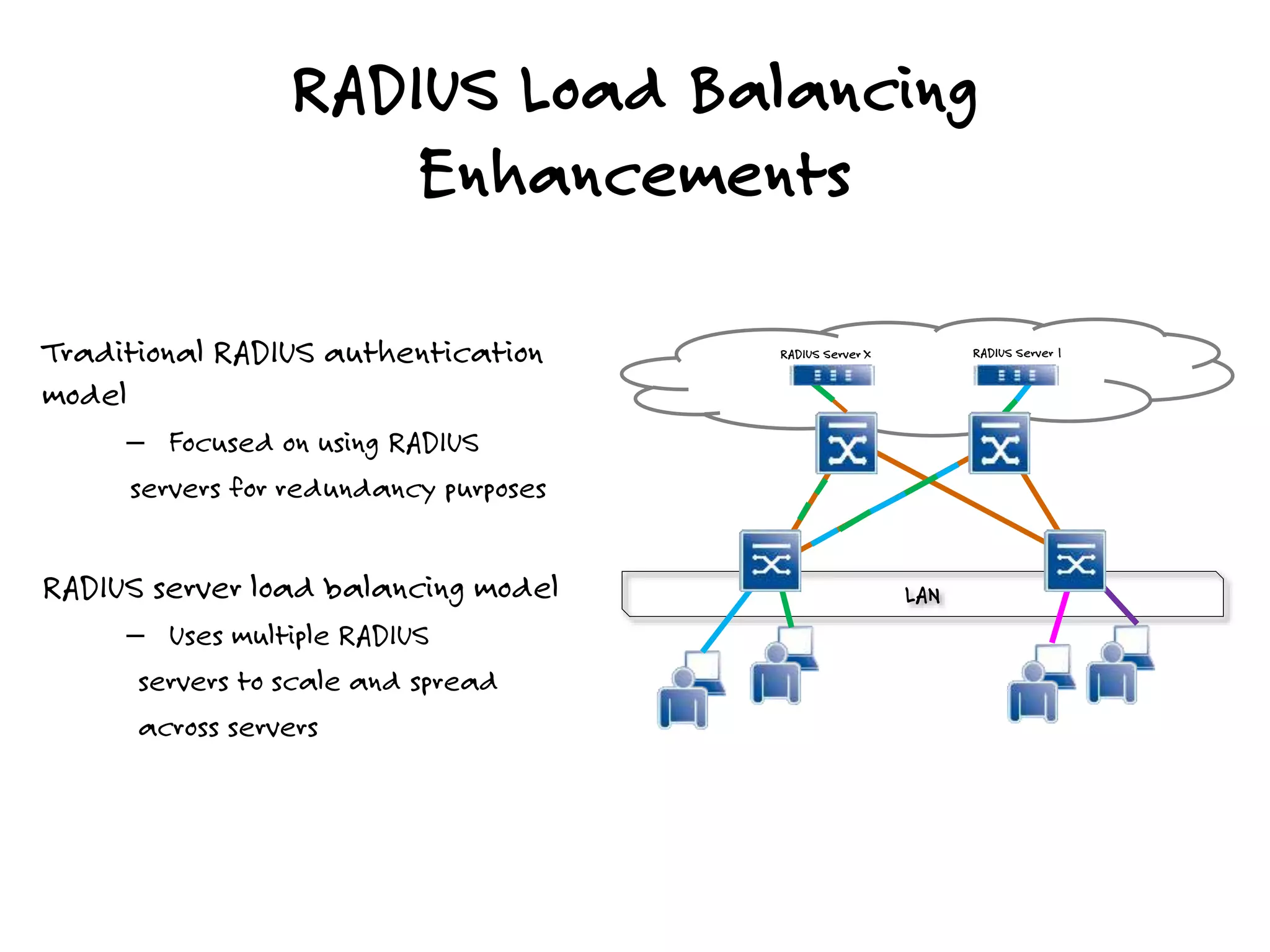
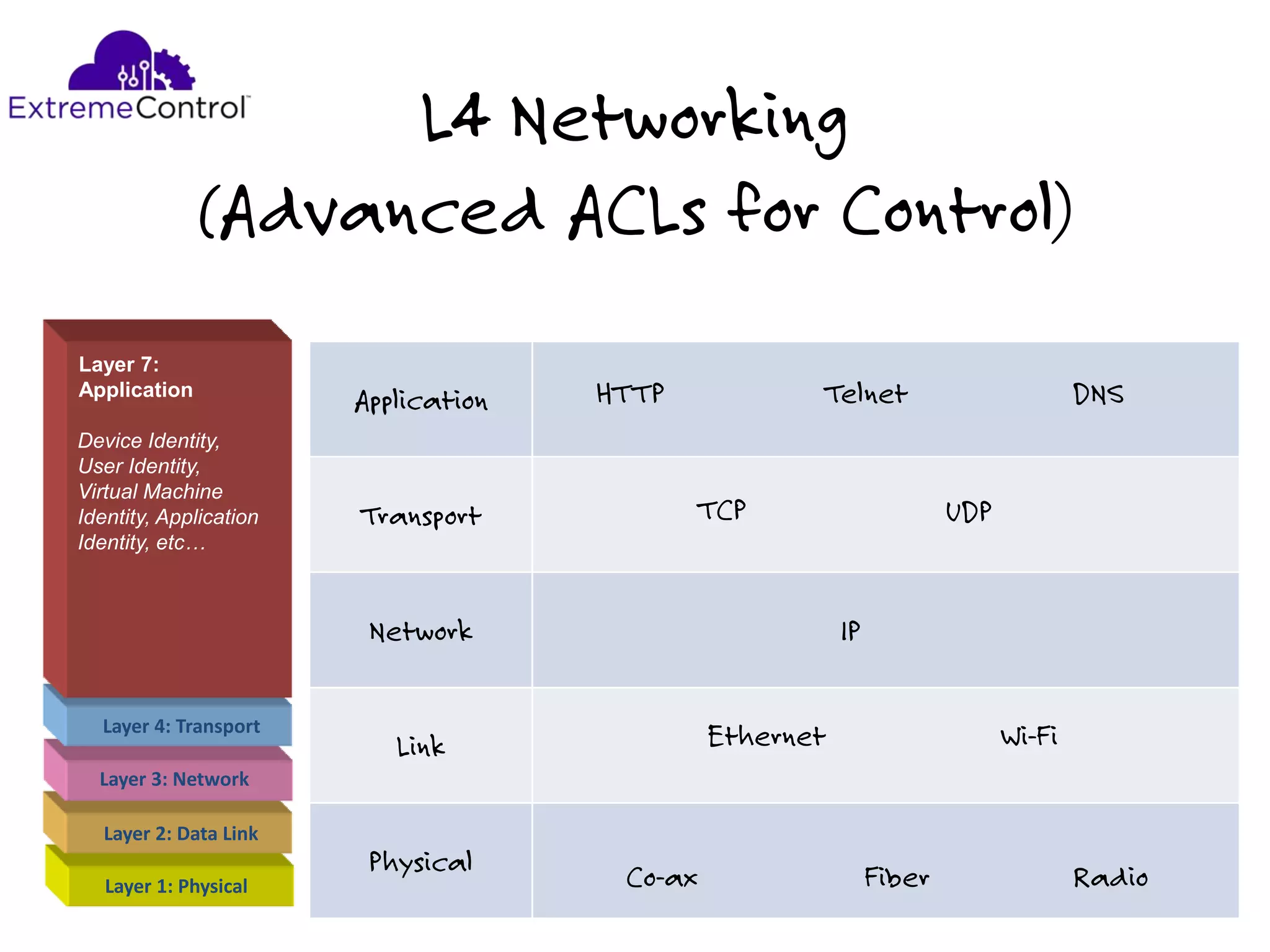
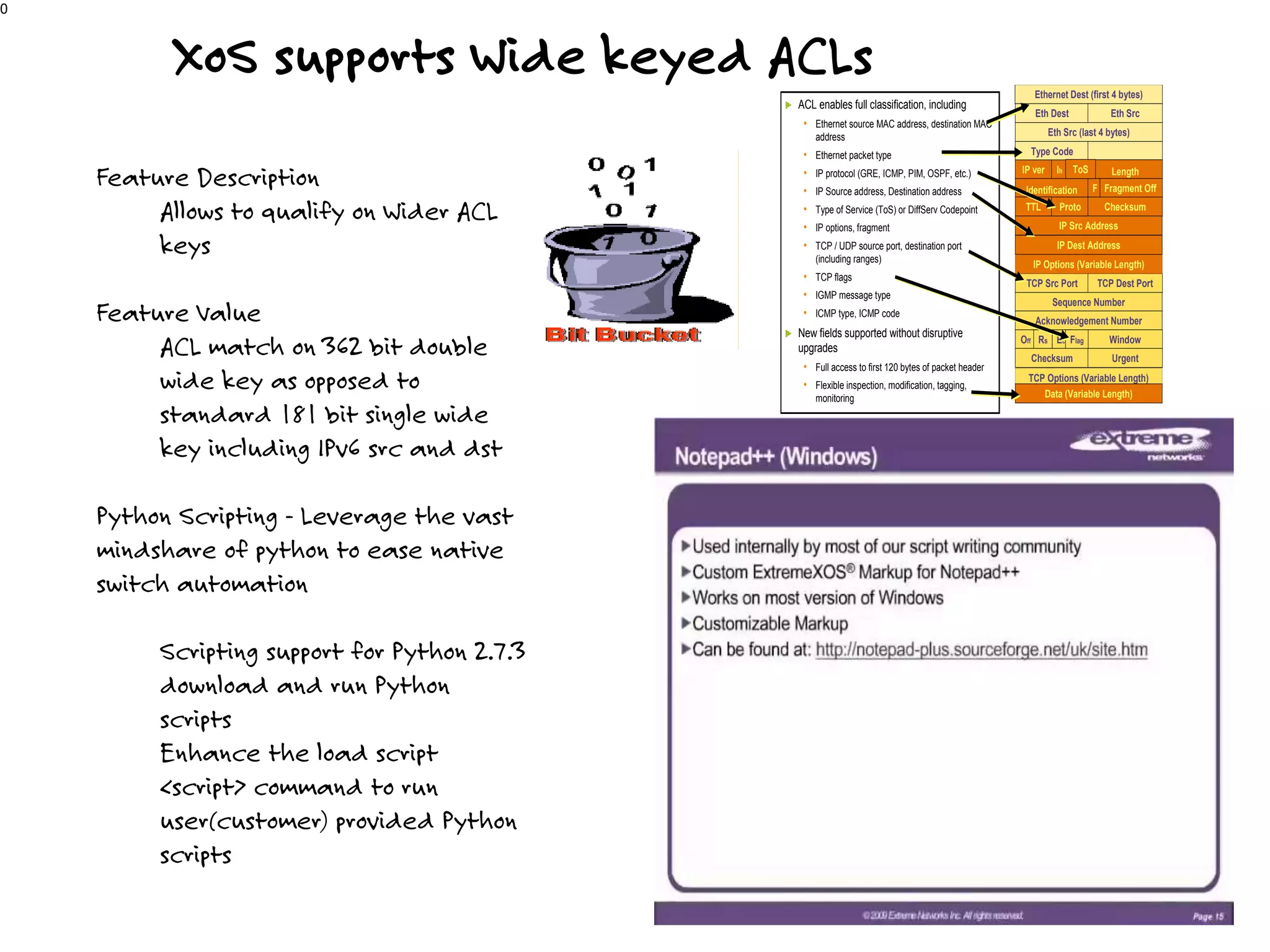
