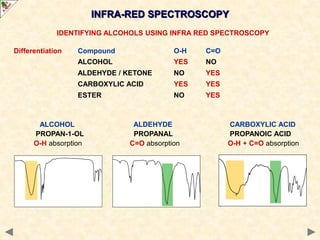
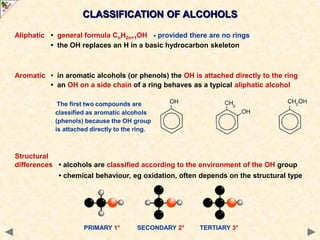
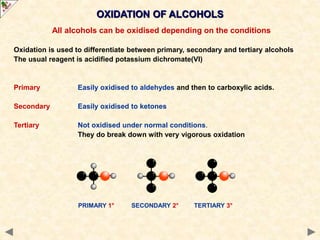
This document provides an introduction to the chemistry of alcohols. It begins with classifying alcohols as either aliphatic or aromatic based on whether the OH group is attached to the carbon chain or ring. Primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols are distinguished based on the number of carbon groups attached to the carbon with the OH group. Key chemical properties discussed include hydrogen bonding leading to higher boiling points than alkanes, elimination reactions producing alkenes, and oxidation reactions that convert primary alcohols to aldehydes and aldehydes to carboxylic acids or convert secondary alcohols to ketones. Tertiary alcohols are resistant to oxidation due to lacking






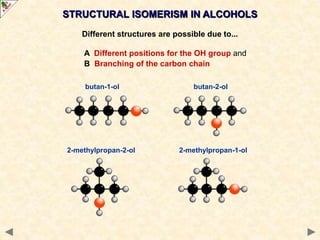




![OXIDATION OF PRIMARY ALCOHOLS
Primary alcohols are easily oxidised to aldehydes
e.g. CH3CH2OH(l) + [O] ——> CH3CHO(l) + H2O(l)
ethanol ethanal
it is essential to distil off the aldehyde before it gets oxidised to the acid
CH3CHO(l) + [O] ——> CH3COOH(l)
ethanal ethanoic acid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15alcpp1-231117133110-3ab63169/85/15alcpp-1-ppt-18-320.jpg)
![OXIDATION OF PRIMARY ALCOHOLS
Primary alcohols are easily oxidised to aldehydes
e.g. CH3CH2OH(l) + [O] ——> CH3CHO(l) + H2O(l)
ethanol ethanal
it is essential to distil off the aldehyde before it gets oxidised to the acid
CH3CHO(l) + [O] ——> CH3COOH(l)
ethanal ethanoic acid
Practical details
• the alcohol is dripped into a warm solution of acidified K2Cr2O7
• aldehydes have low boiling points - no hydrogen bonding - they distil off immediately
• if it didn’t distil off it would be oxidised to the equivalent carboxylic acid
• to oxidise an alcohol straight to the acid, reflux the mixture
compound formula intermolecular bonding boiling point
ETHANOL C2H5OH HYDROGEN BONDING 78°C
ETHANAL CH3CHO DIPOLE-DIPOLE 23°C
ETHANOIC ACID CH3COOH HYDROGEN BONDING 118°C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15alcpp1-231117133110-3ab63169/85/15alcpp-1-ppt-19-320.jpg)
![OXIDATION OF PRIMARY ALCOHOLS
Controlling the products
e.g. CH3CH2OH(l) + [O] ——> CH3CHO(l) + H2O(l)
then CH3CHO(l) + [O] ——> CH3COOH(l)
Aldehyde has a lower boiling point so
distils off before being oxidised further
OXIDATION TO ALDEHYDES
DISTILLATION
OXIDATION TO CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
REFLUX
Aldehyde condenses back into the
mixture and gets oxidised to the acid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15alcpp1-231117133110-3ab63169/85/15alcpp-1-ppt-20-320.jpg)
![OXIDATION OF SECONDARY ALCOHOLS
Secondary alcohols are easily oxidised to ketones
e.g. CH3CHOHCH3(l) + [O] ——> CH3COCH3(l) + H2O(l)
propan-2-ol propanone
The alcohol is refluxed with acidified K2Cr2O7. However, on prolonged treatment
with a powerful oxidising agent they can be further oxidised to a mixture of acids
with fewer carbon atoms than the original alcohol.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15alcpp1-231117133110-3ab63169/85/15alcpp-1-ppt-21-320.jpg)
![OXIDATION OF SECONDARY ALCOHOLS
Secondary alcohols are easily oxidised to ketones
e.g. CH3CHOHCH3(l) + [O] ——> CH3COCH3(l) + H2O(l)
propan-2-ol propanone
The alcohol is refluxed with acidified K2Cr2O7. However, on prolonged treatment
with a powerful oxidising agent they can be further oxidised to a mixture of acids
with fewer carbon atoms than the original alcohol.
OXIDATION OF TERTIARY ALCOHOLS
Tertiary alcohols are resistant to normal oxidation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15alcpp1-231117133110-3ab63169/85/15alcpp-1-ppt-22-320.jpg)

![OXIDATION OF ALCOHOLS
Why 1° and 2° alcohols are easily oxidised and 3° alcohols are not
For oxidation to take place easily you must have two hydrogen atoms on
adjacent C and O atoms.
H H
R C O + [O] R C O + H2O
H H
1°](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15alcpp1-231117133110-3ab63169/85/15alcpp-1-ppt-24-320.jpg)
![OXIDATION OF ALCOHOLS
Why 1° and 2° alcohols are easily oxidised and 3° alcohols are not
For oxidation to take place easily you must have two hydrogen atoms on
adjacent C and O atoms.
H H
R C O + [O] R C O + H2O
H H
H H
R C O + [O] R C O + H2O
R R
1°
2°](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15alcpp1-231117133110-3ab63169/85/15alcpp-1-ppt-25-320.jpg)
![OXIDATION OF ALCOHOLS
Why 1° and 2° alcohols are easily oxidised and 3° alcohols are not
For oxidation to take place easily you must have two hydrogen atoms on
adjacent C and O atoms.
H H
R C O + [O] R C O + H2O
H H
H H
R C O + [O] R C O + H2O
R R
This is possible in 1° and 2° alcohols but not in 3° alcohols.
1°
2°](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15alcpp1-231117133110-3ab63169/85/15alcpp-1-ppt-26-320.jpg)
![OXIDATION OF ALCOHOLS
Why 1° and 2° alcohols are easily oxidised and 3° alcohols are not
For oxidation to take place easily you must have two hydrogen atoms on
adjacent C and O atoms.
H H
R C O + [O] R C O + H2O
H H
H H
R C O + [O] R C O + H2O
R R
R H
R C O + [O]
R
This is possible in 1° and 2° alcohols but not in 3° alcohols.
1°
2°
3°](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15alcpp1-231117133110-3ab63169/85/15alcpp-1-ppt-27-320.jpg)