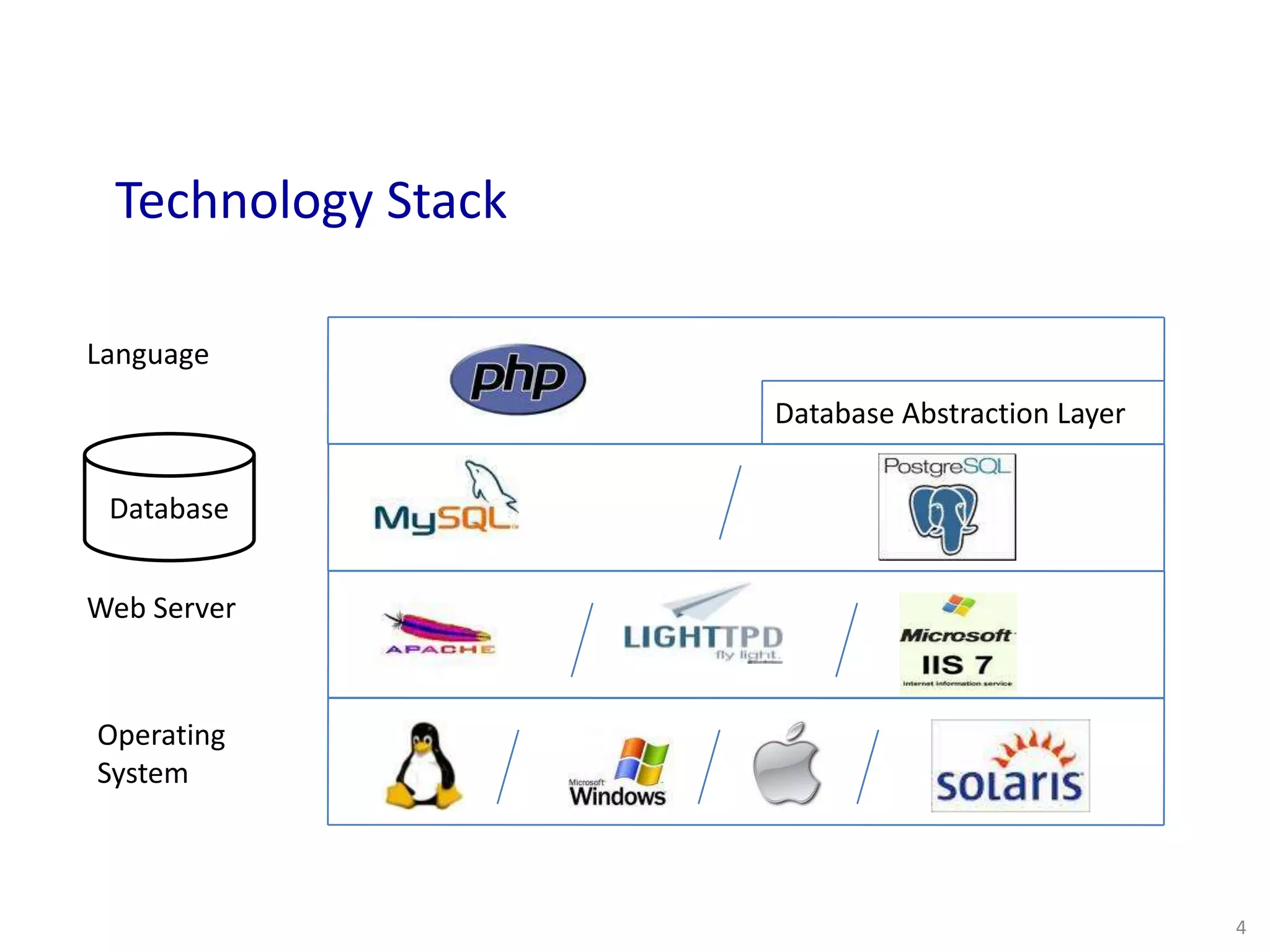
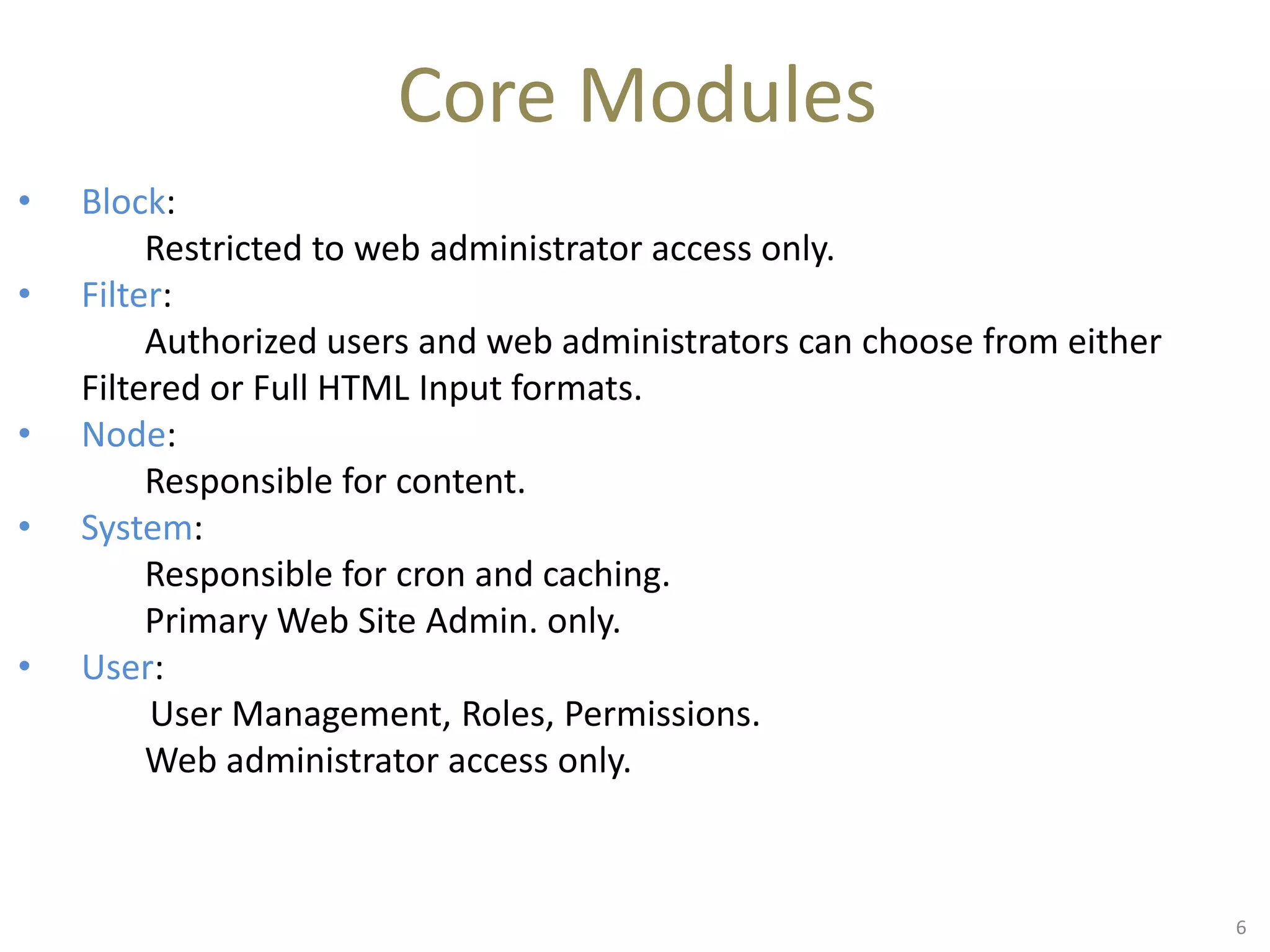
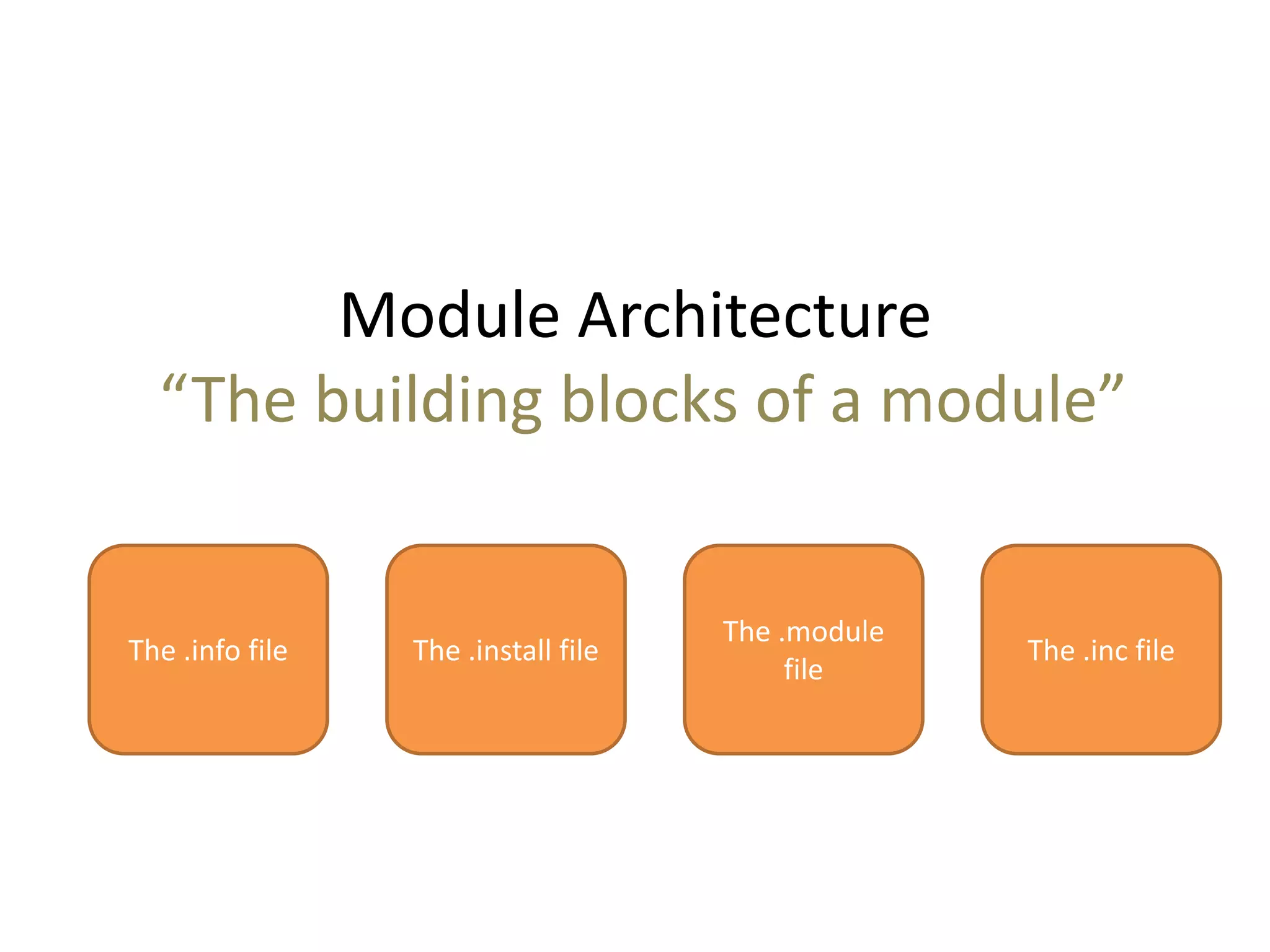
This document provides an overview of Drupal module development. It discusses Drupal architecture and the different types of modules, including core, contributed, and custom modules. It also covers the key components of a module like the .info, .module, and .inc files. The document introduces hooks and explains how they allow modules to extend Drupal's functionality by implementing callback functions. It provides examples of major hooks like hook_permission, hook_menu, and hook_nodeapi. Finally, it lists some common Drupal API functions that can be used when building custom modules.