The document discusses the historical context and implications of the 14th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution, highlighting the polarizing issue of slavery from the nation’s independence through the Civil War. It details the amendment's provisions, including citizenship rights and equal protection under the law, and its role in addressing the status of freedmen after the Civil War. The document also notes the amendment's significance in overturning prior court decisions, such as Dred Scott v. Sandford, and its impact on civil rights jurisprudence.

![BRED SCOTT v. SANDFORD
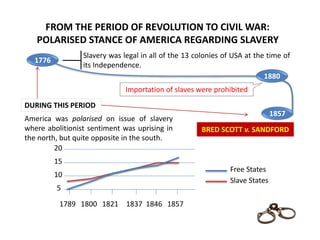
On the escalating tension regarding fate of slavery into America,
Judgment from US Supreme Court came out with the following:
“A negro, whose ancestors were imported into [the U.S.], and sold
as slaves", whether enslaved or free, could not be an American
citizen and therefore had no standing to sue in federal court, and
that the federal government had no power to regulate slavery in
the federal territories acquired after the creation of the United
States
“WORST JUDGMENT IN US SUPREME COURT HISTORY”
> Chief Justice Tany Began believed that the decision represented a
compromise that would settle the slavery question once and for all by
transforming a contested political issue into a matter of settled law.
“INDIRECT CATALYST OF AMERICAN CIVIL WAR”
INTENSIFICATION OF STRAIN THROUGH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14thamendment-160417235519/85/14th-Amendment-of-USA-Constitution-3-320.jpg)


![14th AMENDMENT
OTHER PROVISIONS
Apportionment of representation in House of Representatives [section 2]
Participants in rebellion [section 3]
Apportionment of representatives in the Houses on the basis of counting
total number of residents.
Reduction of a state's apportionment if it wrongfully denies any adult male's
right to vote.
Prohibition of the election or appointment to any federal or state office of
any person who had held any of certain offices and then engaged in
insurrection, rebellion or treason.
However, a two-thirds vote by each House of the Congress can override this
limitation. In 1898, Congress enacted a general removal of section 3’s
limitation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14thamendment-160417235519/85/14th-Amendment-of-USA-Constitution-7-320.jpg)
![14th AMENDMENT
OTHER PROVISIONS
Validity of Public Debt (section 4)
Power of Enforcement [section 5]
Confirmed the legitimacy of all public appropriated by the Congress.
Neither the United States nor any state would pay for the loss of slaves or
debts that had been incurred by the Confederacy
It enables Congress to pass laws enforcing the amendment's other
provisions
CONTINUED….](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14thamendment-160417235519/85/14th-Amendment-of-USA-Constitution-8-320.jpg)