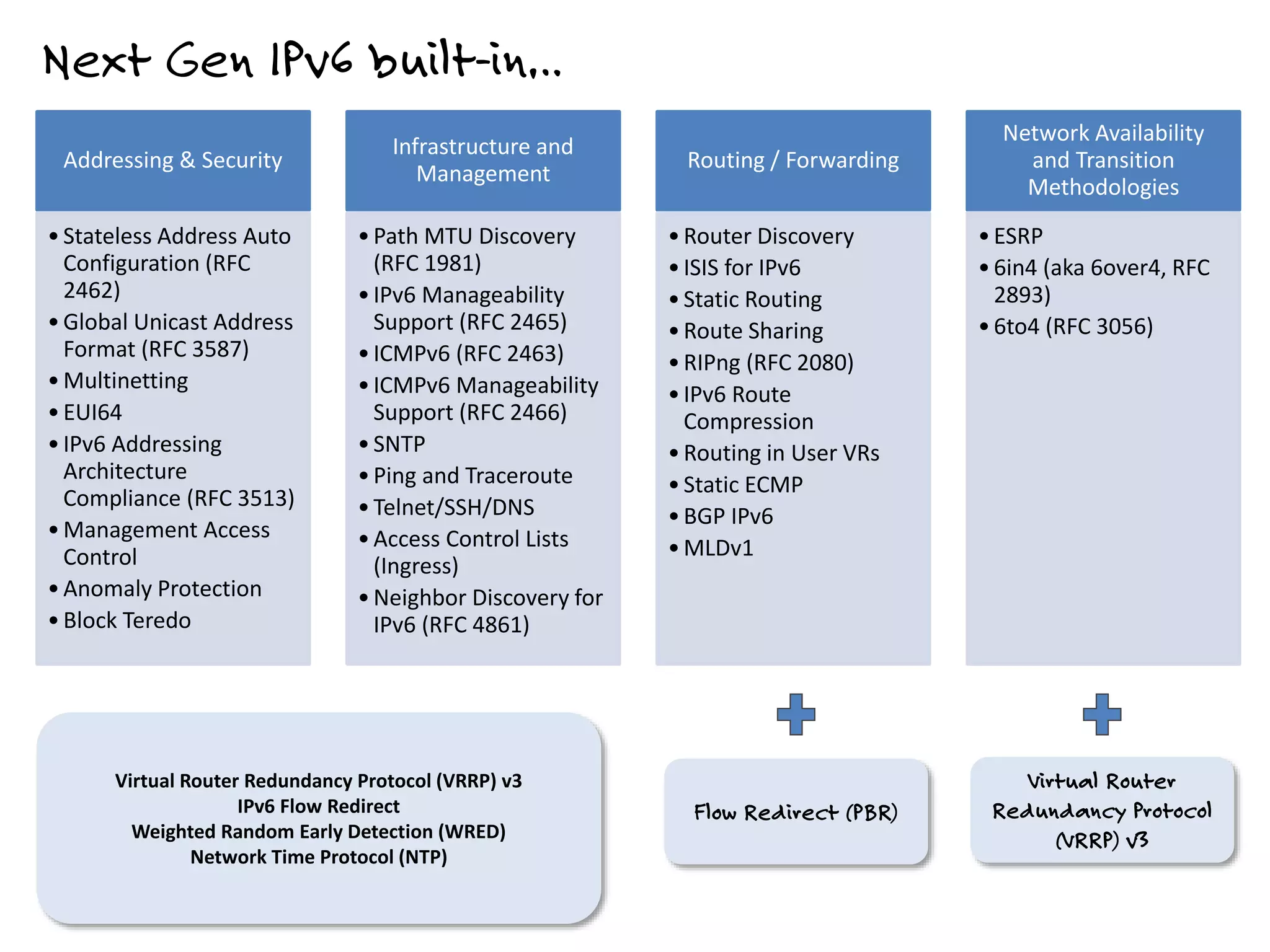
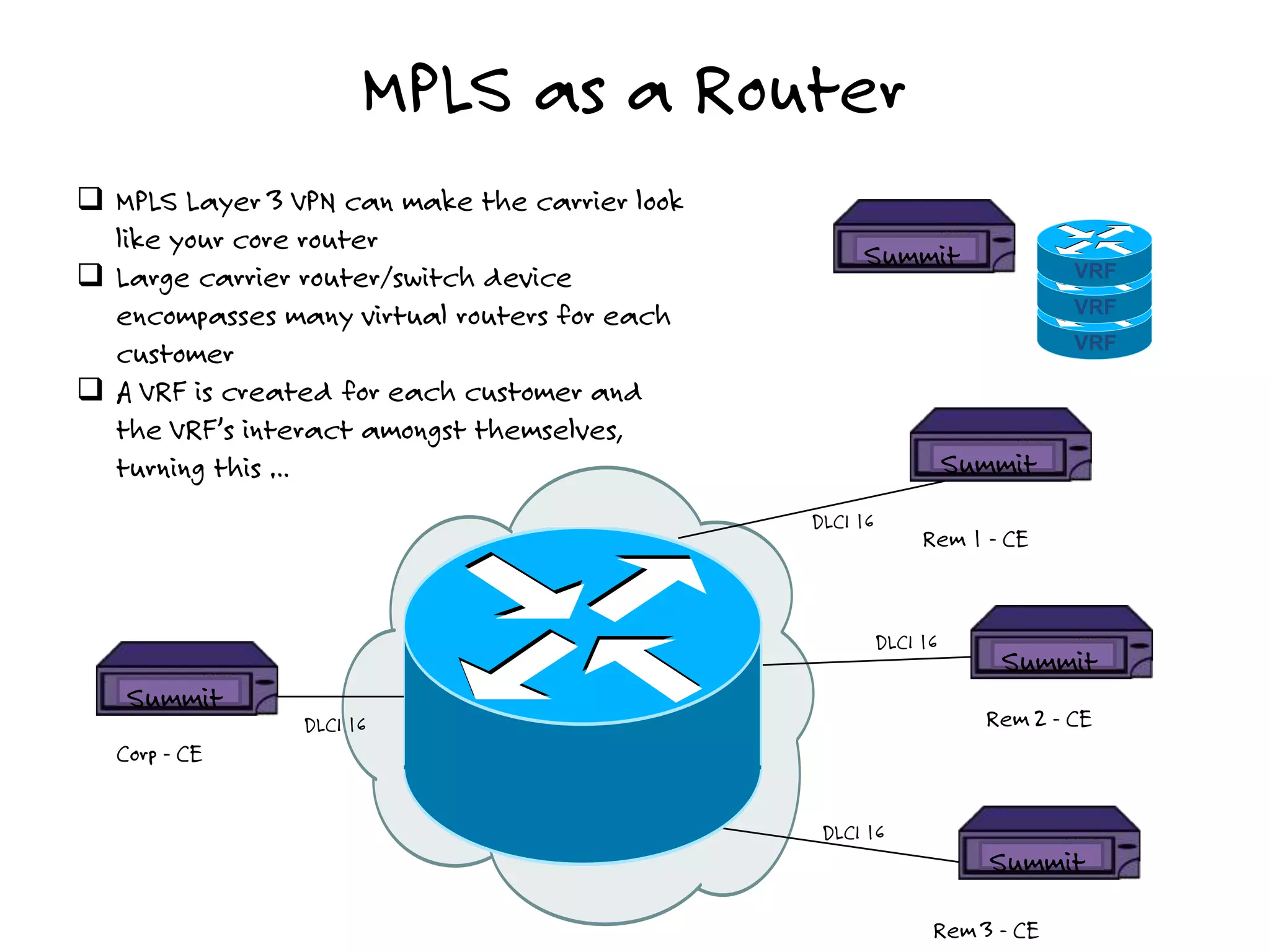
