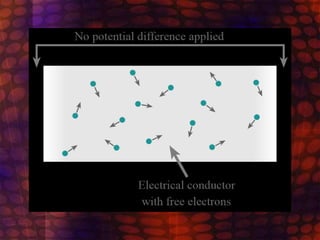
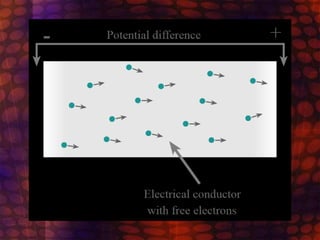
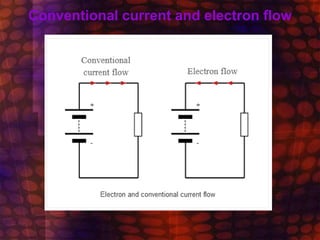
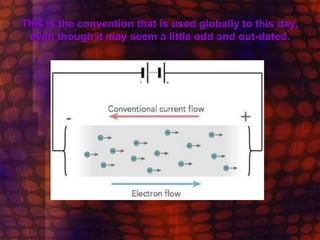
Electricity flows through a circuit as an electric current, which is the movement of tiny particles called electrons. The electrons flow in a loop from the battery around the circuit and back to the battery, pushed along by the electromotive force or voltage from the battery. While electrons actually flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal, the conventional current is defined as flowing in the opposite direction, from positive to negative, for simplicity.