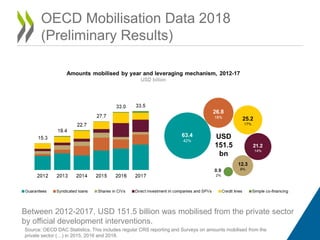
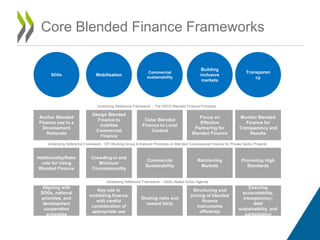
The document discusses blended finance, which is the strategic use of development finance to mobilize additional private finance for sustainable development projects. It provides the OECD's definition of blended finance and outlines its Blended Finance Principles. The OECD is working to enable development cooperation through facilitating transparency, evidence, and best practices related to mobilizing commercial finance using blended finance. It discusses building an evidence base around blended finance through data collection and reports. Key frameworks that guide the OECD's work on blended finance are also mentioned, including aligning investments with development priorities and the SDGs.