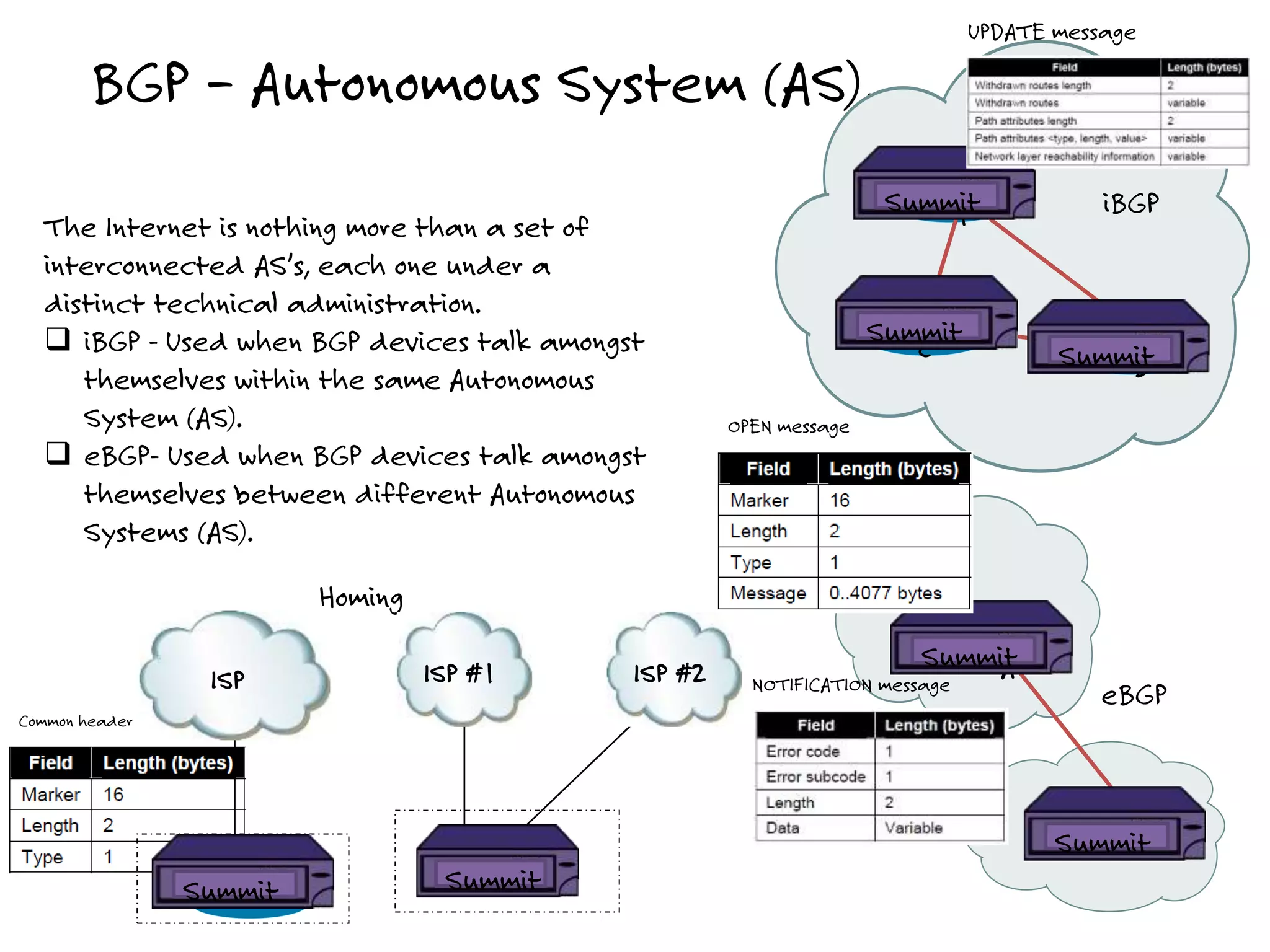
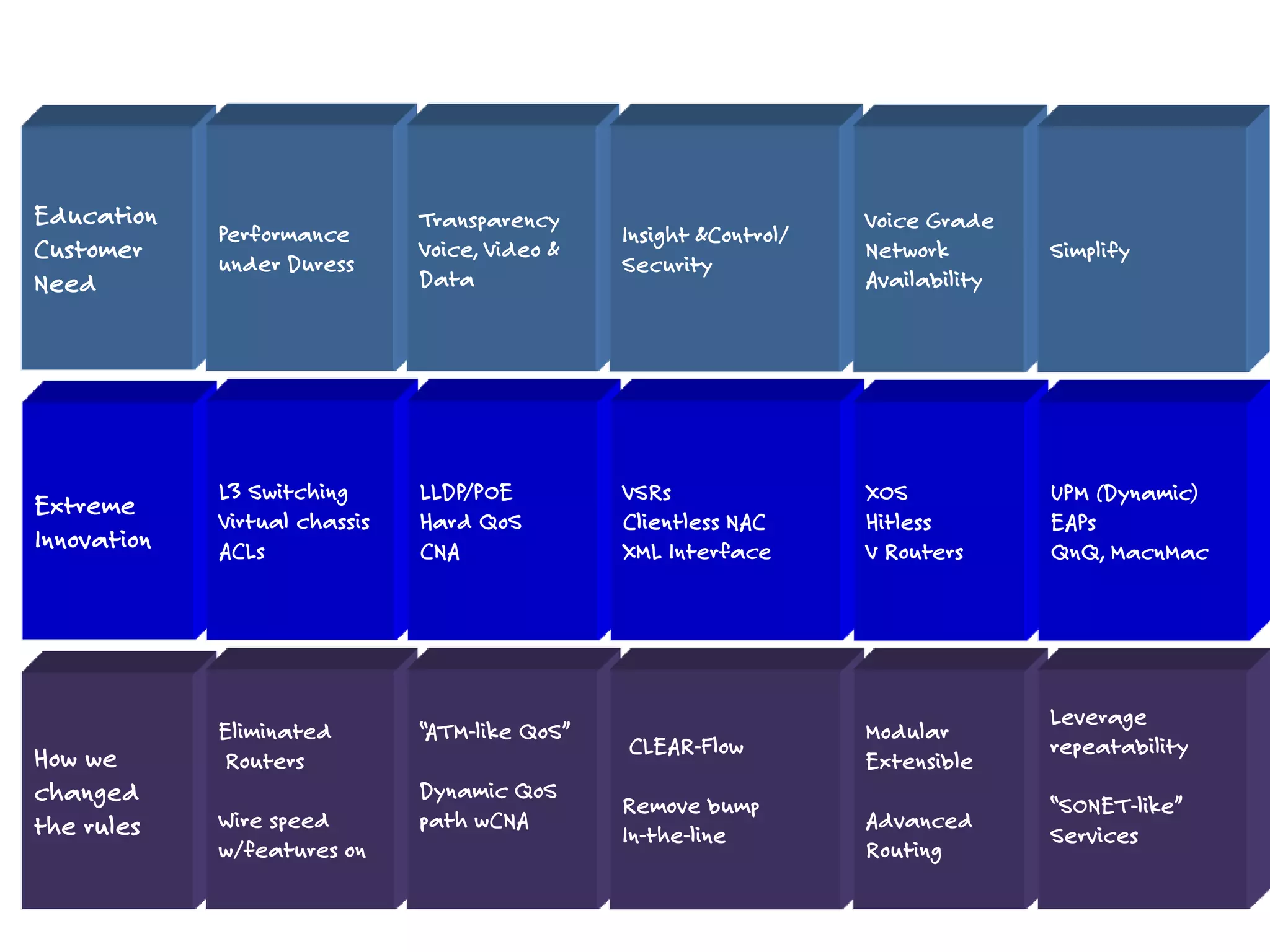
The document discusses the features and capabilities of the xos network operating system, highlighting its router-like functionalities and various licenses, protocols, and advanced networking features. It emphasizes aspects such as policy-based routing, multicast capabilities, virtual router redundancy, and security enhancements. Additionally, it outlines the advantages of using xos for efficient routing, managing virtual routers, and supporting scalability in networks.