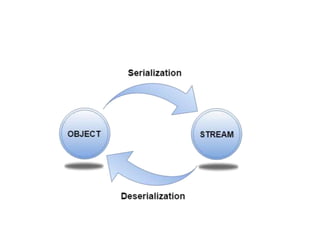
This document discusses object serialization in Java. Serialization is the process of converting an object's state into a byte stream to store or transmit the object. Deserialization reconstructs the object from the byte stream. The Student class implements the Serializable interface, allowing its objects to be serialized. ObjectOutputStream writes objects to an output stream, while ObjectInputStream deserializes objects from an input stream and reconstructs the object. An example demonstrates serializing a Student object to a file and then deserializing and printing its attributes.



![import java.io.*;
class Depersist{
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("f.txt"))
;
Student s=(Student)in.readObject();
System.out.println(s.id+" "+s.name);
in.close();
}
}
OP : 211 ravi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13243967-200908072612/85/13243967-5-320.jpg)

![Example of Java Deserialization
import java.io.*;
class Depersist{
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("f.txt"))
;
Student s=(Student)in.readObject();
System.out.println(s.id+" "+s.name);
in.close();
}
}
211 ravi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13243967-200908072612/85/13243967-7-320.jpg)




