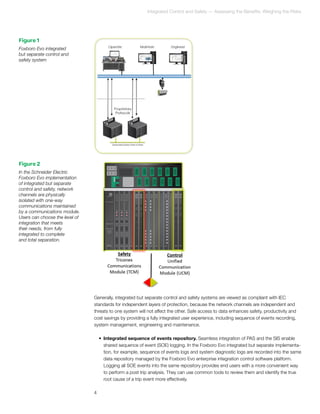
The document discusses the integration of control and safety systems in industrial environments, presenting three models of integration: interfaced, integrated but separate, and common. It analyzes the benefits and risks associated with each approach concerning safety standards, cost efficiencies, and operational effectiveness. The authors conclude that an integrated but separate architecture is increasingly preferred as it balances safety and cost, while the choice of integration depends on individual companies' business strategies and risk tolerance.