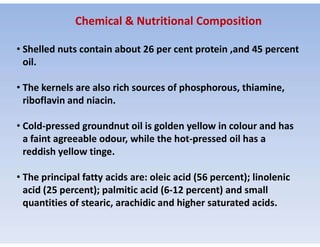
Groundnuts are the second largest source of vegetable oils after soybeans. They are native to Brazil but have spread throughout tropical and subtropical regions. The fruit of the groundnut plant develops underground as a pod containing 1-5 seeds that are rich in protein and oil. India is the largest producer of groundnut oil, which is extracted from the seeds using expellers or hydraulic presses. The oil is used for cooking, margarine, hydrogenated vanaspati ghee, and packing sardines before export. Lower grades are used for soap, lubricants, and rubber substitutes while the residual cake is used as cattle feed and manure.